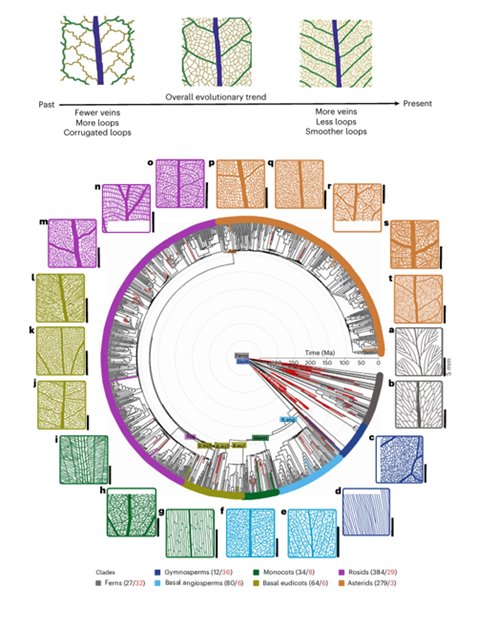
The shape of adaptation: Evolution of venation patterns in plants
Plant Science Research WeeklyLeaf venation patterns display remarkable diversity across both living and fossil plant lineages, yet key questions remain about when and how these architectural differences emerged and what functional roles they serve. In their recent review, Mantos et al. explored the evolutionary history of venation…
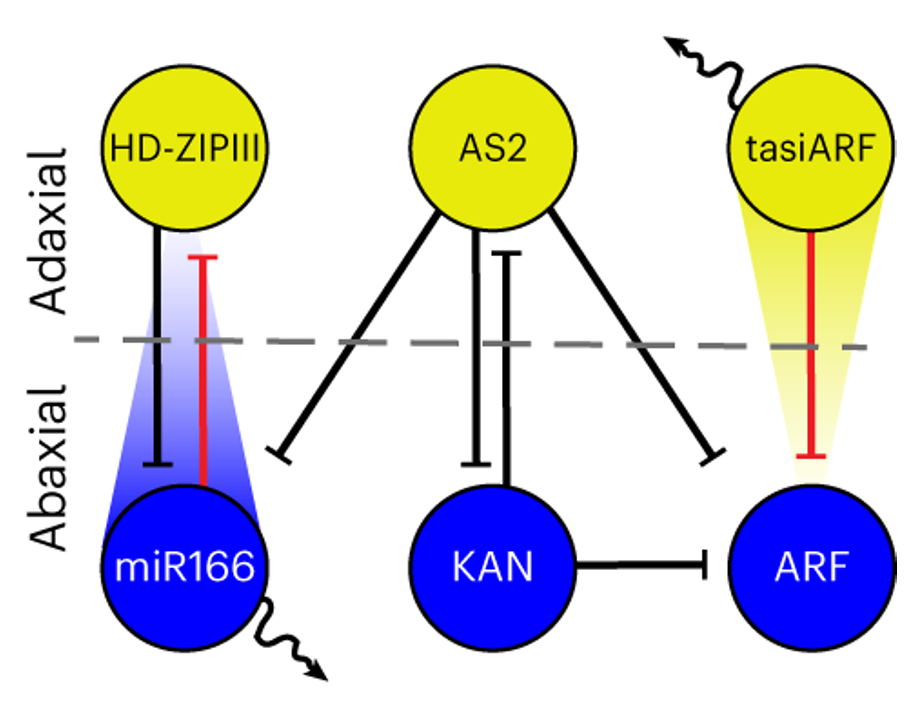
A diffusible small-RNA-based Turing system dynamically coordinates organ polarity
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe establishment of adaxial-abaxial polarity during the growth of the leaf primordium is a prerequisite for the formation of the flat, thin leaves observed in most (but not all) plants. The micro-RNAs tasiARF and miR165/6, which form concentration gradients within leaf primordia, are major contributors…
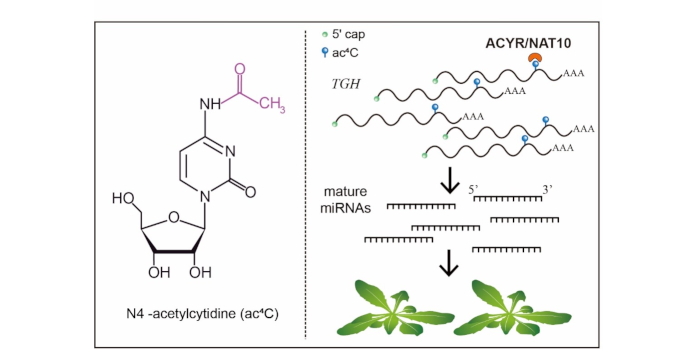
ac4C modification of mRNA is required for plant development
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellWang et al. reveal the wide occurrence and biological function of N4-acetylcytidine in plant mRNA.
https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koad189
Huijie Liu and Mingjia Chen
College of Life Sciences, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing 210095, P.R. China
Background: Eukaryotic mRNA harbors more…

