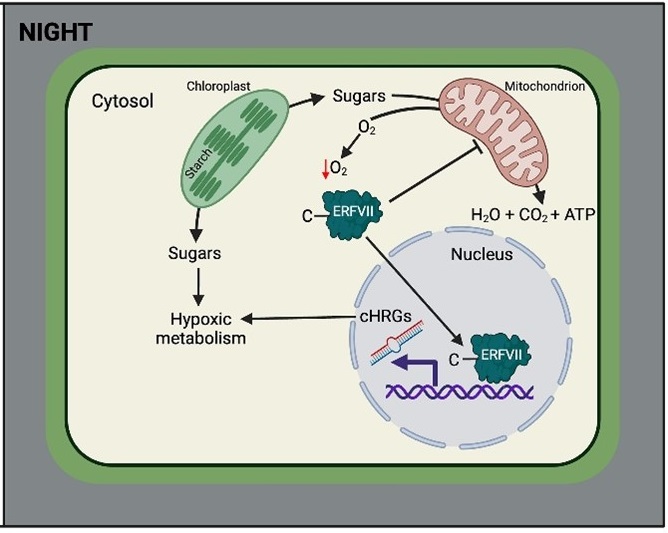
Oxygen supply dictates growth and metabolism in young leaves
Plant Science Research WeeklyWhen thinking of hypoxia or low oxygen in plants, the image that often comes to mind is one of flooding stress. However, it’s not just plants exposed to excess of water that face hypoxia. Even in growing plants, hypoxia sensing and the existence of hypoxic niches play a vital role in their development.…
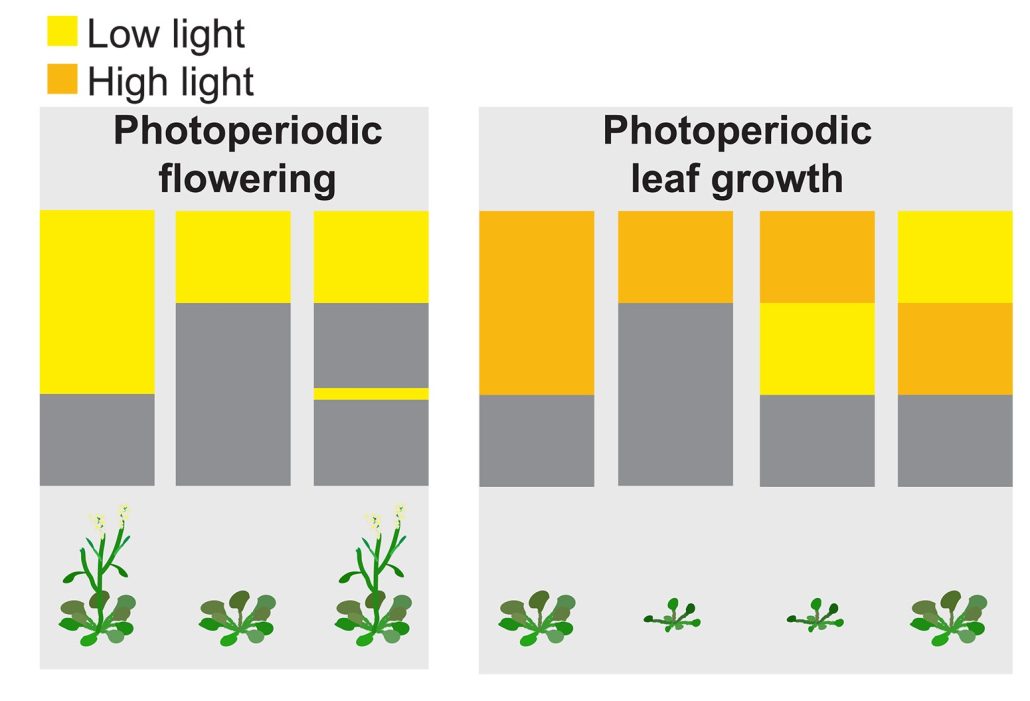
Seasonal flowering and seasonal growth measure light duration differently
Plant Science Research WeeklyOne of the first lessons a plant biologist learns is that many plants coordinate their seasonal flowering through measuring daylength, and that this process involves both photoreceptors and the biological clock that functions inside of cells. Of course, daylength also affects plant metabolism, in part…

Brassinosteroid coordinates cell layer interactions via cell wall and tissue mechanics
Plant Science Research WeeklyOrganismal growth requires extensive coordination between cells and tissues with different identities, and this is particularly important for plants with their rigid cell walls and lack of cell motility. A key mechanism for tissue coordination involving brassinosteroids has been identified by Kelly-Bellow…
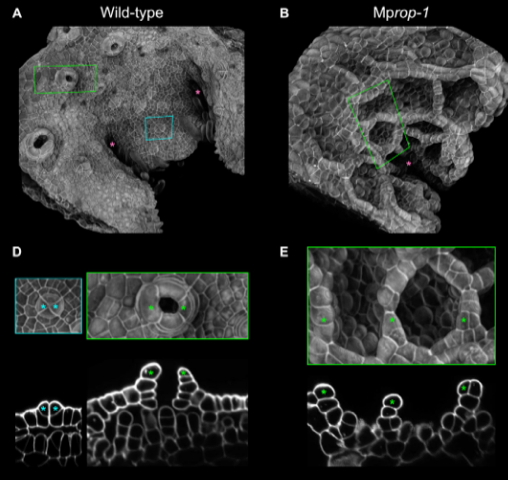
