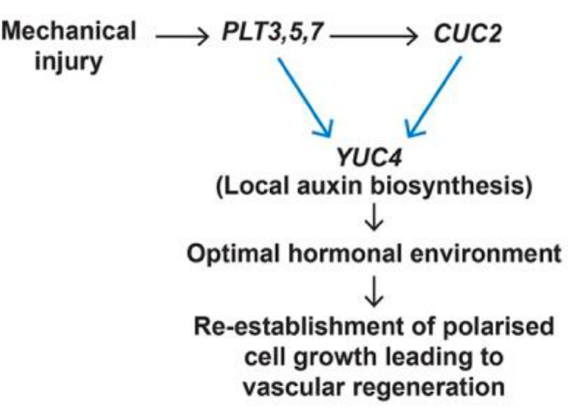
A feedforward loop controls vascular regeneration and tissue repair through local auxin biosynthesis (Development)
Plants are constantly exposed to biotic and biotic stresses that can cause tissue damage, and, as a response, plants have evolved remarkably plastic regenerative mechanisms in response to wounding. Although some genes required for regeneration have been identified in the Arabidopsis root context, most…
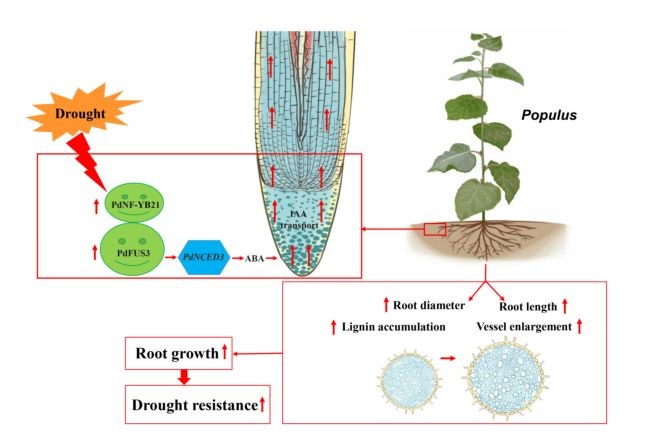
Transcription factor NF‐YB21 positively regulate the root growth in Populus (New Phytol)
Nuclear factor Y (NF-Y) proteins are heterotrimeric transcription factors made up of A, B and C subunits that exist in higher eukaryotes. Previous work has implicated NF-Ys in root growth. Recently, Zhou et al. isolated a root-specific NF-Y family transcription factor in Populus designated as PdNF-YB21.…
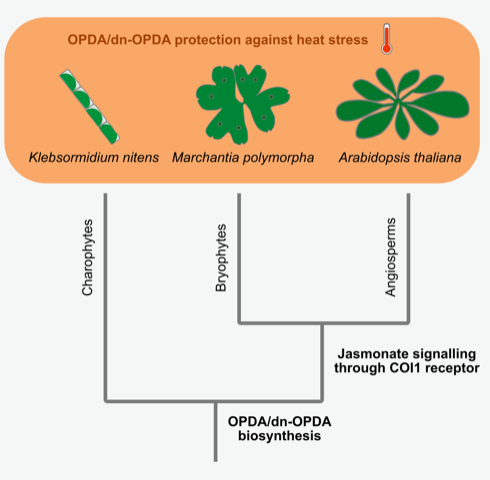