Anisotropic cell growth at the leaf base promotes age-related changes in leaf shape
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe Arabidopsis thaliana leaf exhibits dramatic phenotypic changes across the juvenile-to-adult phase transition during vegetative development. For example, juvenile leaves are small, round, and lack trichomes (leaf hairs). By contrast, adult leaves contain trichomes on the abaxial (or lower) leaf surface,…
Leaf cell-specific and single-cell transcriptional profiling reveals a role for the palisade layer in UV light protection (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLeaves are the specialized organs of the plant that have evolved to maximize the use of light and CO2 for efficient photosynthesis. Although knowledge of photosynthesis has exploded recently, the molecular intricacies underlying leaf anatomy, especially mesophyll, remains unravelled. The palisade mesophyll…

Shapeshifting in the amphibious plant, Callirtriche palustris
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellKoga et al. identified a mechanism that produces heterophylly in aquatic plants grown either submerged in water or in air. Plant Cell. https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koab192
By Hiroyuki Koga, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1, Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, 113-0033, Japan.
Background: Amphibious plants,…

The secret to leaf forever: Mechanisms controlling simple leaf development (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe final shape of a leaf is a consequence of differential growth at its margins. Simple (or lightly serrated) leaves result from limited growth in the margins, while compound leaves result from a constant initiation of leaflets. A recent work by Challa, Rath, and colleagues dissected the regulatory…
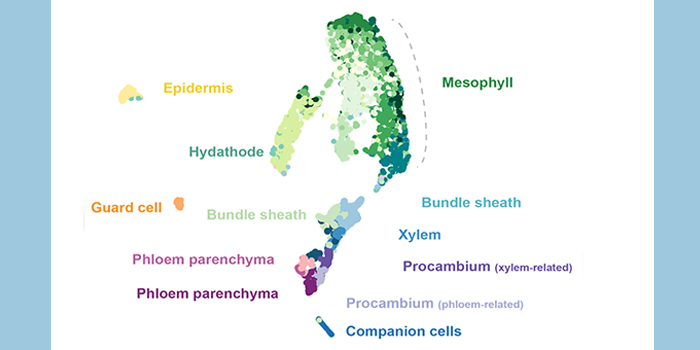
Sweeter than SWEET: A Single-Cell Leaf Vasculature Transcriptome Atlas
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellKim et al. provide insight into leaf vascular cell types and new resources to build hypotheses and strategies regarding transport of ions, metabolites, and signals.
Plant Cell http://bit.ly/2MKOR8M
Ji-yun Kim and Wolf Frommer
Background: Transport processes are critical for all multicellular…
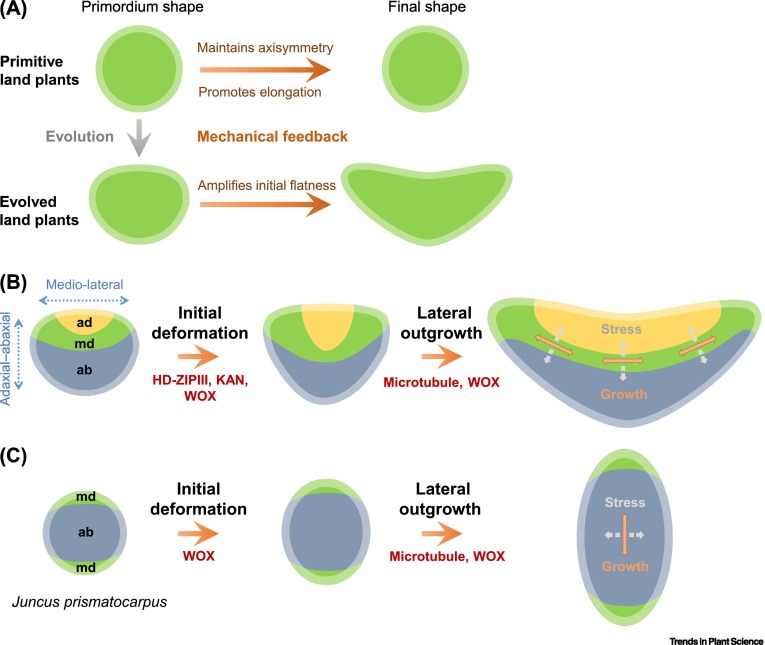
Review: The mechanical feedback theory of leaf lamina formation ($) (Trends Plant Sci.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe contribution of microtubule orientation to the direction of cell expansion is familiar to most; when microtubules wrap around the middle of a cell like a belt, the cell expands in the perpendicular direction to become longer. Recent studies have extended this idea and proposed that the mechanical…

