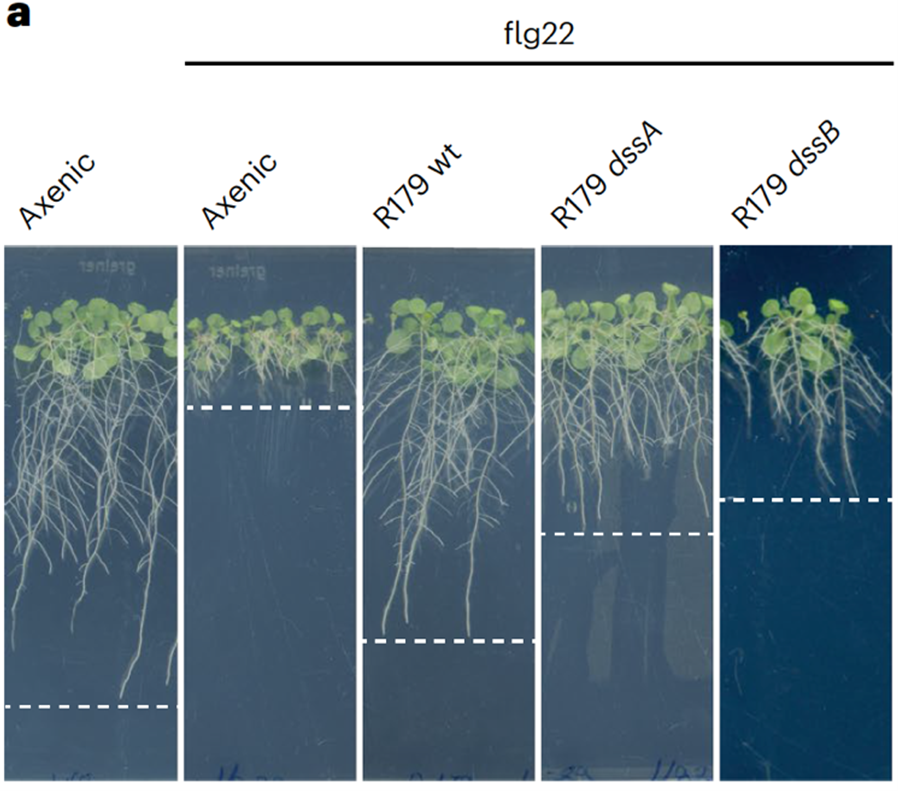
Stealth mode: How Rhodanobacter R179 evades plant immunity
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe soil microbiome harbors a vast diversity of microorganisms that can be pathogenic, beneficial, or commensal to plants. A fundamental question in plant biology is how plants actively detect, differentiate, and optimize their associations with the microbiome to maintain optimal fitness. In a recent…
Virtual issue: The chemical language of plant–microbe–microbe associations
Plant Science Research WeeklyDon’t miss this exciting Virtual Issue from New Phytologist on “plant-microbe-microbe” interactions. That’s not a typo – many of the articles address the signals that coordinate such multi-factorial interactions, as there is a growing recognition that interrelations between microbes influence…
