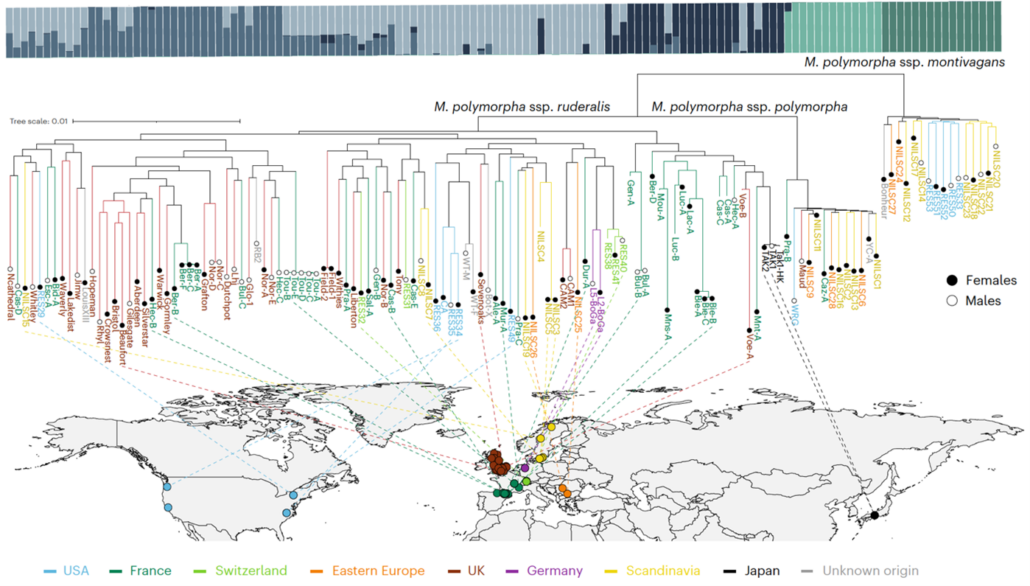
From water to land: What bryophytes reveal about plant evolution and adaptations
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe transition of plants from aquatic to terrestrial environments occurred approximately 400 million years ago, leading to the diversification of two major lineages: tracheophytes (vascular plants) and bryophytes (non-vascular plants). While most studies on plant adaptation to environmental stressors…
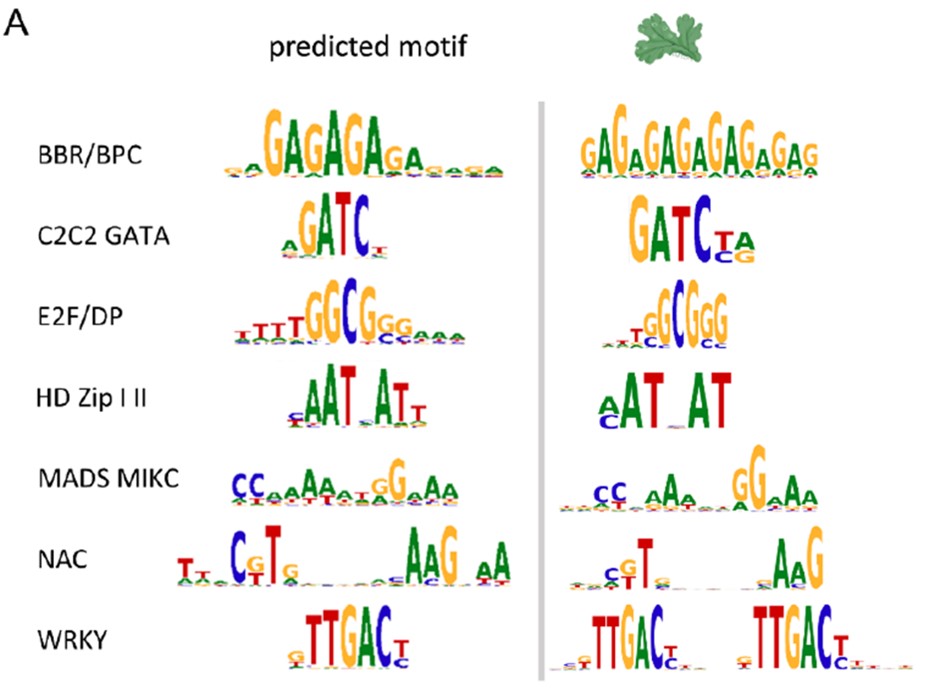
Many plant transcription factor families have evolutionarily conserved binding motifs
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe regulated expression of genes is fundamental to all biological processes, including development, cell growth, and responses to environmental