RHO GTPase of plants regulates polarized cell growth and cell division orientation during morphogenesis
Plant Science Research WeeklyPrecise spatial control of cell division and cell growth is necessary to produce the specific cellular organizations demanded by the complex tissues and organs of morphologically complex organisms One of many factors that guide cell division/growth is cell polarity, of which RHO GTPase-type proteins…
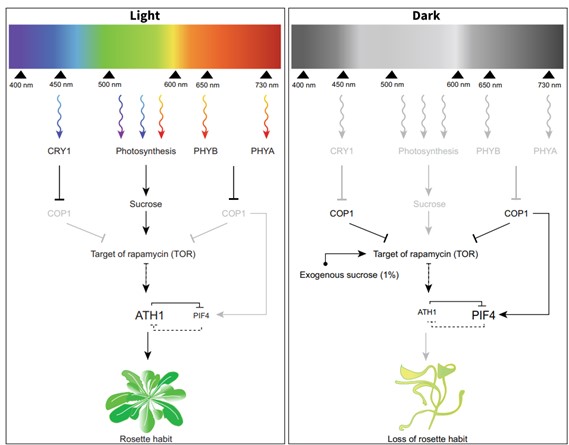
Light and sucrose signaling converge at TOR kinase to control plant development
Plant Science Research WeeklyDifferent photoreceptors (mainly phytochromes and cryptochromes) perceive light, which acts as a signal for controlling plant growth and development. Similarly, light is absorbed by chlorophylls (and carotenoids) for generating energy via photosynthesis. In search of a link between these two light-mediated…
Review: Not only turgor can shape plant growth!
Plant Science Research WeeklyCell wall tensile stress and turgor pressure are two important determinants of cell growth. Turgor pressure has been regarded as a passive contributor, however recent evidence reviewed by Ali et al. suggests that turgor is an emergent property that determines growth. Wall stress and turgor pressure are…
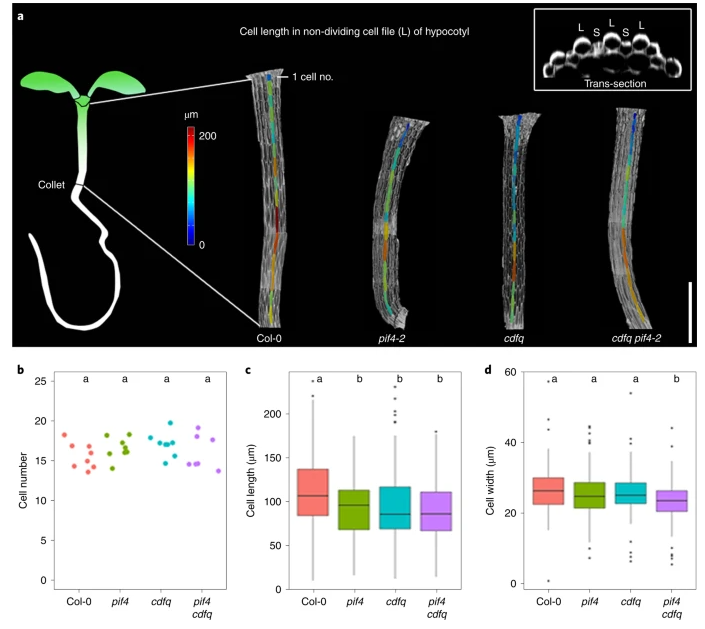
