
Special Science Issue: Plants and Heat
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe June 12 issue of Science has a focus on plants and heat that includes several excellent review and research articles. In a very interesting review, Singh Yadav et al. discuss the complex and fascinating question of how plants sense temperature, emphasizing both the biophysical nature of temperature…
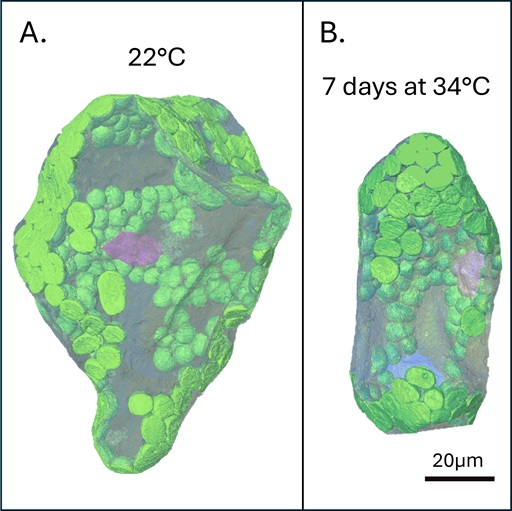
Sweet heat: Organelle-specific carbohydrate metabolism in heat stress
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant metabolism varies substantially between developmental stages, cell types, and intracellular environments. Similarly, biochemical responses to abiotic stress often deviate between neighboring cell types, but discerning what is changing where becomes more challenging in smaller and more fragile sub-compartments. …
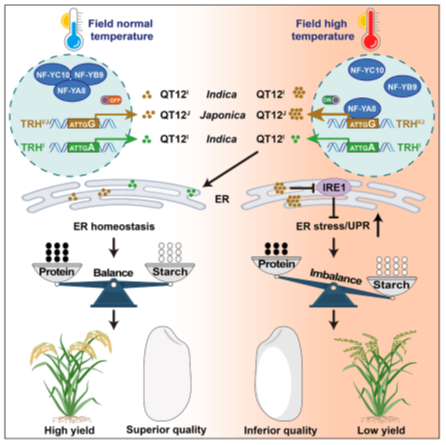
Cracking the code of rice grain quality under heat stress
Plant Science Research WeeklyRice is one of the most important food crops globally, providing more than 20% of the world’s calorie intake and over 75% for the population in Asia. Therefore, apart from yield, grain quality is another critical agronomic trait for breeding and improvement, especially under stressful environmental…
