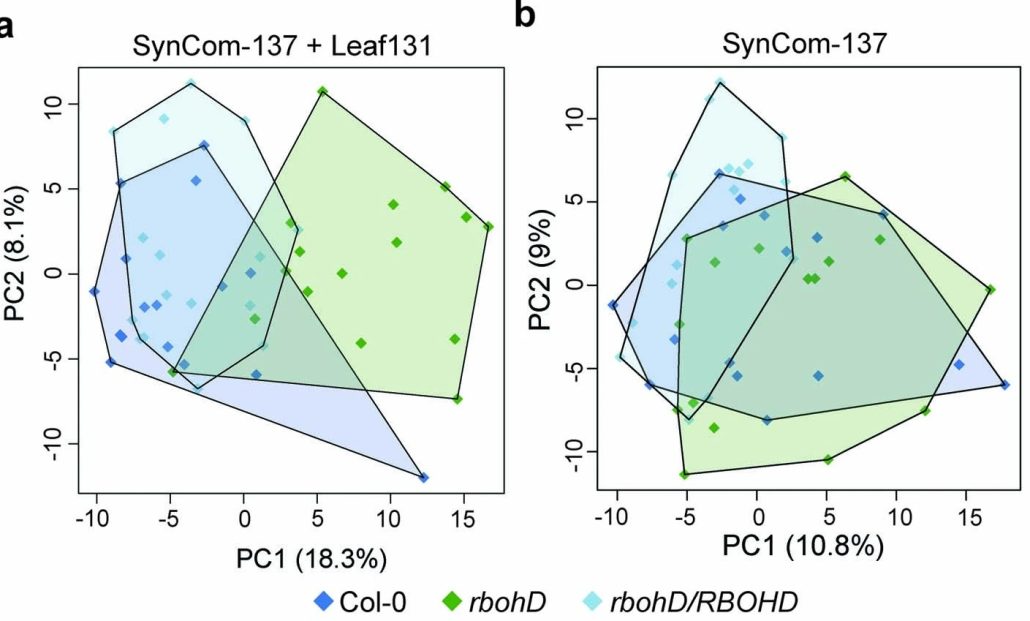
An opportunistic plant pathogen disrupts leaf microbiome through secretion of plant cell wall degrading enzymes
Plant Science Research WeeklyHealthy plants possess a functional immune system, and their leaves harbor a structured microbial community, including opportunistic pathogens. These opportunistic pathogens can trigger plant diseases under conducive conditions, such as when plant immunity is compromised, and the microbial community…
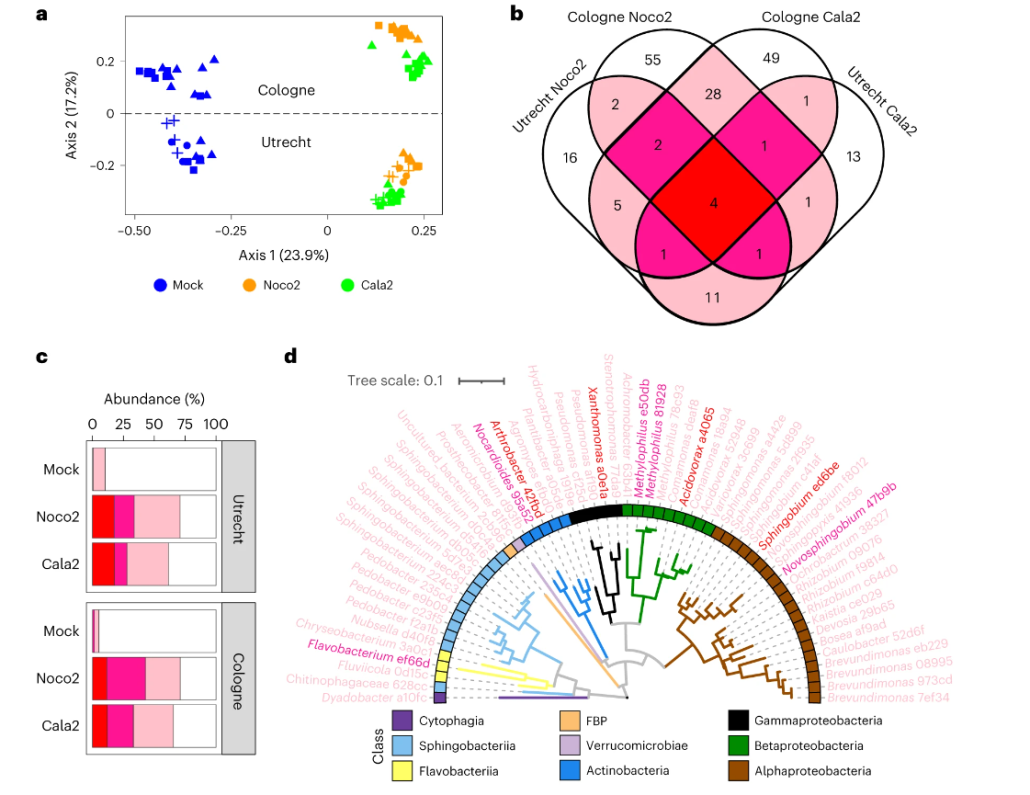
Shooting yourself in the foot: Obligate biotrophic pathogen induces protective microbiome in Arabidopsis
Plant Science Research WeeklyObligate plant pathogens cannot survive without their host plant. Therefore, understanding how the plant and its microbiome respond to the obligate biotrophs has