PIF4 enhances DNA binding of CDF2 to co-regulate target gene expression and promote Arabidopsis hypocotyl cell elongation (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyResponses to environmental and internal signals require the recruitment of transcription factors (TFs). TFs recognize simple DNA sequences to activate specific genes that will accomplish the required functions. DOF (DNA-binding with one finger) is a large family of plant TFs that encloses the CYCLING…
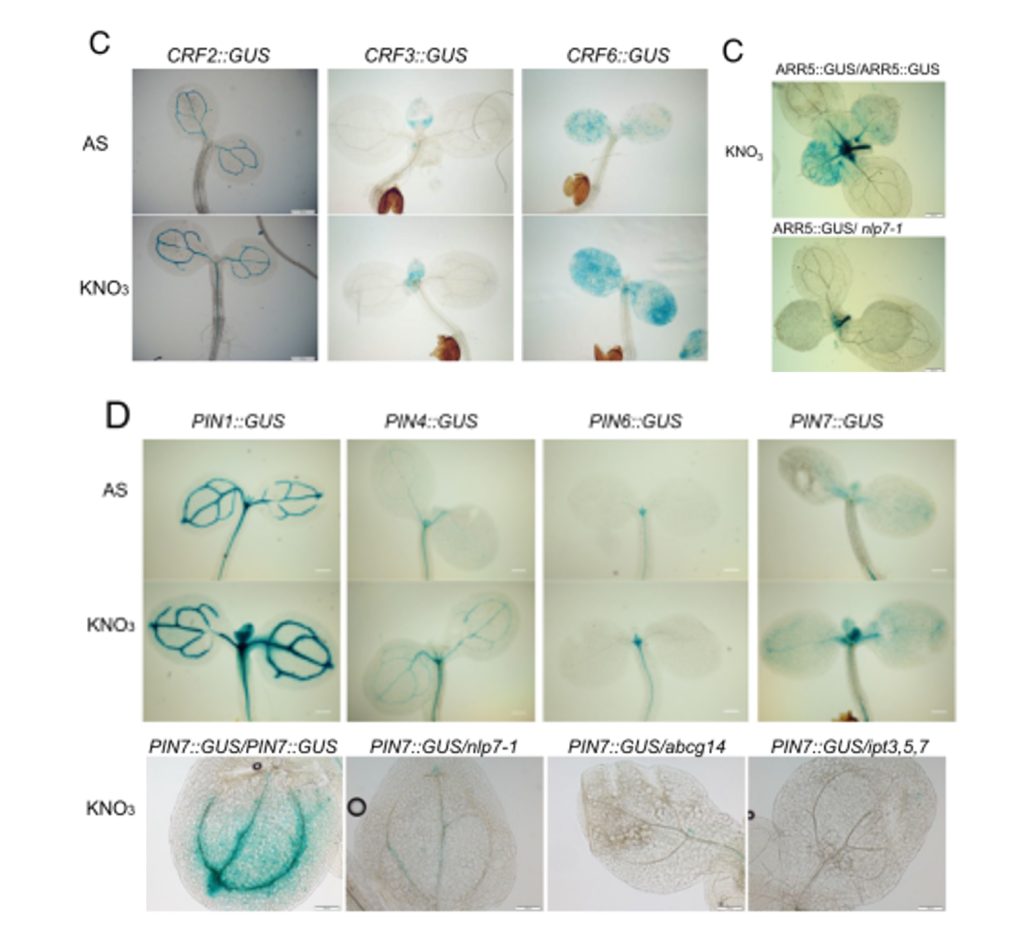
NLP7-CRF-PIN, the nitrate-cytokinin-auxin crosstalk module, conveys root nitrate signals and regulates shoot growth adaptive responses (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyNitrate, the prominent form of nitrogen used by most land plants, is a signal regulating plant growth and development. Nitrate sensing by roots not only regulates root development to facilitate nutrient foraging, but also the growth of distant plant organs. Cytokinin is a mobile signal coordinating nitrate…
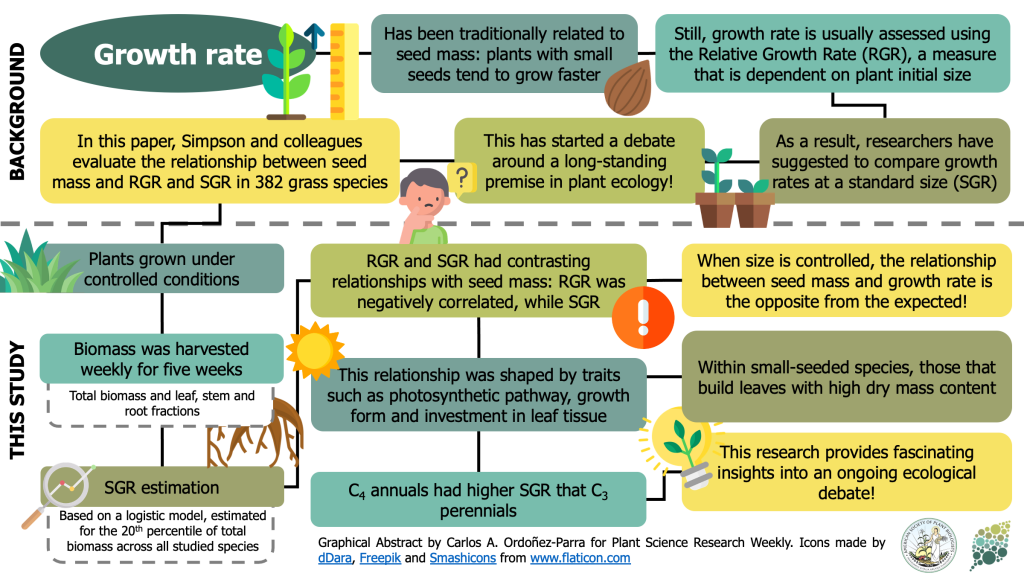
Large seeds provide intrinsic growth advantage that depends on leaf traits and root allocation (Funct. Ecol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyA long-standing premise in plant ecology is that seed mass and growth rate are negatively correlated, meaning that small-seeded species grow faster than large-seeded ones. However, this relationship remains controversial given that the most common measurement for growth rate –Relative Growth Rate (RGR)–…

