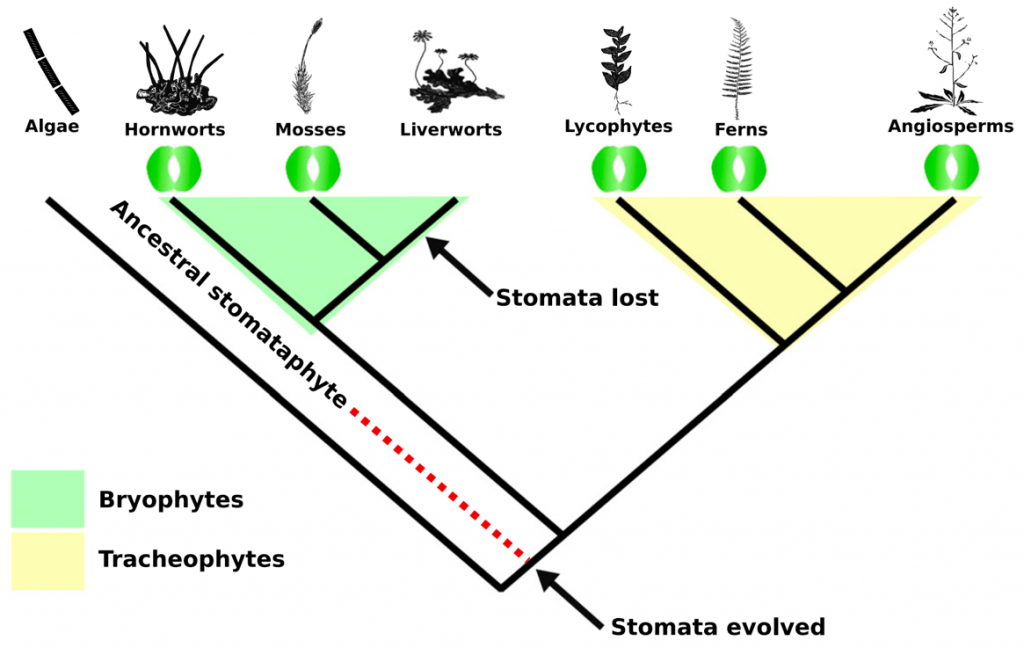
Phylogenomic evidence for reductive evolution of stomata (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyColonization of the terrestrial environment by land plants (embryophytes), a monophyletic clade that evolved from freshwater streptophyte algae, forever changed Earth by transforming biogeochemical cycles. The evolution of stomata was a key adaptation that allowed the colonization of terra firma. Present…
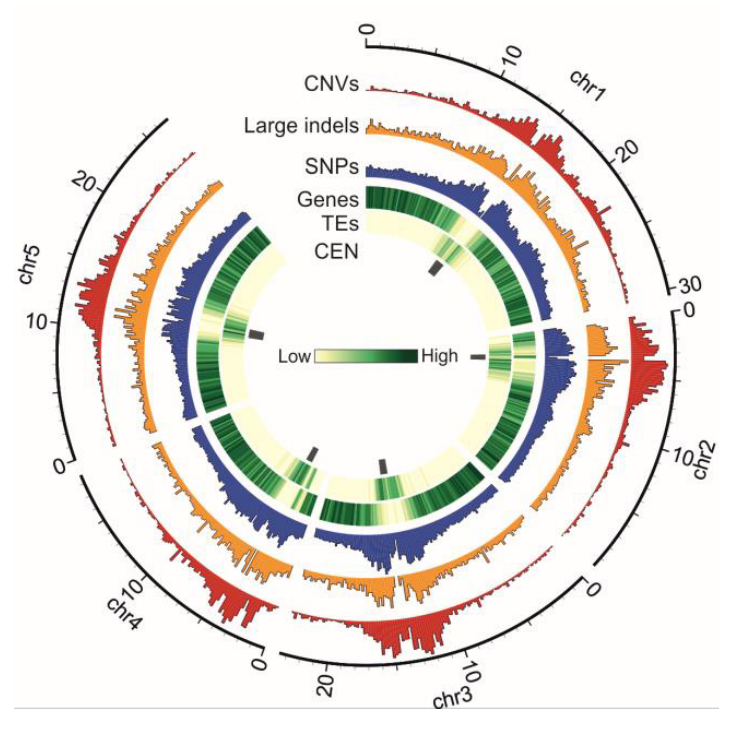
AthCNV: A map of DNA copy number variations in the Arabidopsis thaliana genome (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIntraspecific phenotypic variability can be attributed to differences at the genome level such as copy number variations (CNVs). CNVs are large DNA fragments which differ in number between individuals and likely have a crucial evolutionary role. Due to the 1001 Genomes Project, over 1,000 Arabidopsis…
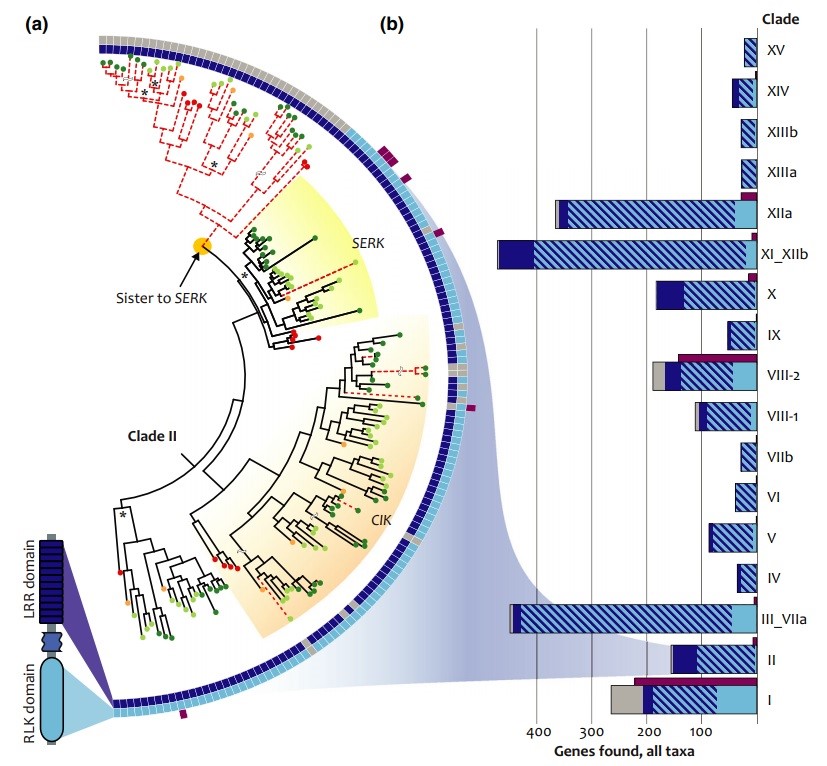
Structural evolution drives diversification of the large LRR-RLK gene family (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLeucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinases (LRR-RLKs) act as signaling