Heat tolerance regulated by an ancient jasmonate signaling pathway (Curr. Biol)
Jasmonate responses are regulated not only by the well-studied pair of the bioactive hormone jasmonoyl-isoleucine (JA-Ile) and the receptor COI1, but also the cyclopentenone OPDA and the JA-Ile precursor dn-OPDA can activate jasmonate signaling. However, the OPDA/dn-OPDA signaling and their physiological…
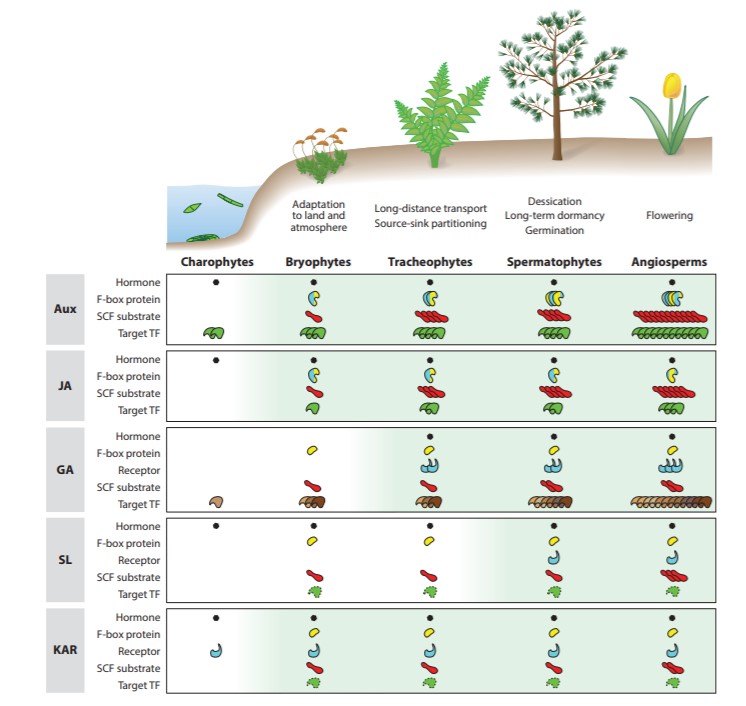
Review: Evolution of plant hormone response pathways ($) (Annu. Rev. Plant Biol.)
Spatio-temporal action of hormones is essential for proper growth and development of plants. In this review, Blázquez et al. discuss the evolution of the shared features of signaling pathways of different plant hormones. Auxin, jasmonic acid, gibberellic acid, and strigolactone signaling pathways…
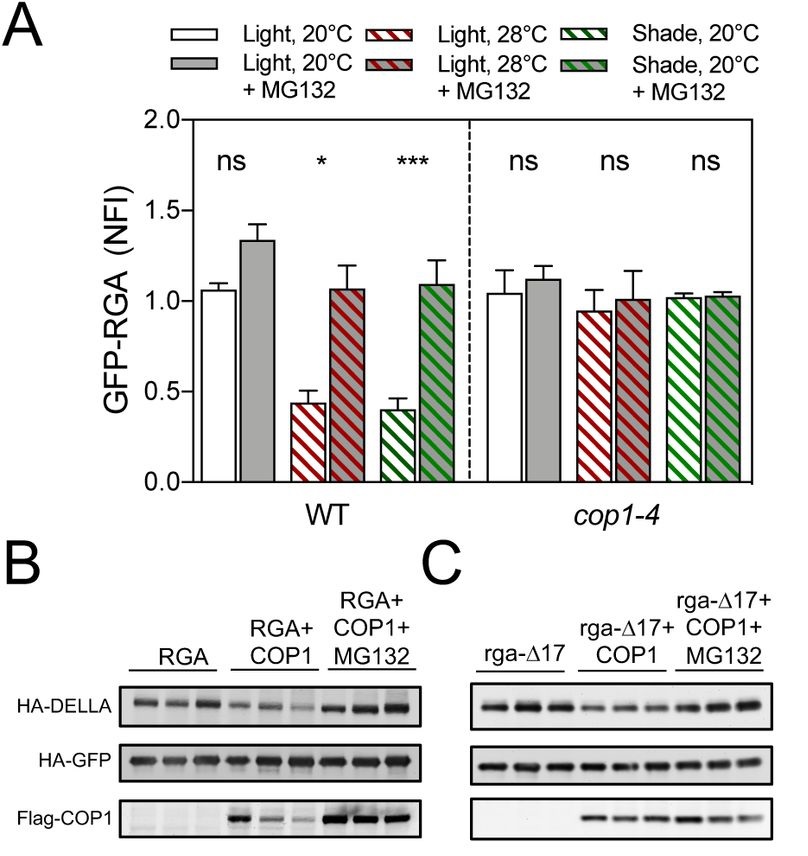
COP1 destabilizes DELLA proteins in Arabidopsis (bioRxiv)