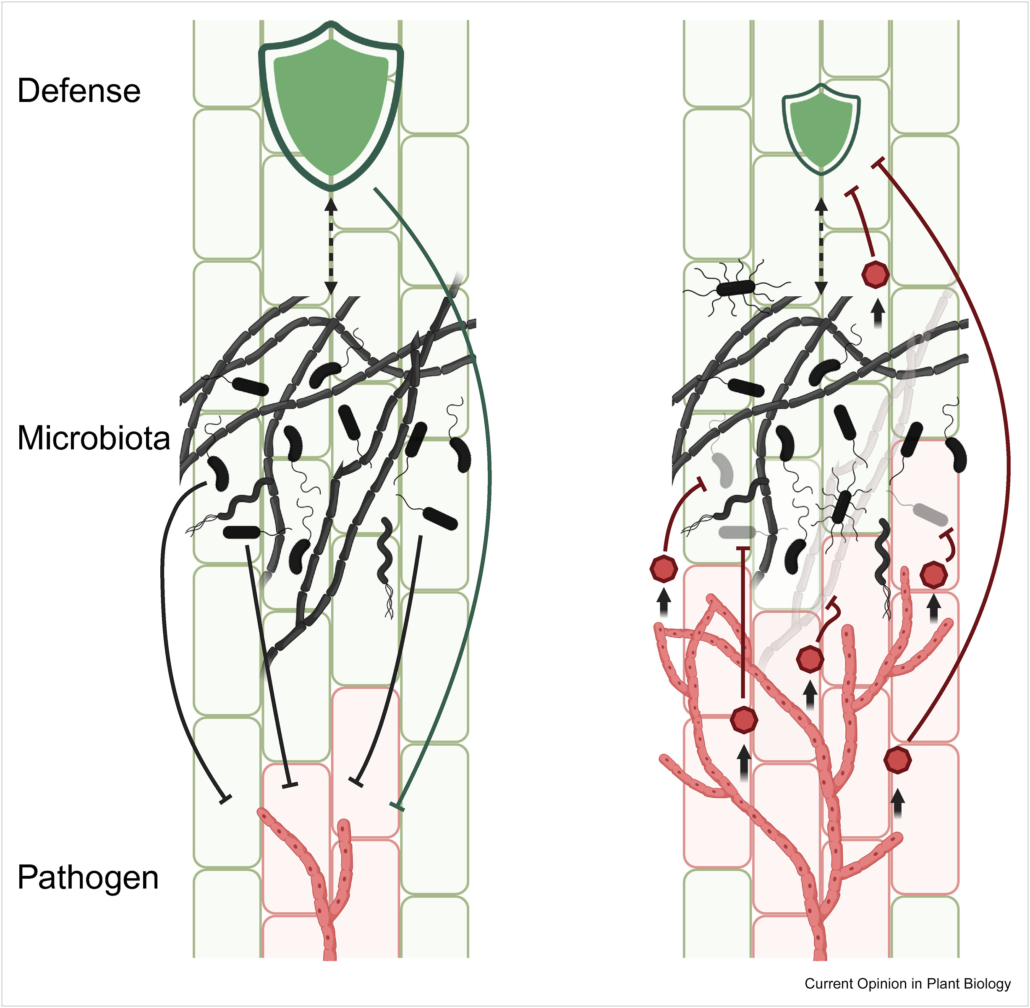
Review. Microbial tug-of-war: How plants and pathogens manipulate microbiomes
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe composition of plant-associated microbes is influenced by plant genetics, immune responses, environmental factors, and interactions between microbes. During disease development, the microbial community at infection sites changes due to tissue damage, altered immune responses, and manipulation via…
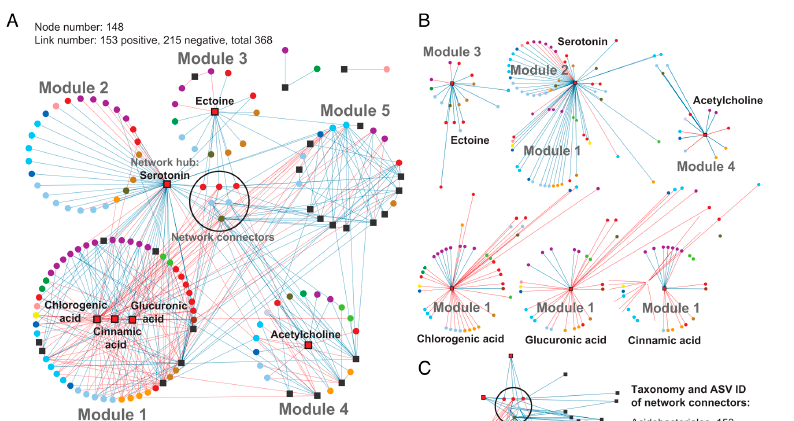
Keystone metabolites influence rhizosphere metabolomes and microbiomes
Plant Science Research Weekly
Rhizosphere interactions between plants and microbes are essential for nitrogen cycling, stress tolerance, and plant health in general. Metabolites secreted by plant roots can