Inhibition of TOR, Nitrogen Assimilation, and Amino Acid Biosynthesis: Lessons from Chlamydomonas
The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefTo survive, organisms must sense their nutritional status (including nutrient availability and quality) and regulate their growth and metabolism accordingly. In plants, animals, and fungi, the Target of Rapamycin (TOR) kinase regulates metabolism, nutrient sensing, and growth (reviewed in Dobrenel et…
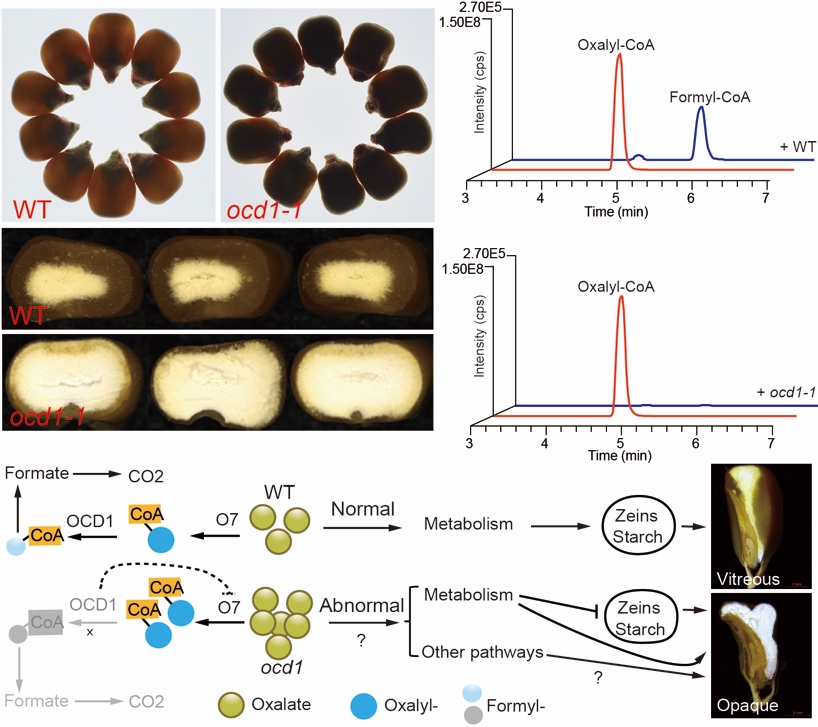
Studies have found that key enzymes of plant oxalate metabolism affect corn nutrition quality
Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: News(From a press release written in Chinese - original here)
On September 10th , The Plant Cell published a research paper entitled Maize Oxalyl-CoA Decarboxylase1 Degrades Oxalate and Affects the Seed Metabolome and Nutritional Quality by the Wu Yongrui Research Group of the Institute of Plant and Plant…