The canonical model of gibberellic acid (GA) signaling pathway includes the recognition of the hormone by the receptor GID1 and the further degradation of the DELLA proteins by the proteasome. In this paper, Blanco-Touriñan et al. observed in Arabidopsis that the DELLA protein REPRESSOR OF ga1-3 (RGA)…
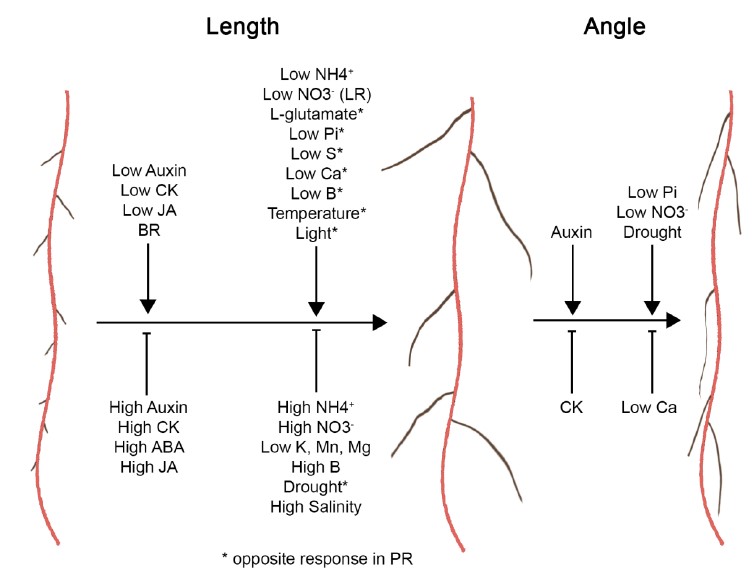
Review. Same, but different: growth responses of primary and lateral roots ($) (J. Exp. Bot.)
Lateral roots arising from programmed cell division from primary roots in both monocots and dicots share some similarities and dissimilarities in developmental signaling. In this review, Waidmann et al. discuss lateral root organogenesis and elongation with respect to hormone, nutrient, and abiotic conditions.…
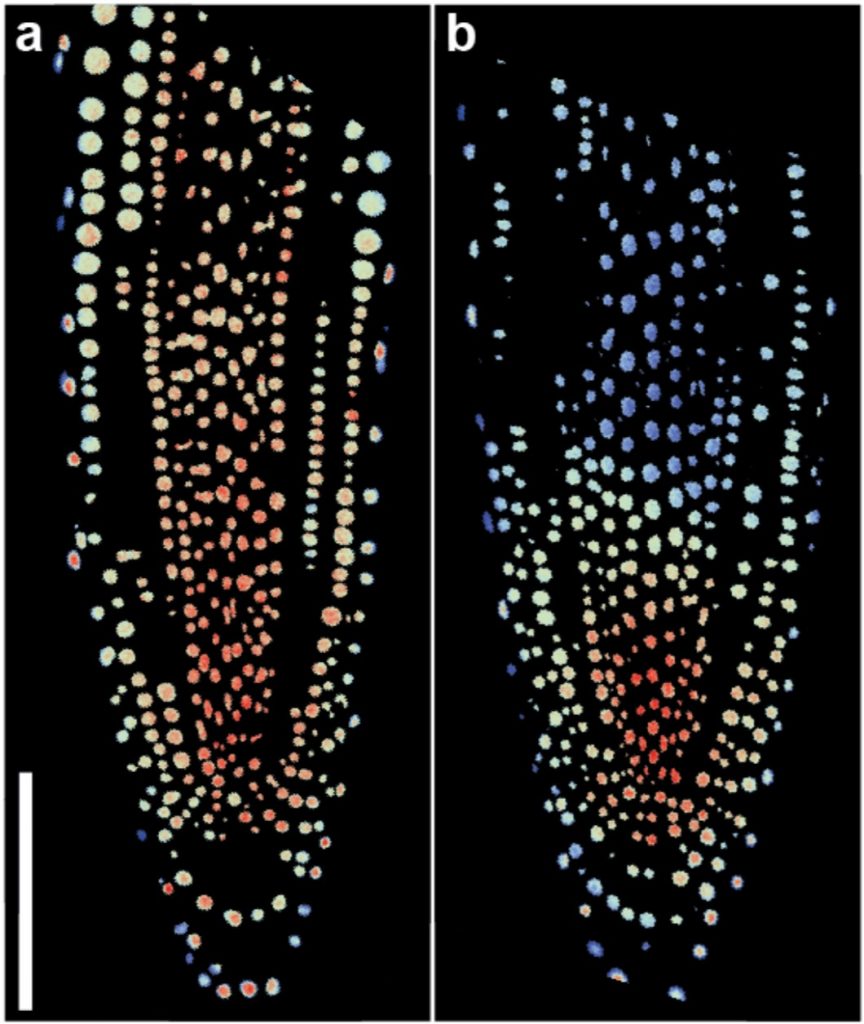
AuxSen: a biosensor for direct visualization of auxin (bioRxiv)
Auxins participate in nearly every aspect of plants' life cycle, but the information about the actual distribution of this hormone is scarce. The location of the hormone has been inferred using reporters based on auxin-transcriptional responses or auxin-dependent degradation signals. For a direct visualization,…
