
Endosperm turgor pressure both promotes and restricts seed growth and size (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklySeed size is a plant trait with agricultural and ecological relevance. However, the mechanisms that determine the final size of seeds are still subject to debate. Here, Creff and colleagues use computational models and mutant experiments to dissect the role of endosperm turgor in Arabidopsis seed size.…

Review: Can smart nutrient applications optimize the plant's hidden half to improve drought resistance? (Physiol. Plant.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe root system has three key functions: support/anchoring, uptake of water, and uptake of nutrients. Many questions remain about how roots integrate all of these functions into the architecture of a single system. Here, Bardhan et al. explore whether modifying the nutrient environment (hence root’s…
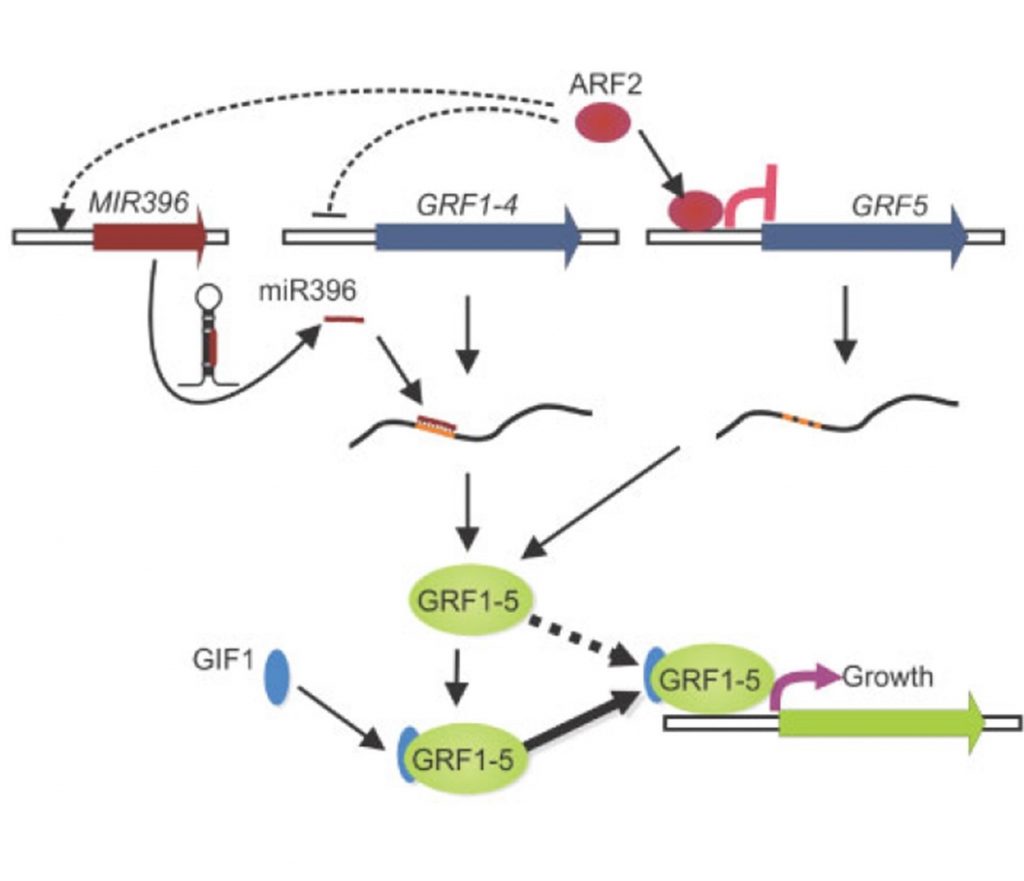
A complementary mechanism to the microRNA-mediated control of leaf size (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants form leaves with highly reproducible sizes and shapes by employing a conserved set of developmental regulators. During early leaf growth, a zone of high cell proliferation is formed towards the proximal end of the lamina. Proliferating cells progressively exit this zone and enter the distal…