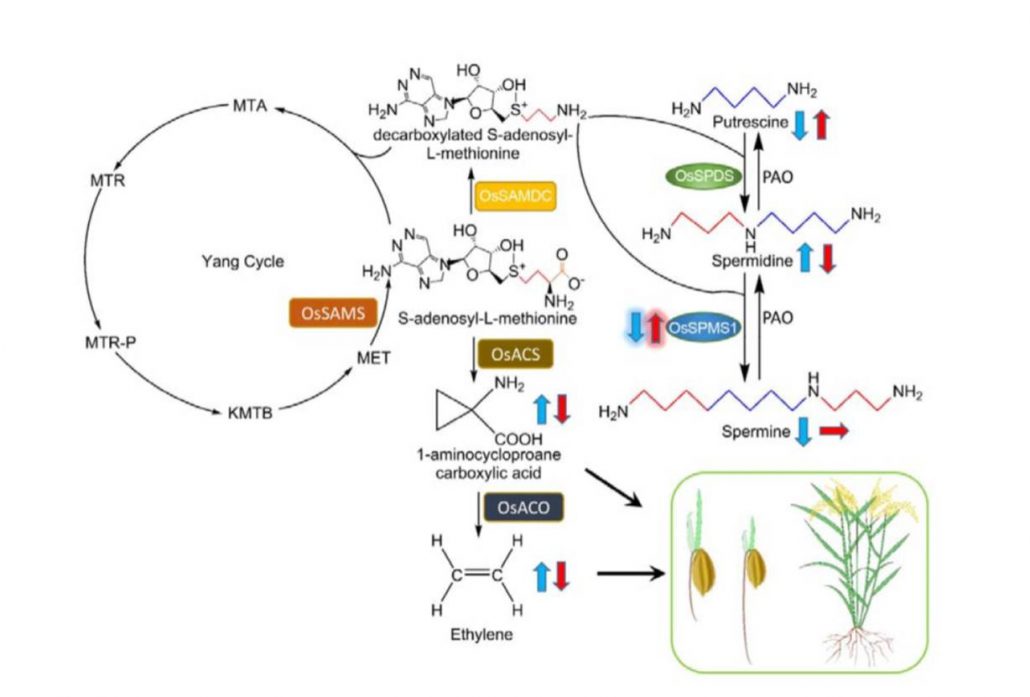
The spermine synthase OsSPMS1 regulates seed germination, grain size, and yield (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPolyamines including spermine and spermidine are present in all eukaryotes and have diverse roles. In plants they have been implicated in responses ranging from abiotic and biotic stresses to grain filling. Tao et al. examined the function of OsPMS1, encoding a spermine synthase, through genetic methods…
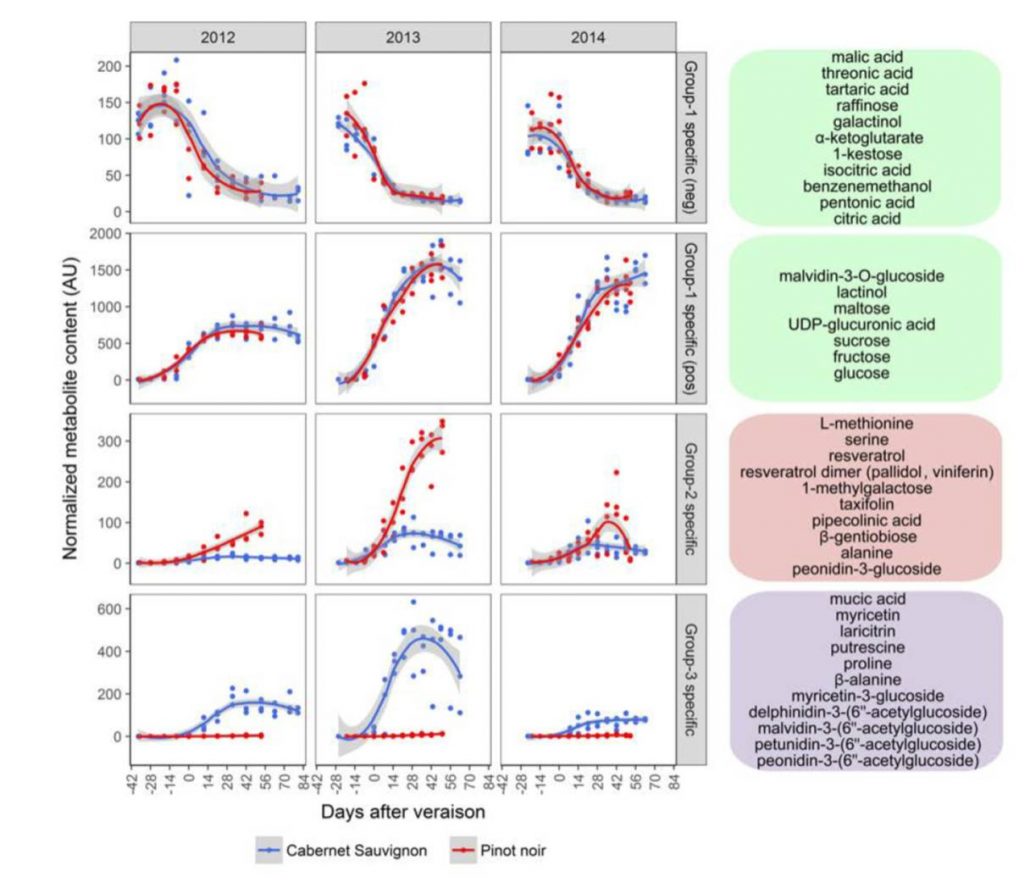
Molecular events marking the onset of berry ripening in grapevine (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyDo you know the difference between a wine made from Pinot noir grapes and one made from