signals. Transcription factors (TFs) are sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins that play a central role in transcriptional regulation by directly interacting…
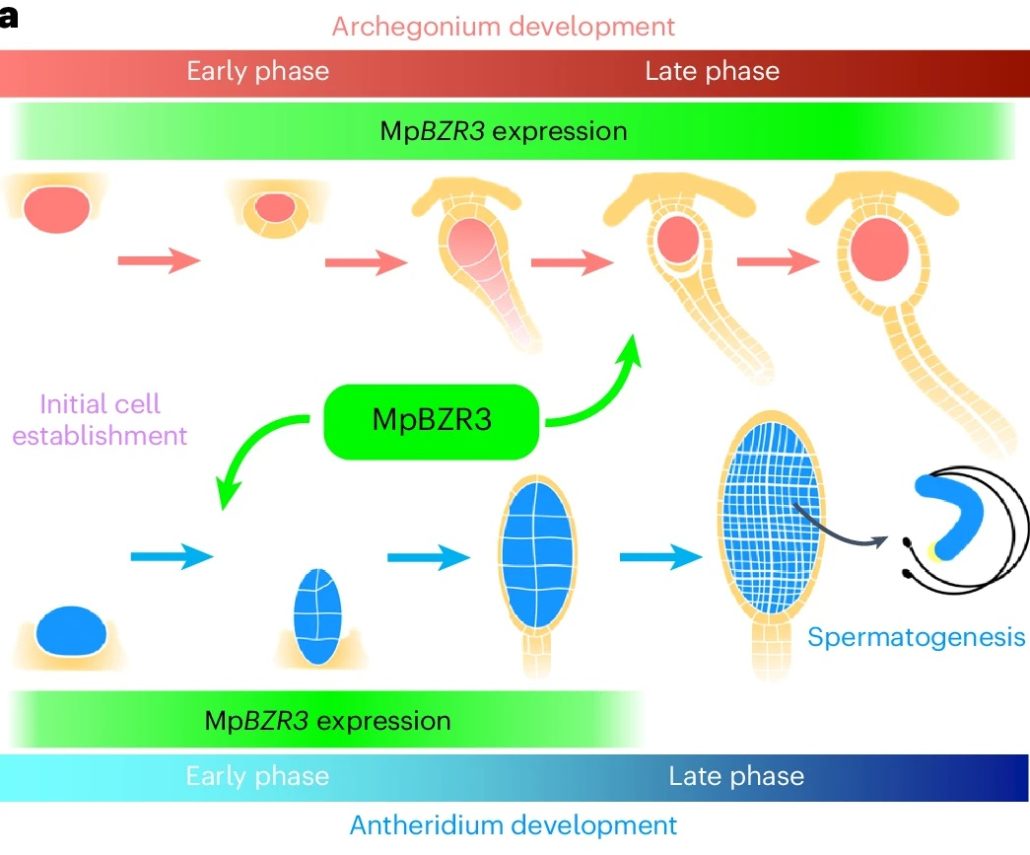
A novel BZR/BES transcription factor controls the development of haploid reproductive organs in Marchantia polymorpha
Plant Science Research WeeklyGametogenesis is essential for sexual reproduction. In bryophytes, lycophytes, and ferns, gametogenesis takes place in gametangia: antheridia for sperm production and archegonia for egg production. How these specialized reproductive organs develop at the molecular level remains unclear. Furuya et al.…
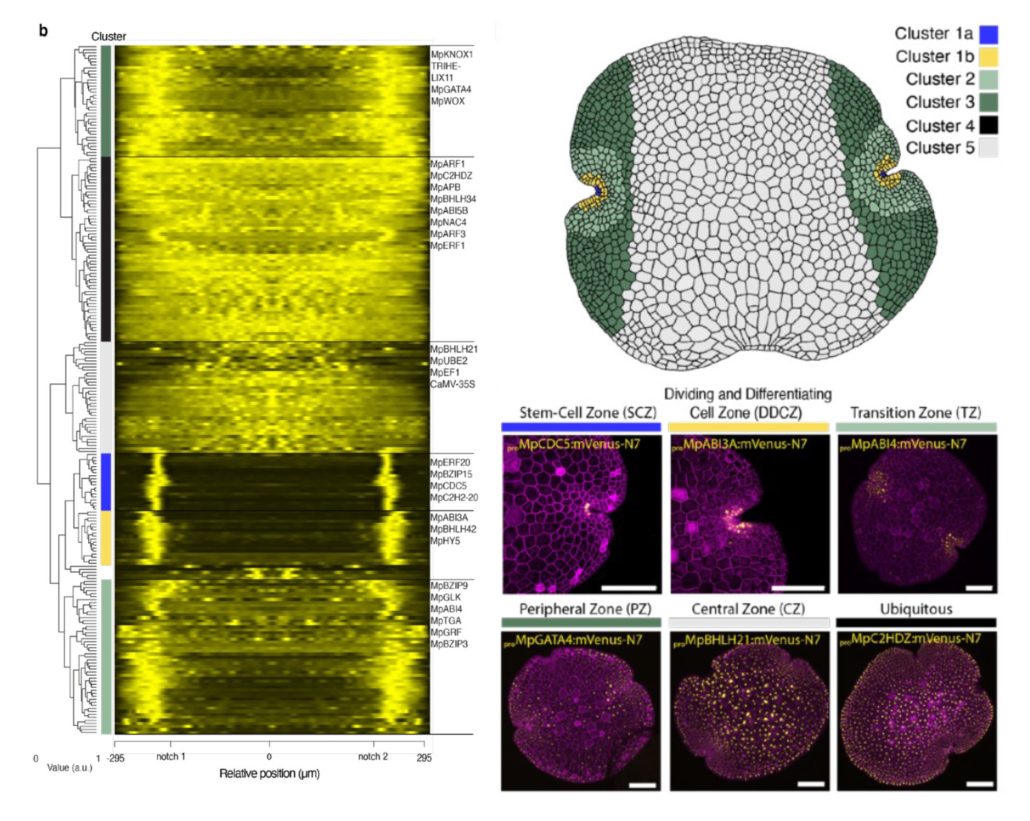
The Marchantia transcription factor atlas