greatly influence microbial community composition, although how different environmental conditions impact these interactions…
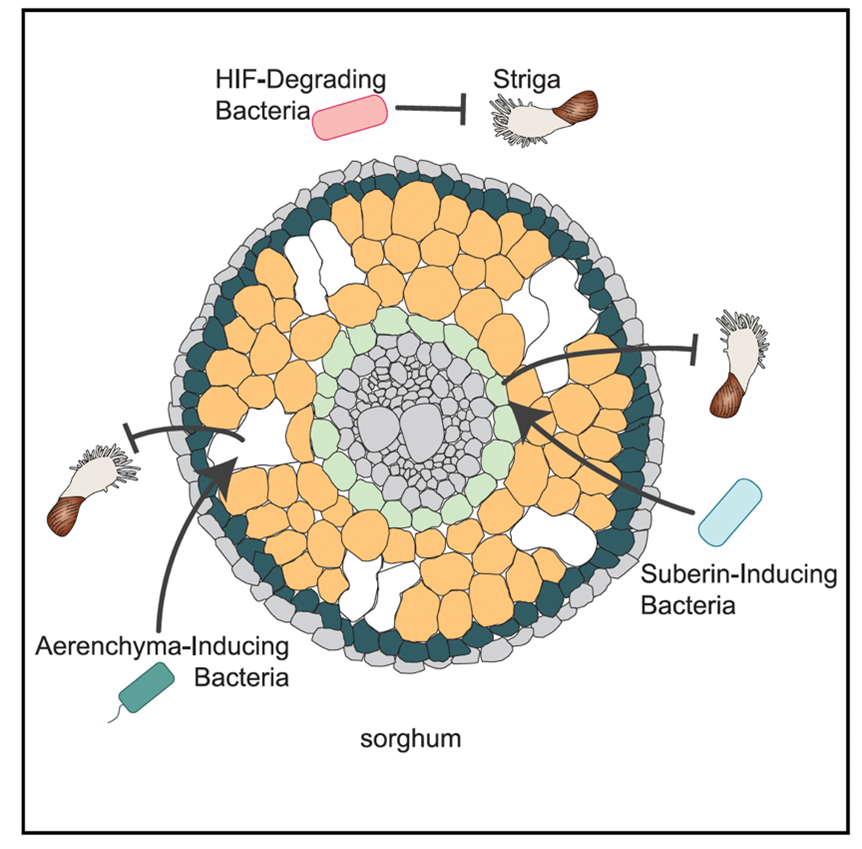
Harnessing the potential of soil microbial allies to combat Striga infection in sorghum roots
Plant Science Research WeeklyMicrobial neighbors of plants in the soil comprise of a vast array of bacteria and fungi, collectively known as the microbiome. This soil microbial community forms close associations with plants and regulates plant growth and development by inducing changes in the plant and soil metabolites. In this…
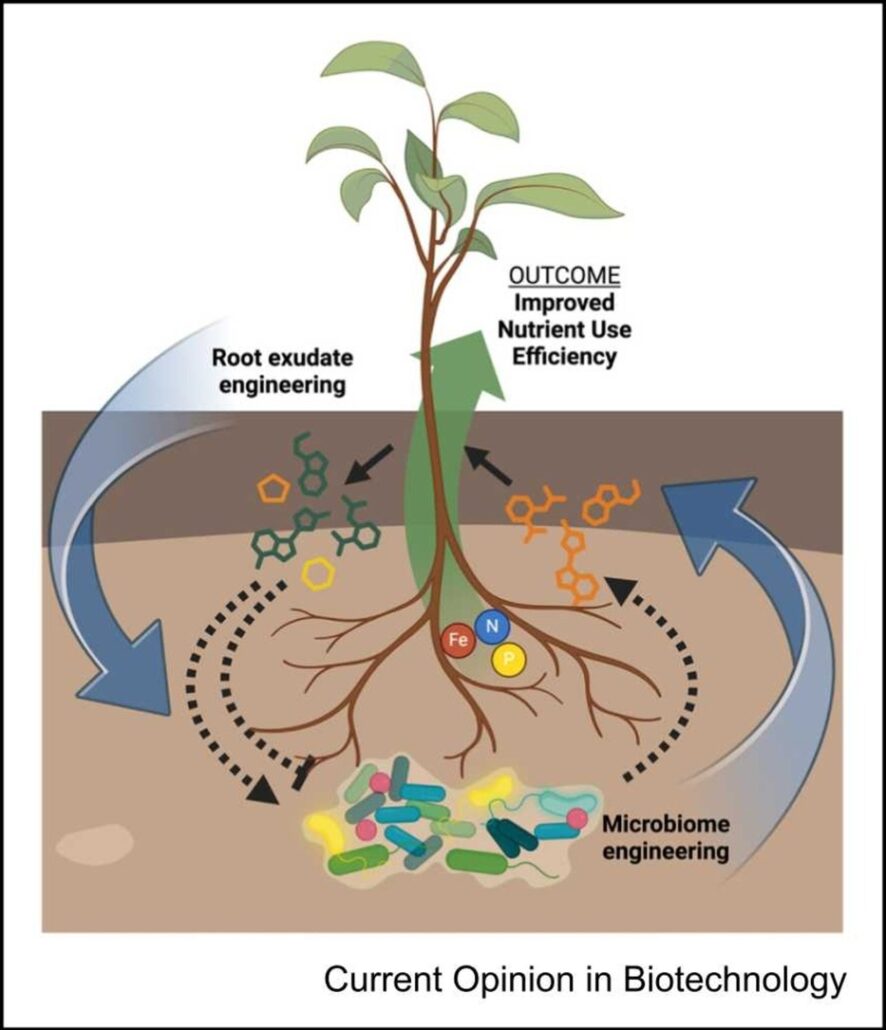
Review: Engineering plant–microbe communication for plant nutrient use efficiency