real challenges in making sure that the response that is being monitored is not an artifact of the experimental step up. A recent study by…
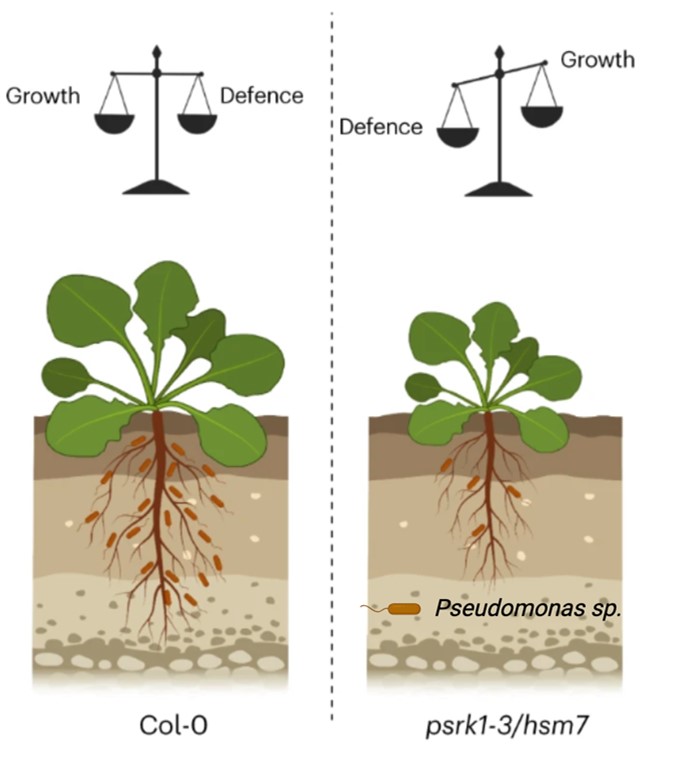
PSKR1 balances the plant growth–defence trade-off in the rhizosphere microbiome
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants are colonized by numerous beneficial microorganisms in the rhizosphere, including Pseudomonas fluorescens, that provide benefits including nutrient acquisition and pathogen protection. Host plants must tune their immune systems to restrict microbial overgrowth, while avoiding overstimulation of…
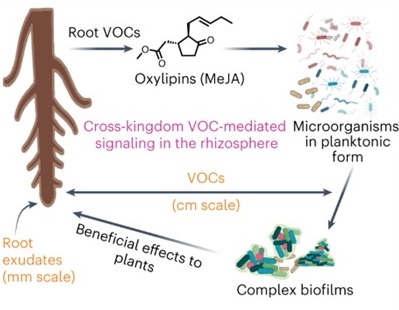
Volatile methyl jasmonate from roots triggers host-beneficial soil microbiome biofilms
