KARRIKIN INSENSITIVE2-dependent signaling in the liverwort Marchantia polymorpha
Yohei Mizuno and Junko Kyozuka
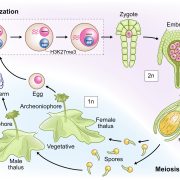
Background: Plants hormones play crucial roles in growth and development. Karrikins are smoke-derived germination signals, perceived by KARRIKIN INSENSITIVE2 (KAI2) in seed plants. An endogenous KAI2-ligand has not been identified. Land plants evolved from an algal ancestor more than 450 million years ago. The bryophyte lineages, including liverworts, mosses, and hornworts, are sisters to and represent the first land plant lineage diverged from the vascular plants. Components of the KAI2-dependent signaling pathway are present in bryophyte genomes, but their functions are unknown.
 Question: Our question was what is the ancestral role of the KAI2-dependent signaling pathway? To answer this question, we asked whether the KAI2-dependent signaling pathway of bryophytes works in a similar way as in seed plants and what is the role of the signaling pathway in bryophytes.
Question: Our question was what is the ancestral role of the KAI2-dependent signaling pathway? To answer this question, we asked whether the KAI2-dependent signaling pathway of bryophytes works in a similar way as in seed plants and what is the role of the signaling pathway in bryophytes.
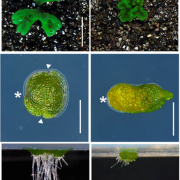
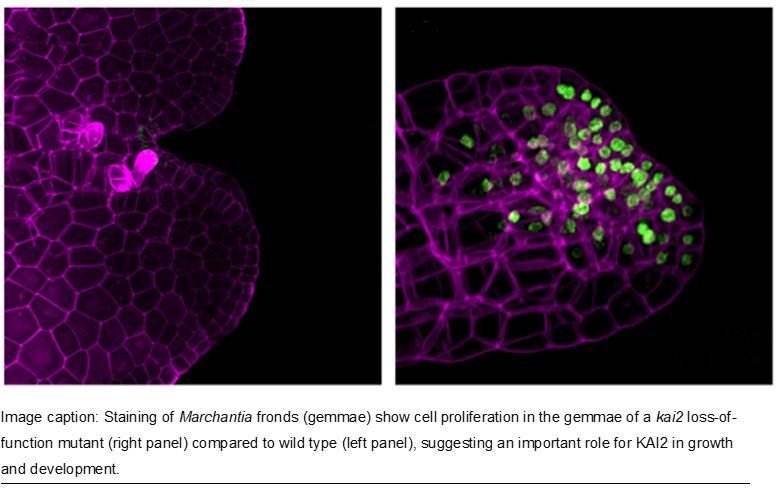
Findings: The main components in the KAI2-dependent signaling pathway in seed plants are KAI2, MAX2, and SMXL. In the absence of the karrikin hormone, SMXL suppresses the function of downstream genes. When KAI2 perceives the hormone, the SMXL protein is degraded with the aid of MAX2. We produced knock out mutants of MpKAI2a, MpKAI2b, MpMAX2, and MpSMXL genes of the liverwort Marchantia polymorpha. We found that early thallus growth was affected in Mpkai2a and Mpmax2 loss-of-function mutants. Similar defects were observed in the Mpsmxld53 mutants, in which a sequence required for degradation was mutated. These findings imply that degradation of MpSMXL is necessary for MpKAI2A-dependent signaling in M. polymorpha, and the basic mechanisms in the KAI2-dependent signaling pathway are conserved in M. polymorpha.
Next steps: We wish to know what kind of genes are regulated by the KAI2-dependent signaling pathway in M. polymorpha. In addition, identifying the KAI2-ligand, the molecule that triggers the KAI2-dependent signaling is crucial to fully understand the function of this signaling pathway.
Yohei Mizuno, Aino Komatsu, Shota Shimazaki, Satoshi Naramoto, Keisuke Inoue, Xiaonan Xie, Kimitsune Ishizaki, Takayuki Kohchi, Junko Kyozuka (2021) Major components of the KARRIKIN INSENSITIVE2-dependent signaling pathway are conserved in the liverwort Marchantia polymorpha. https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koab106