Plant Science Research WeeklyMarchantia’s power as a model organism continues to grow! Here, Ramoni et al. have investigated the expression pattern of the proximal promoters of most of its 450 transcription factor (TF)-encoding genes. The promoter elements were fused to nuclear-localized fluorescent reporters and introduced into…
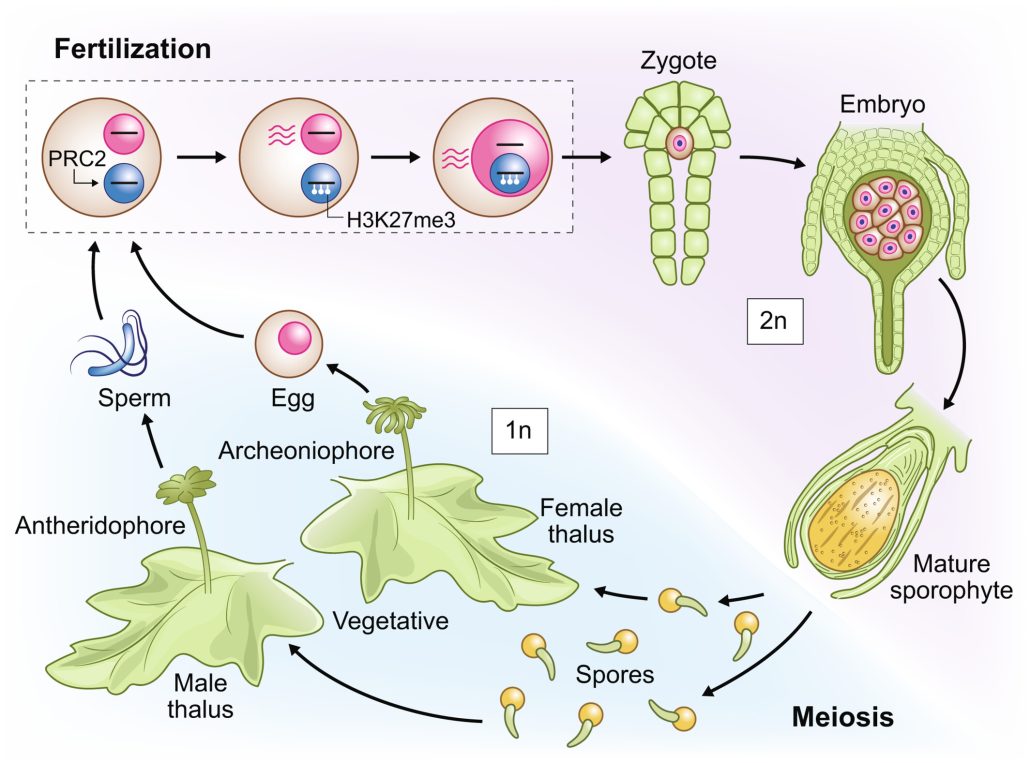
Review: Paternal imprinting in Marchantia polymorpha
Plant Science Research WeeklyHumans and flowering plants spend most of their lives in a diploid state with two copies of each chromosome in most cells, but to reproduce they produce haploid gametes through meiosis. By contrast, bryophytes (liverworts, hornworts, and mosses), spend most of their lives in the haploid state. They produce…
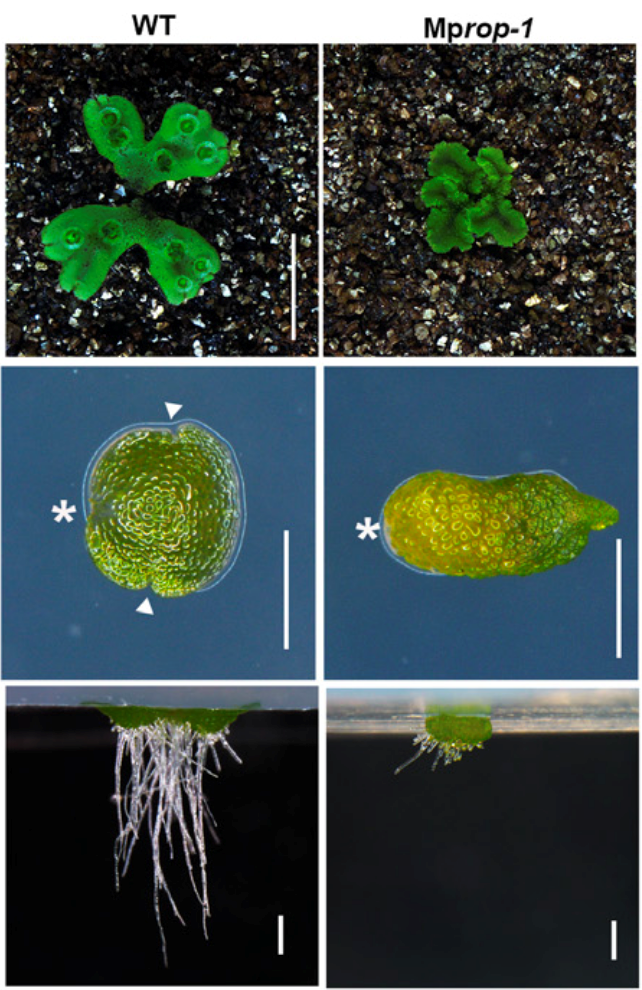
Developmental functions of Marchantia ROP
