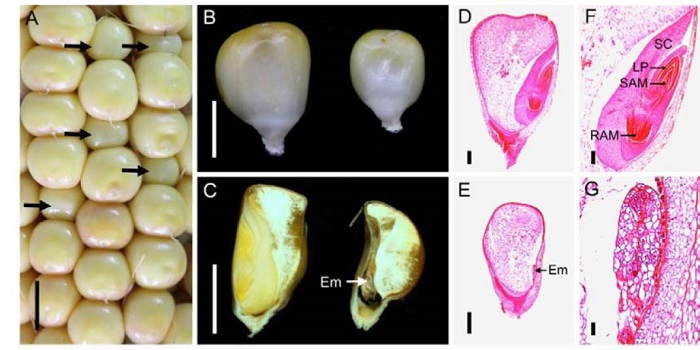
Vitamin B6 Is Essential for Maize Embryogenesis
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research0 Comments
/
Vitamin B6 is synthesized de novo in plants, fungi, archeae, and most eubacteria, but not in animals, including humans, which have to obtain it from dietary sources. Vitamin B6 is an essential cofactor for a range of biochemical reactions and a potent antioxidant. In plants, it plays important roles…

Folate, DNA Methylation and Flowering Time
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, ResearchTetrahydrofolate (THF) and its derivatives, collectively termed folates, are a group of essential B-complex vitamins that have long been recognized as necessary nutrients to support normal cell differentiation and growth. Folates function as co-enzymes in one-carbon transfer reactions and play a central…
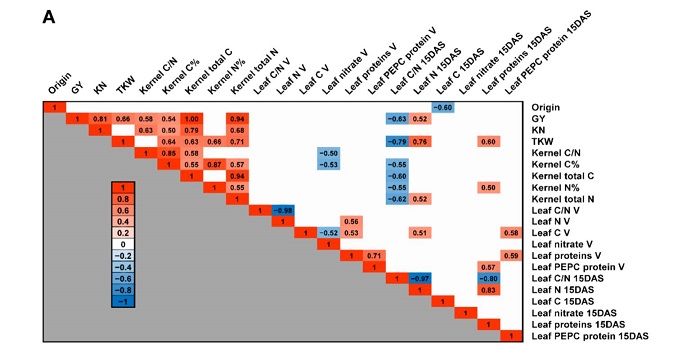
Exploiting maize genetic diversity: Metabolomic, enzyme activity profiling, and metabolic modelling to link leaf physiology to kernel yield ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe path from genome to phenome is difficult to predict. Cañas et al. tried to identify biochemical markers that are correlated with kernel yield that could be selected for in breeding. Specifically, they collected data from metabolomics, enzyme activity assays and metabolic modeling, taken during the…

Chasing Scattered Genes: Identifying Specialized Metabolite Pathway Genes through Global Co-expression Analysis
Research, The Plant Cell: In BriefPlants produce scores of specialized metabolites (SMs) to attract or repel the organisms around them and to cope with life in a variable environment. For thousands of years, we have been exploiting these compounds to feed, heal, and adorn us. Many more SMs remain to be discovered: the chemical constituents…
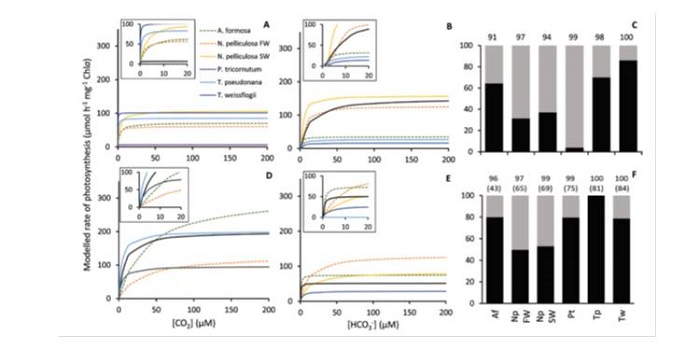
Diversity of CO2 concentrating mechanisms and responses to CO2 concentration in marine and freshwater diatoms ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe CO2-fixing enzyme ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase (Rubisco) works most efficiently at high concentrations of CO2. Many organisms have evolved CO2-concentrating mechanisms (CCMs), such as the PEP-carboxylation that occurs upstream of Rubisco in C4 plants. Diatoms and other eukaryotic algae use a…

Changes in the chloroplastic CO2 concentration explain much of the observed Kok effect: a model ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchWhen the uptake of CO2 (A) is plotted against absorbed irradiance (I), at low I there is a noticeable bend that occurs around the light compensation point (I where CO2 release due to mitochondrial respiration is balanced by CO2 uptake by photosynthesis). When the slopes of both parts of the curve are…

Opinion: Increasing crop yield and resilience with trehalose 6-phosphate ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchTrehalose 6-phosphate (T6P) is a disaccharide formed from two glucose sugars, and more importantly is a signal of glucose availability and regulator of energy homeostasis. Acting via the protein kinase SnRK1, T6P controls the allocation of carbon, leading the plant down a “feast” (growth) or “famine”…

Review: Mechanisms to mitigate the tradeoff between growth and defense ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchIt is widely recognized that defense incurs a cost in terms of reduced growth. Karasov et al. explore the nature of this tradeoff. They observe that rather than tradeoff being driven directly by metabolic competition, it appears to occur upstream through regulatory processes including antagonism between…
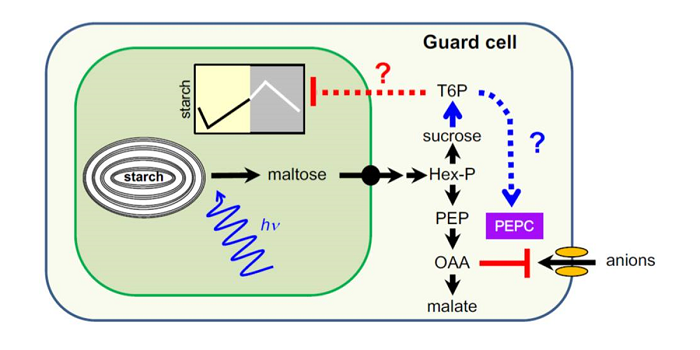
Update: Transitory starch metabolism in guard cells: unique features for a unique function
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchIn leaf mesophyll cells, some of the sugars produced by photosynthesis are stored as transitory starch, which is then broken down to provide the cells with energy during the night. Recent advances in imaging and staining and the use of mutants have enabled the pattern of accumulation of transitory starch…