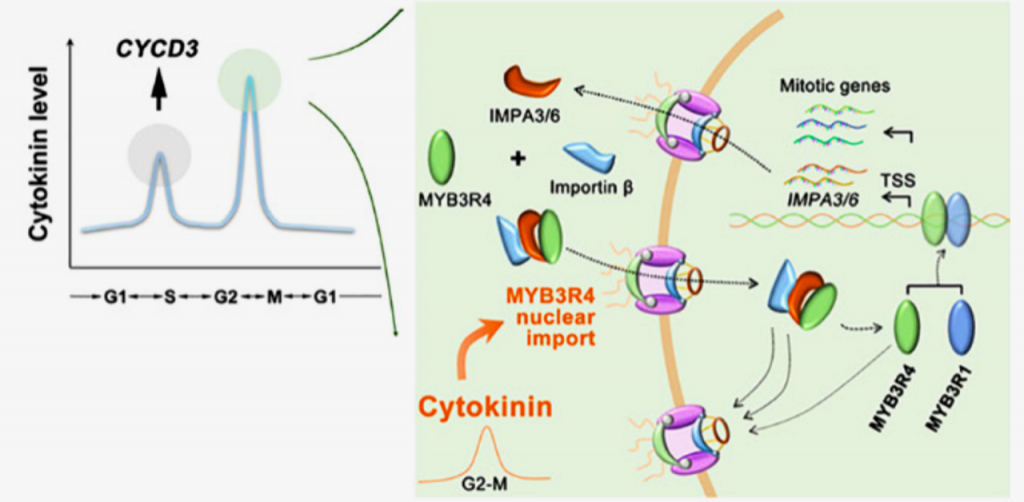
Molecular mechanism of cytokinin-activated cell division in Arabidopsis (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyProper organogenesis depends on the precise control of cell proliferation and differentiation. Cytokinin and auxin have emerged as key regulators of both these processes, where cytokinin promotes proliferation and synergistically with auxin fine-tunes the proliferation and differentiation rate. Years…
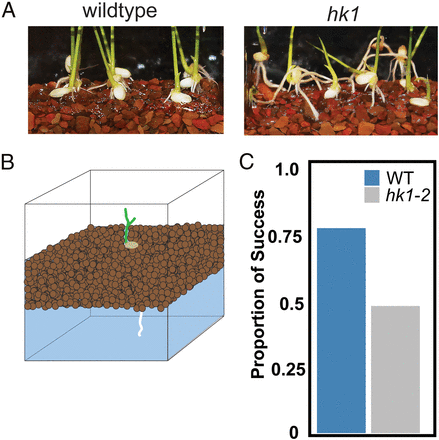
Mechanism and function of root circumnutation (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThis is an engrossing paper. The authors start off with a simple mutant screen for abnormal root growth in rice seedlings, through which they identified three “long root” mutant alleles of a rice mutant in a gene encoding a histidine kinase, HK1. Careful analysis showed that the mutant roots fail…
Jasmonate biosynthesis arising from altered cell walls is prompted by turgor-driven mechanical compression (Sci. Advances)
Plant Science Research WeeklyJasmonate (JA) coordinates plant development and response to a wide range of biotic and abiotic stresses. JA production is stimulated by wounding, which damages cell walls, and increased in plants carrying mutations in cellulose biosynthetic genes. Nevertheless, the intracellular events connecting mechanical…
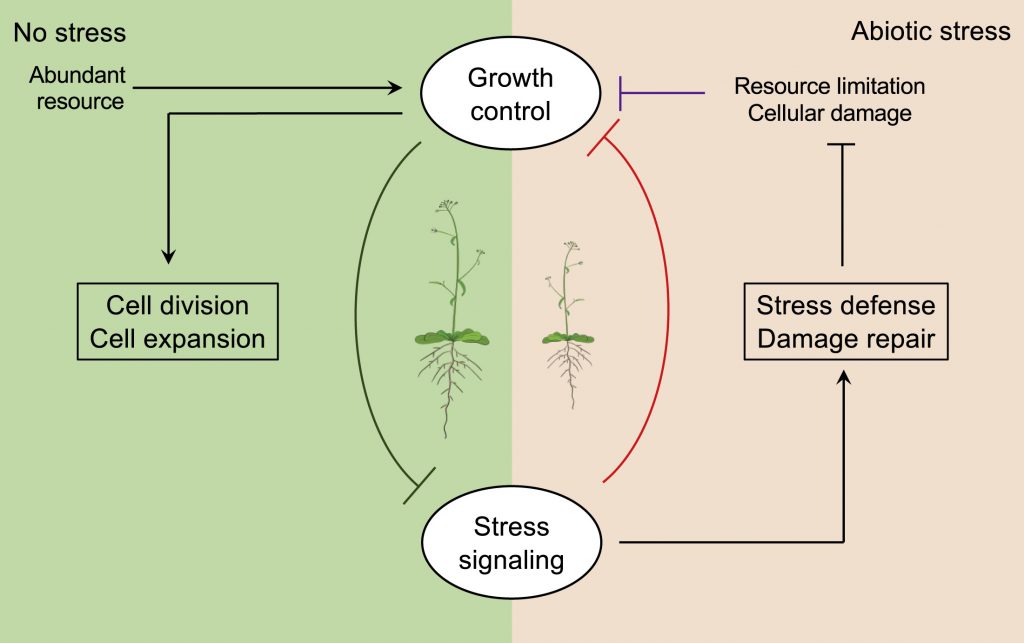