Plant Science Research WeeklyVolatile molecules released from plant roots (root VOCs, rVOCs) can diffuse over long distances, thereby increasing the sphere of plant influence. However, their influence on complex soil microbial communities (or microbiomes) and ecological implications are poorly understood, mainly due to technical…
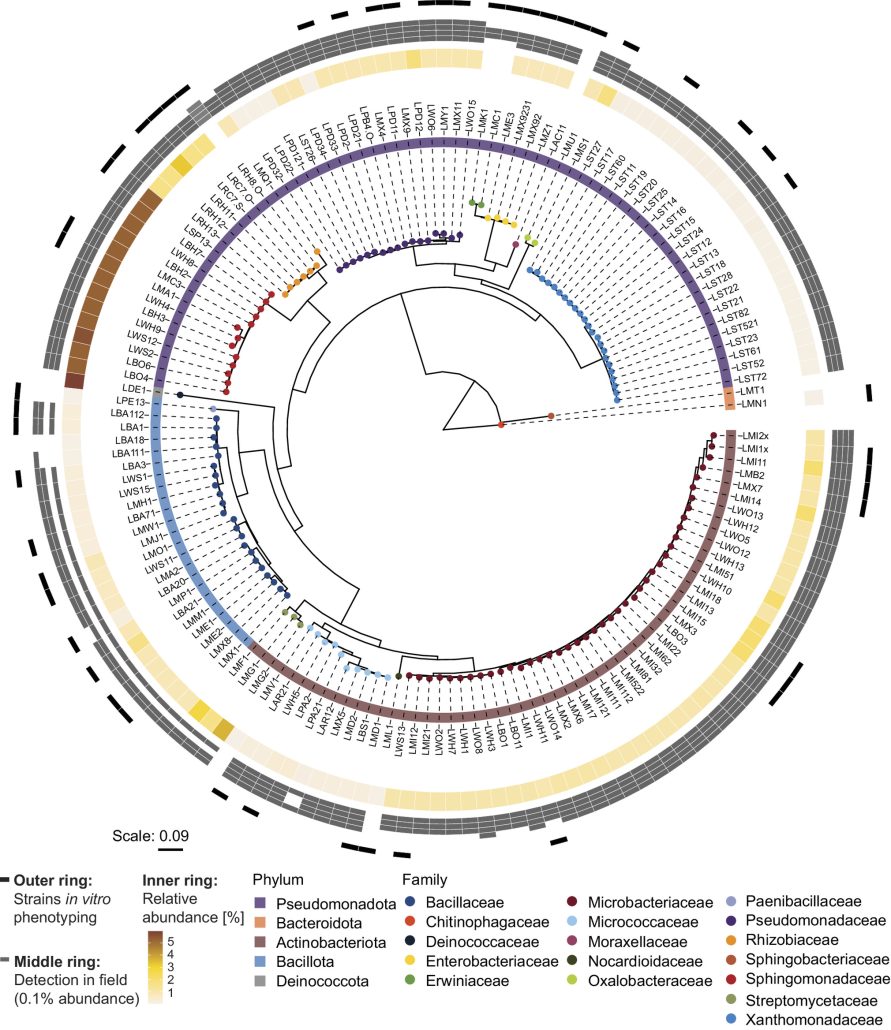
Bacterial tolerance to host-exuded specialized metabolites structures the maize root microbiome
Plant Science Research WeeklyBenzoxazinoids (BXs) are alkaloid specialized metabolites produced by important crops like maize. Their role in shaping the root and rhizosphere microbiomes and in plant defense against pest and pathogens is well known, although the mechanism remains unknown. One of the major BXs produced by maize is…
Review: Scripting a new dialogue between diazotrophs and crops