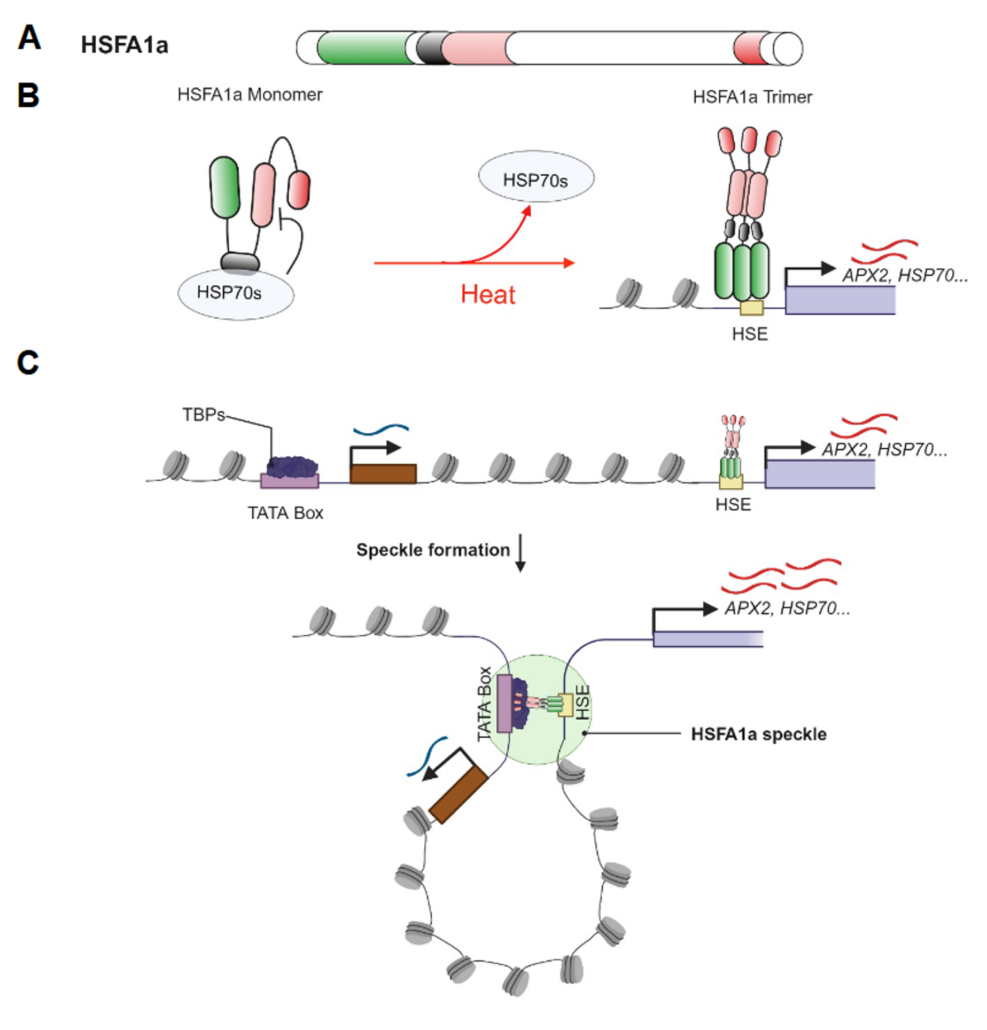
Prion-like domains of sensory HSFs remember heat
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe heat shock response, a rapid transcriptional response to heat, was first observed nearly 60 years ago, and has long been a paradigm for understanding gene responses to exogenous cues. The family of genes encoding heat shock factors (HSFs) is greatly expanded in plants. These HSFs serve as key regulators…
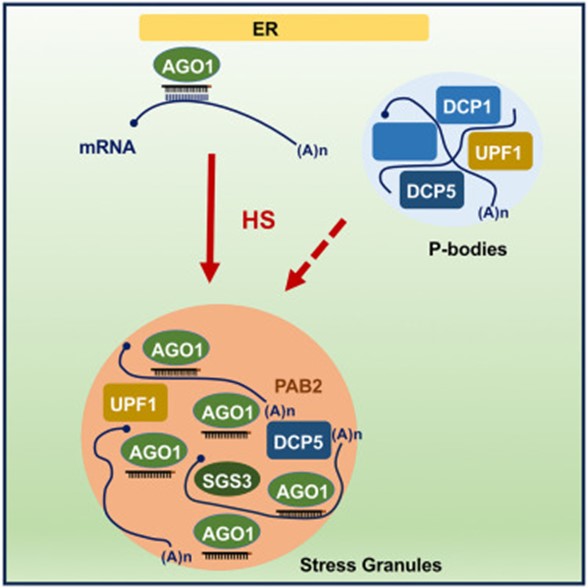
Heat stress promotes Arabidopsis AGO1 phase separation and association with stress granule components
Plant Science Research WeeklyA new article by Blagojevic, Baldrich, and Schiaffini et al. reveals that Arabidopsis ARGONAUTE1 (AGO1) protein, a pivotal agent in miRNA and siRNA-mediated gene silencing associated with the rough endoplasmic reticulum, dynamically localizes within stress granule components during heat stress (HS).…
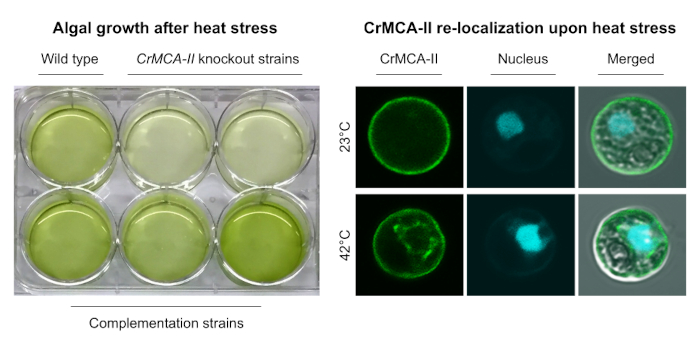
Thermoprotection by a metacaspase
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellZhou et al. examine the fundamental functions of metacaspases in the unicellular green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.