Cabernet Sauvignon grapes? Most people can taste a difference, but to really understand the wines you might want to go a bit deeper through metabolomic and transcriptomic approaches, as done by Fasoli et al. (in a…
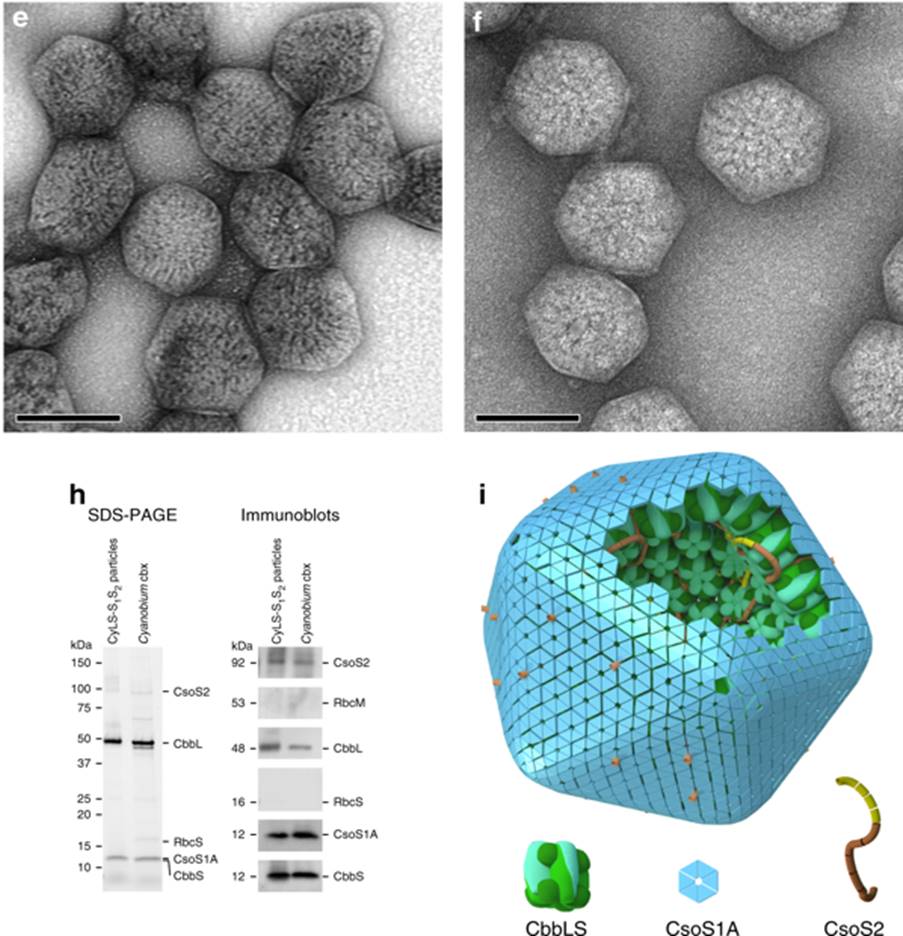
Carboxysome encapsulation of the CO2-fixing enzyme Rubisco in tobacco chloroplasts (Nature Comms.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyOne of the fundamental challenges facing terrestrial plants occurs when CO2 levels are depleted at Rubisco, causing its inefficient oxygenase activity to dominate. Some plants minimize this problem by adding a carbon-fixing step upstream of Rubisco, and various algae and cyanobacteria sequester Rubisco…
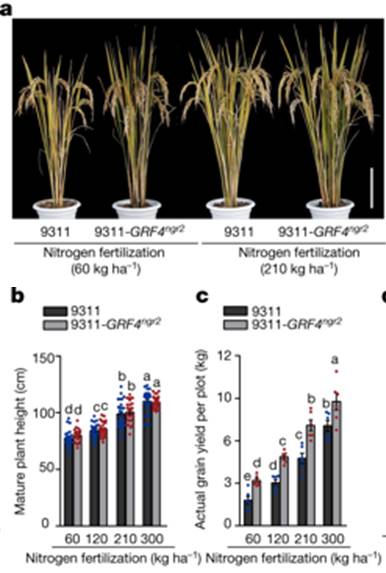
Modulating plant growth–metabolism coordination for sustainable agriculture