Plant Science Research WeeklyAll organisms need nitrogen to produce nucleic and amino acids, but nitrogen-limitation is common for many plants. Although nitrogen is very abundant in the atmosphere, most is inaccessible due to the triple bond that renders N2 relatively inert. Tremendous crop yields in recent decades are attributable…
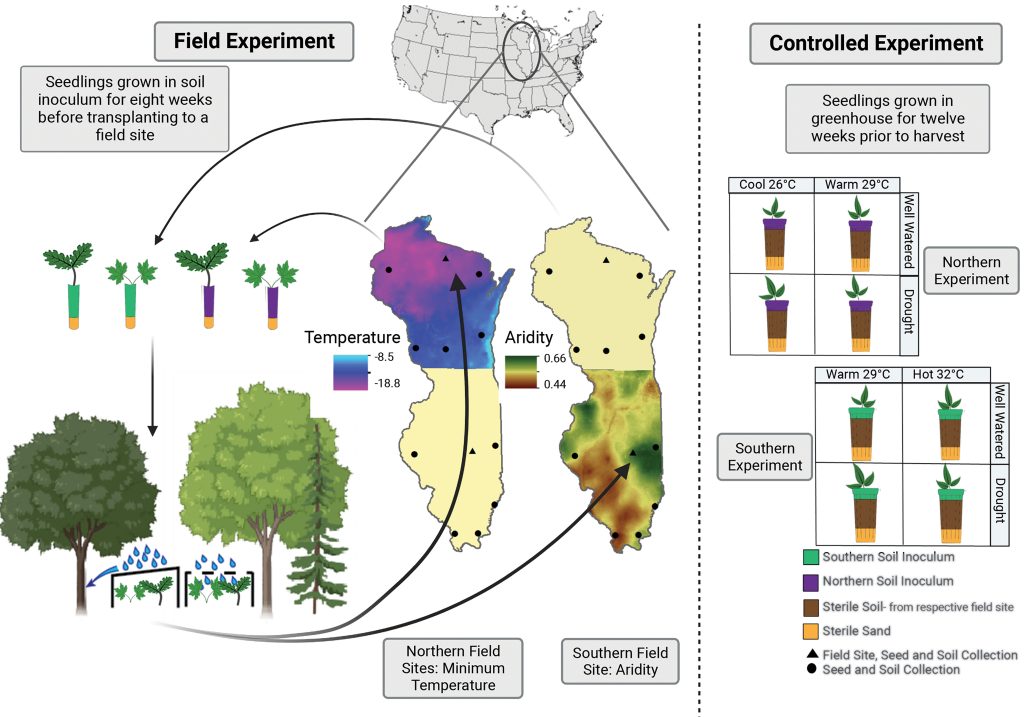
Shifting microbial communities can enhance tree tolerance to changing climates
Plant Science Research WeeklyLike all of Earth’s lifeforms, plants are already experiencing hardships due to the changing climate, and these stresses will get more extreme. Much effort has gone into breeding crops for climate resilience, less on trees which are both more diverse and less genetically tractable. Here, Allsup et…
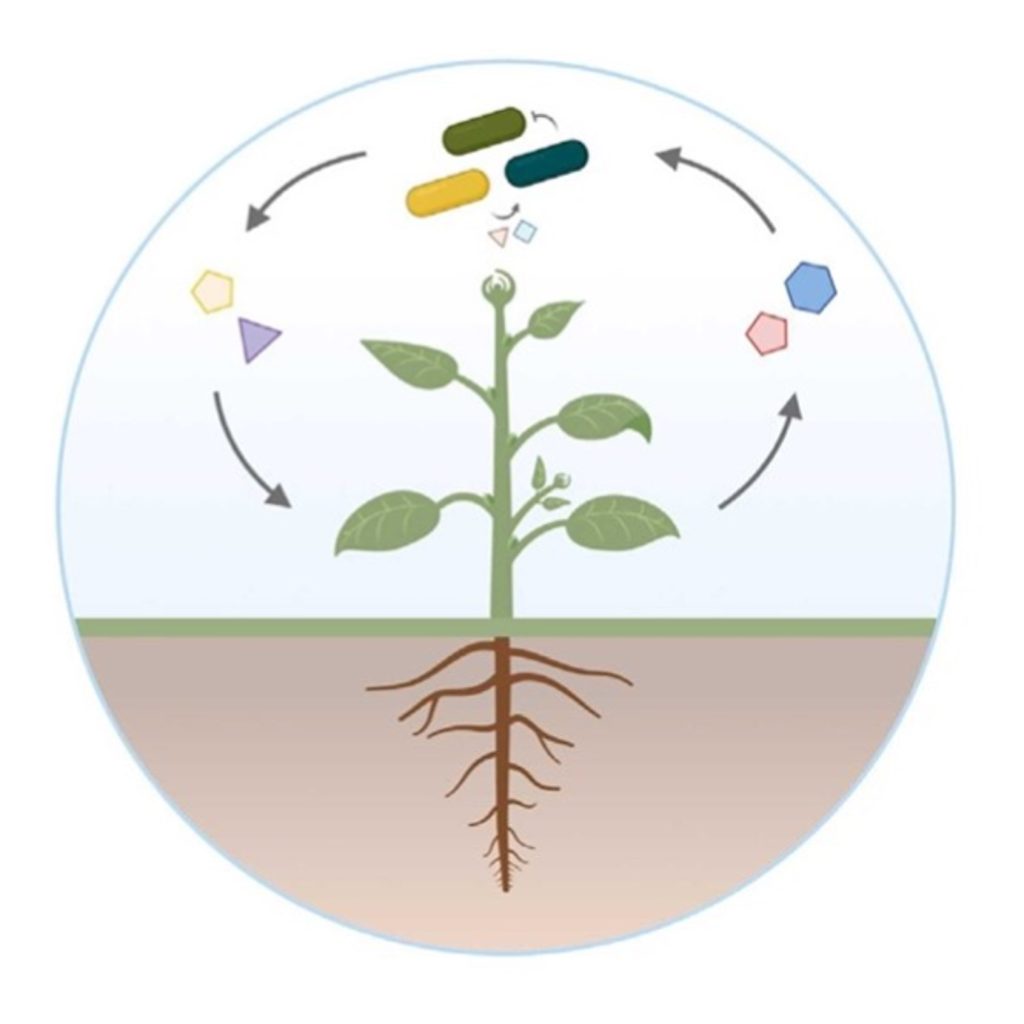
Review: Resolving metabolic interaction mechanisms in plant microbiomes