Plant Science Research WeeklyPrecise control of cell division is an important requirement for proper development in multicellular organisms. Rho-like GTPases from Plants (ROPs) are key conserved regulators of cell polarity and morphogenesis, however, it is unknown if ROP signaling pathways regulate cell division patterning and meristem…
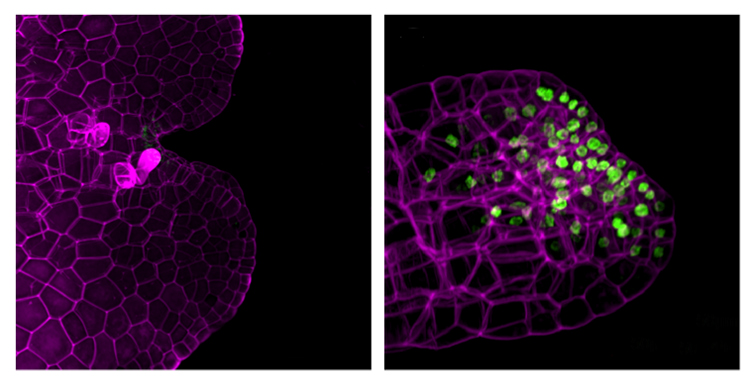
KARRIKIN INSENSITIVE2-dependent signaling in the liverwort Marchantia polymorpha
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellMizuno et al. show that genes in the KARRIKIN INSENSITIVE2-dependent signaling pathway are conserved in the liverwort Marchantia polymorpha and control early development of the thallus.
Yohei Mizuno and Junko Kyozuka
Background: Plants hormones play crucial roles in growth and development. Karrikins…