Plant Science Research WeeklyGreen revolution varieties of rice and wheat are dwarfed, making them resistant to lodging, and DELLA proteins contribute to this dwarfing. At the same time, green-revolution varieties are not very good at taking up nitrogen, so much of the applied fertilizer is wasted (and polluting). Li et al. have…
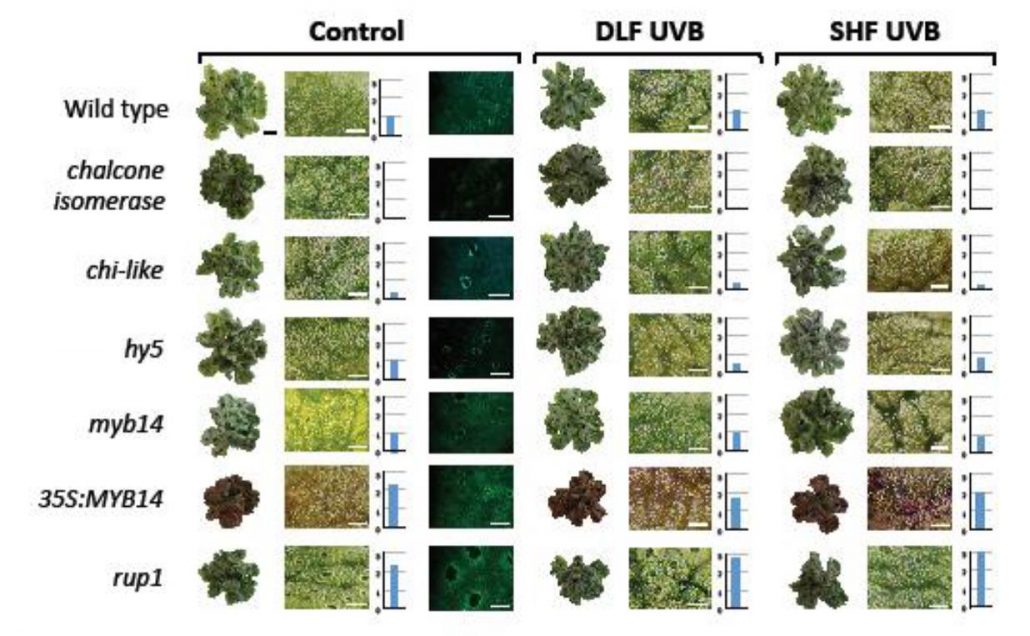

A conserved role for flavonoids in the protection of plant tissues from UV damage ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe transition from aquatic to terrestrial environments exposed the earliest land plants to higher doses of damaging ultraviolet (UV-B) radiation. To cope with this stress, land plants evolved complex signalling mechanisms and an inventory of protective ‘sunscreen-like’ flavonoids. To explore whether…
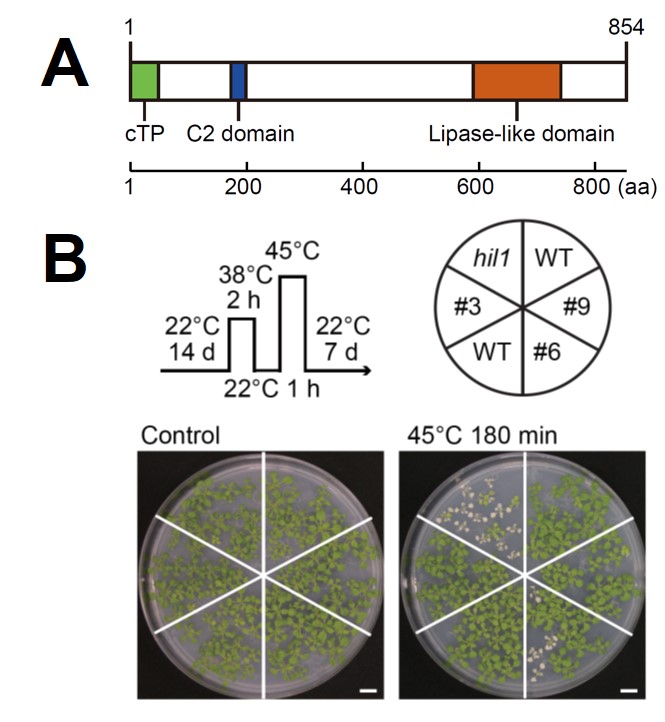