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant nutrient use efficiency (NUE) has become a major concern in recent years as farmers and scientists strive to make agriculture more sustainable. To this end, the manipulation of plant-microbe interactions holds great potential. In this short review, Griffin et al. highlight recent findings, focusing…
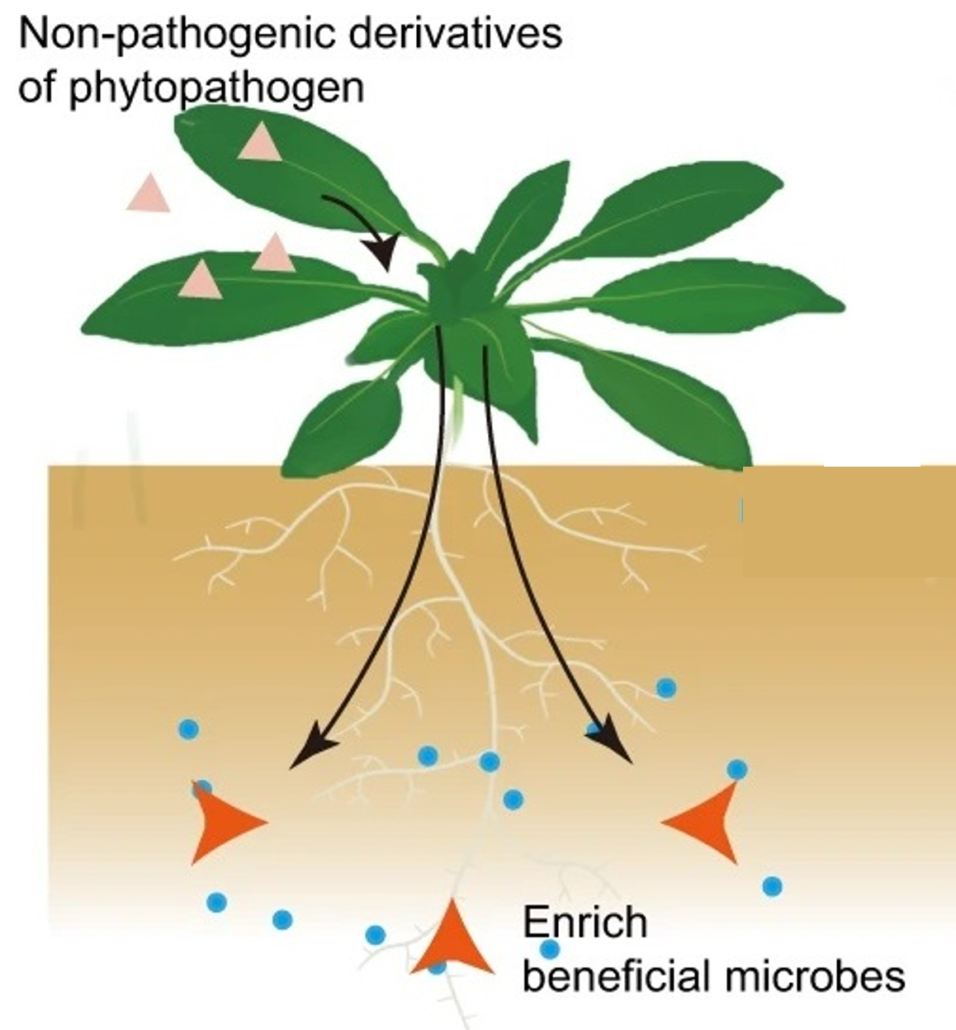
Induction of disease suppressive microbiome by non-pathogenic bacterial derivatives
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants recruit beneficial microbiomes in the rhizosphere in response to aboveground pathogen infections, a mechanism known as “cry for help.” Zhang and Liu et al. investigated this effect to test whether pathogenicity is necessary for assembling a disease-suppressive rhizomicrobiome. By using nonpathogenic…
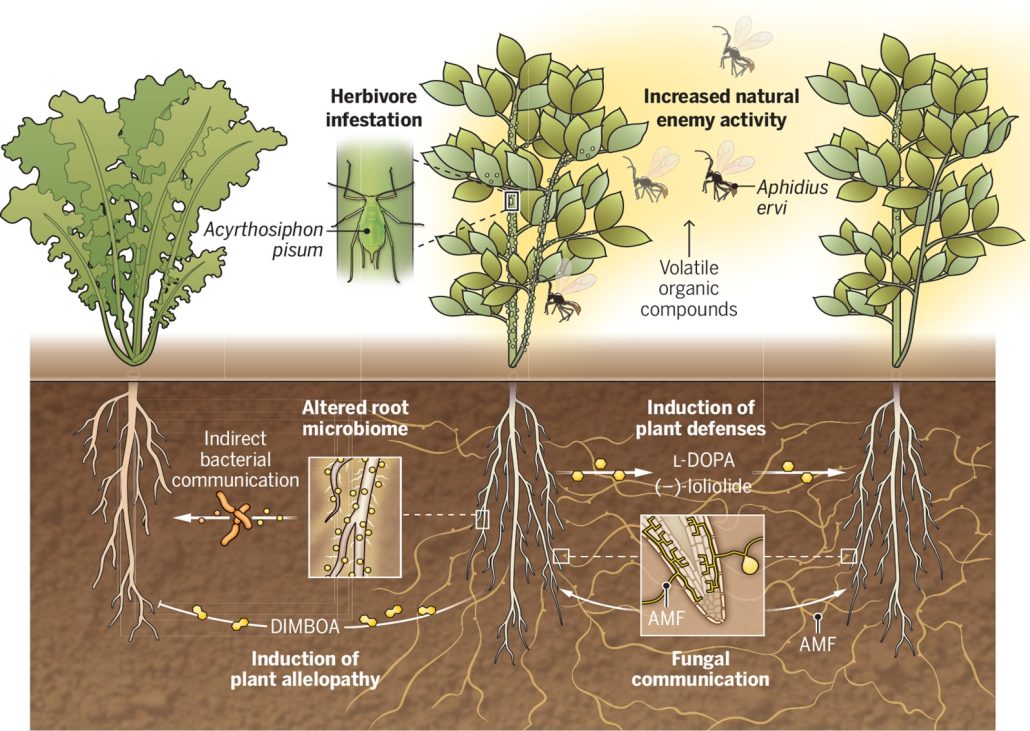
Perspective: Exposing belowground plant communication