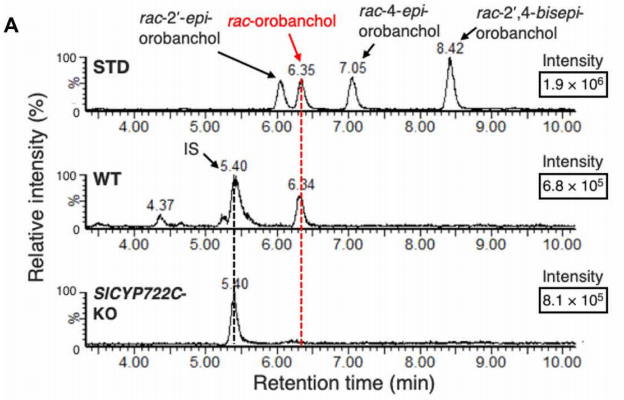
Direct conversion of carlactonoic acid to orobanchol by cytochrome P450 CYP722C in strigolactone biosynthesis
Strigolactones (SL) are a compounds that play important roles as phytohormones and as a rhizosphere signaling. Despite the great advances in their research that occurred recently, their biosynthetic pathway is still not well understood. Until now, the pathway leading to the precursor carlactonic…
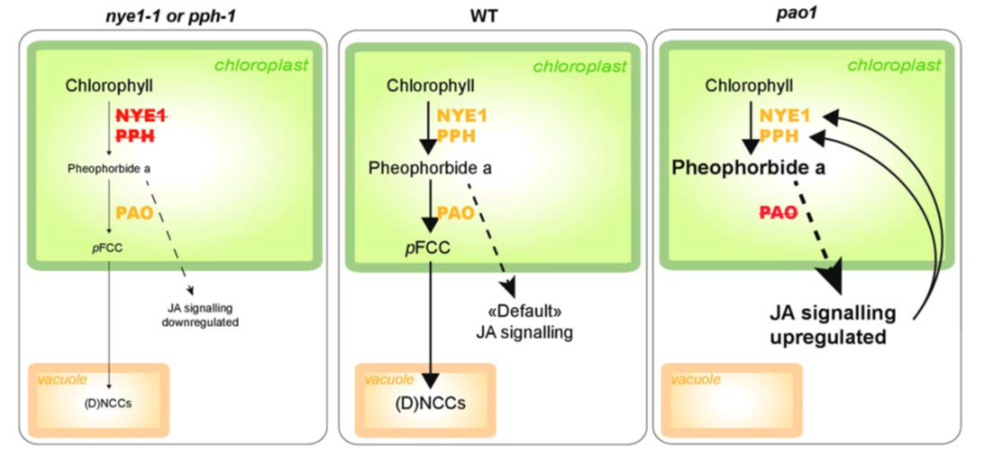
Pheophorbide a may regulate jasmonate signaling during dark-induced senescence
During leaf senescence, nitrogen-rich chlorophyll is broken down through a regulated process so that nitrogen-containing compounds can be reassimilated into the plant body. Chlorophyll catabolites are sequestered in the vacuole as linear tetrapyrroles known as phyllobilins, produced through the action…