Heat Trims the Fat: HIL1 Functions in Lipid Homeostasis
Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefGlobal climate change is one of the most pressing issues facing our world today. The impact of increasing temperatures can be felt in diverse areas, including human health and disease, natural ecosystems, and food security. In the agricultural sector, deciphering how plants respond to changing environmental…
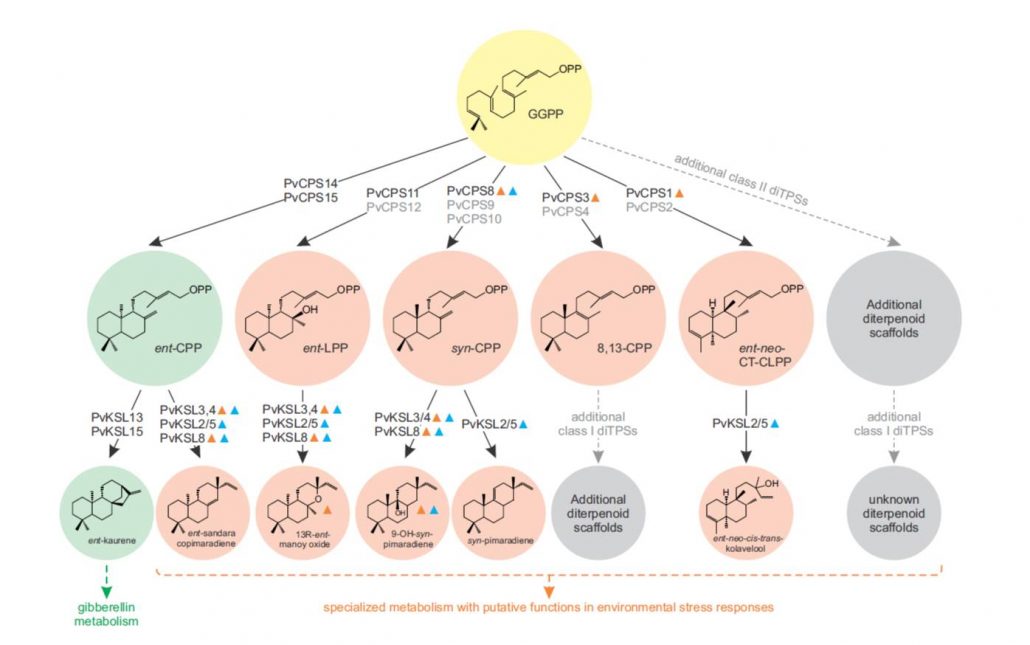
Diterpenoid Metabolism in Switchgrass
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideSwitchgrass (Panicum virgatum) is a perennial C4 grass native to North America primarily valued as a next-generation feedstock for biofuel production. Its high net energy yield and
wide habitat range make switchgrass an attractive crop for cultivation on marginal lands with minimal agronomic inputs,…