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants possess a fascinating ability to communicate with each other through a complex system of chemical signals. Aboveground, they use airborne volatile signals to attract predatory insects, prime defenses in neighbors, facilitate nutrient transfer, and promote plant interactions. However, less is known…
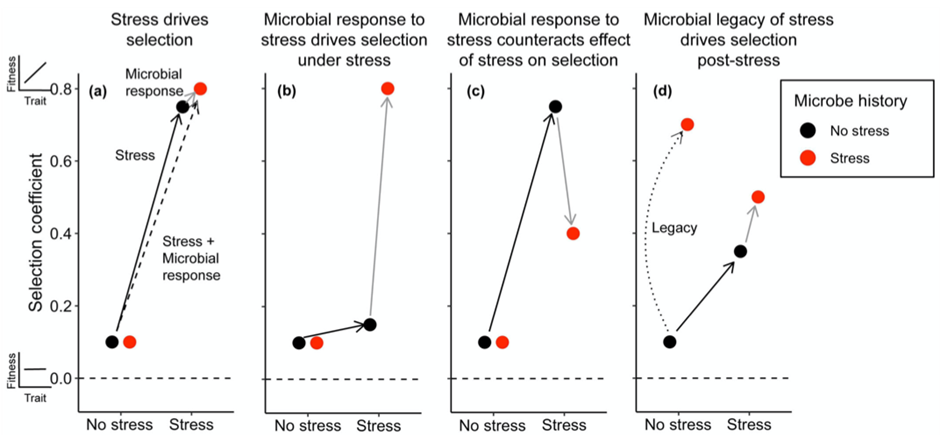
Hidden influence: How microbial stress responses shape plant natural selection
Plant Science Research WeeklySoil microbial communities respond rapidly to stress, potentially leading to altered compositions in stressful environments and consequently impacting plant natural selection. Bolin and Lau investigated the influence of microbial responses to stress and persistent microbial legacy effects on plant selection.…