https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koad289
By Yong Zou, Adrian N. Dauphinee, Simon Stael and Peter V. Bozhkov
Department of Molecular Sciences, Uppsala BioCenter, Swedish University…
Review. Autophagy: A key player in the recovery of plants from heat stress
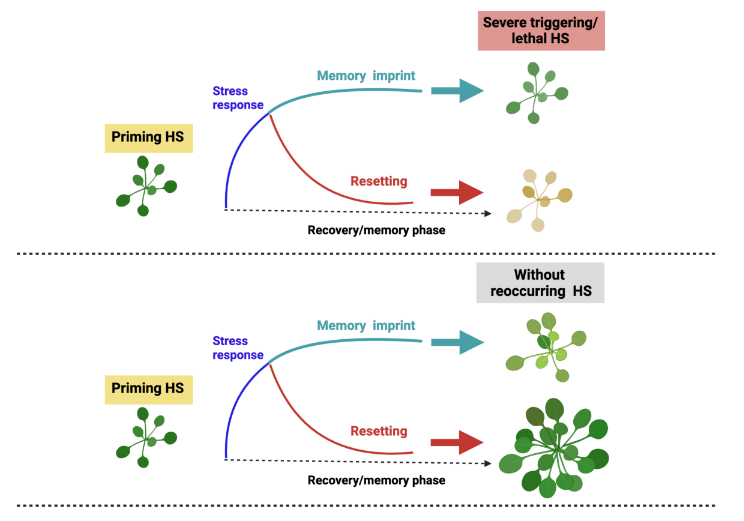
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants have a remarkable ability to adapt to stress. For many stresses, plants respond to short-term mild exposure by becoming more tolerant to subsequent harsher stresses that would otherwise be lethal; this effect is known as priming. Priming occurs through several mechanisms that can include changes…

Runaway transcription makes plants sensitive to heat stress
The Plant Cell: In a Nutshell
Kim et al. investigate the role of a heat shock protein in thermotolerance.
https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koac351
By Minsoo Kim and Elizabeth Vierling at UMass Amherst
Background: Plants can survive heat stress by producing heat shock proteins (HSPs) that protect and rescue other proteins.…
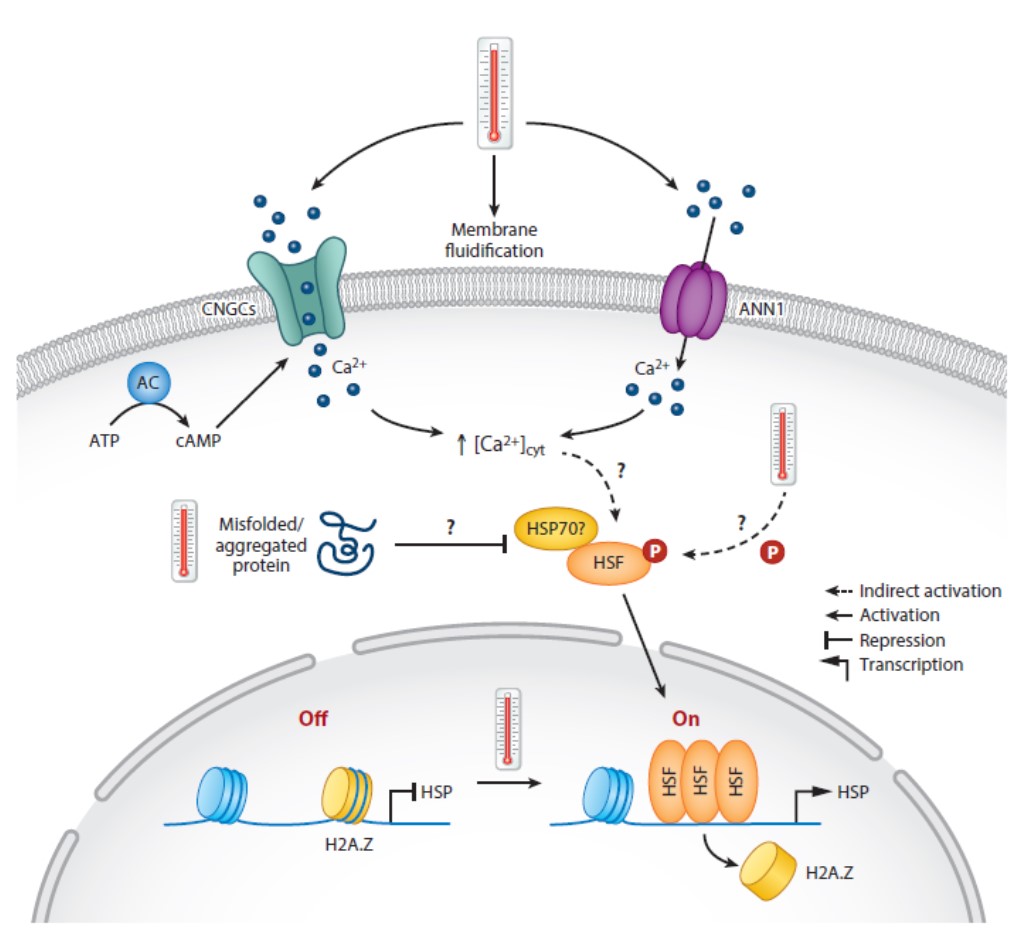
Review: Temperature sensing in plants
Plant Science Research WeeklyLike all organisms, plants respond to changes in temperature by activating pathways that enable them to stay alive in spite of rising or lowering temperatures. Interestingly though, there is no universal temperature sensing mechanism across the domains of life. Changes in membrane fluidity (think of…