Plant Science Research WeeklyLife is spurred forward by the power of metabolic interactions. Within the plant microbiome, microbial communities use diverse mechanisms to thrive, survive, and multiply. In this review, Pacheco & Vorholt describe the interplay of metabolic interactions within plant microbiomes and review current…

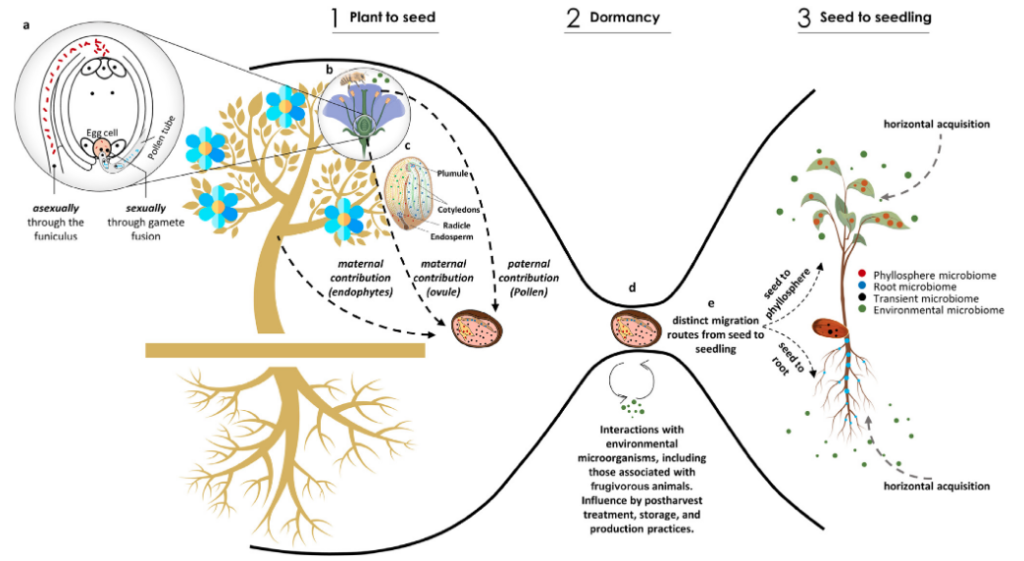
Opinion: The role of microbial inheritance in the assembly of the plant microbiome
Plant Science Research WeeklySeeds not only carry the embryo that will germinate and give rise to a new individual, but they are also the vector to the next generation for microorganisms from the mother plant and the environment. Consequently, seeds link the microbiome between plant generations. In this thorough review, Abdelfattah…