Review: Thriving under stress: How plants balance growth and stress response (Devel. Cell)
Plant Science Research Weekly
What exactly is the growth/defense tradeoff? This review is an excellent place to ask. Zhang et al. review evidence that shows that it is much more than a competition for limiting resources – the plant actively responds to stress in ways that may slow growth but ultimately promote survival. The…
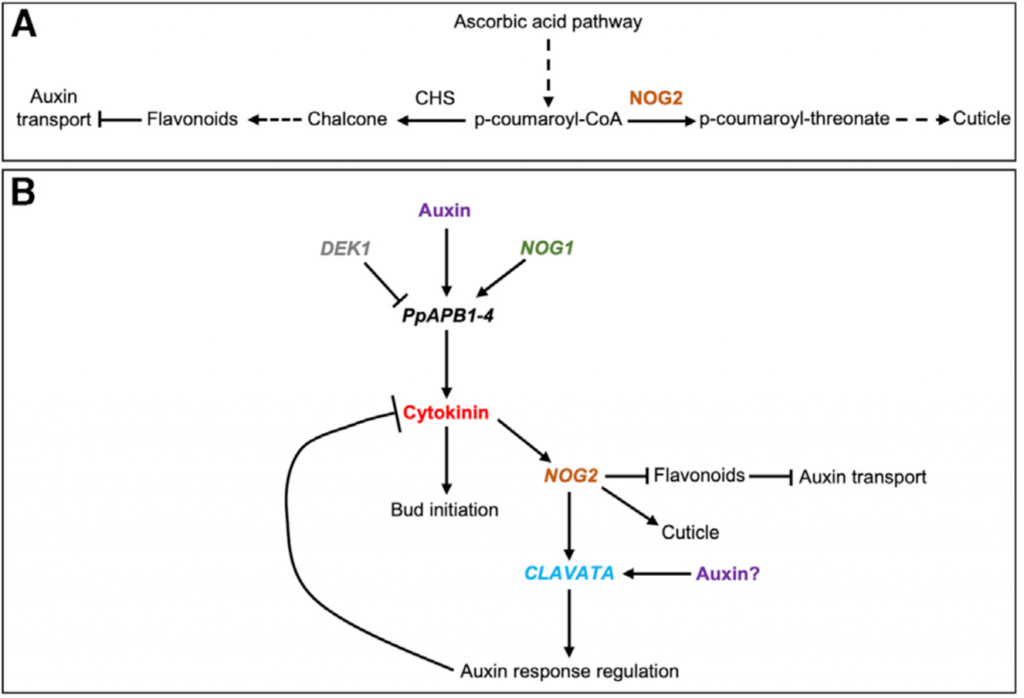
NO GAMETOPHORES 2 is a novel regulator of the 2D to 3D growth transition in the moss Physcomitrella patens (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Three-dimensional (3D) growth was an essential evolutionary innovation that allowed the radiation and diversification of land plants. In most land plants the transition from two-dimensional (2D) to 3D growth takes place during embryo development and its disruption results in lethality, however, the…

SAURs protein antagonistically regulate a phosphatase activity during apical hook development and cotyledon opening (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Upon germination in dark, plants adopt a strategy known as skotomorphogenesis, or etiolation, to protect the shoot apical meristem and cotyledon from damage while the seedling moves through the soil. The seedlings de-etiolate when they perceive light and the apical hook and cotyledon open. Wang et…