receptors, are the largest plant-specific protein kinase family, and are involved in myriad developmental activities and defense systems. Due to the large number of proteins in this group, their diversification and consequent redundancy…

Innovation, conservation, and repurposing of gene function in plant root cell type development (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRoots have many specialized cells arranged in concentric circles that are functionally homologous among various plant species but with varying cell-type-specific developmental programs. To further understand these developmental programs, Kajala et al. performed TRAPseq (Translating Ribosome Affinity…
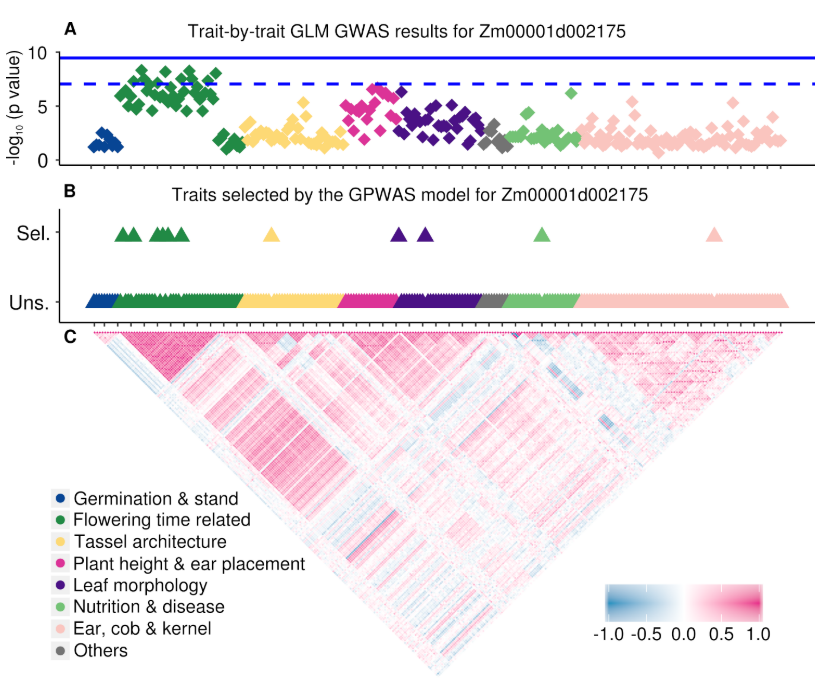
Genome-phenome wide association in maize and Arabidopsis identifies a common molecular and evolutionary signature (Mol. Plant)
Plant Science Research WeeklyGenome-wide association studies (GWAS) are widely used to link natural genetic variation to trait variation, with a single or a select few correlated traits assessed. High-throughput phenotyping allows the scoring of hundreds of individuals for various traits at several time points. An undeniable consequence…
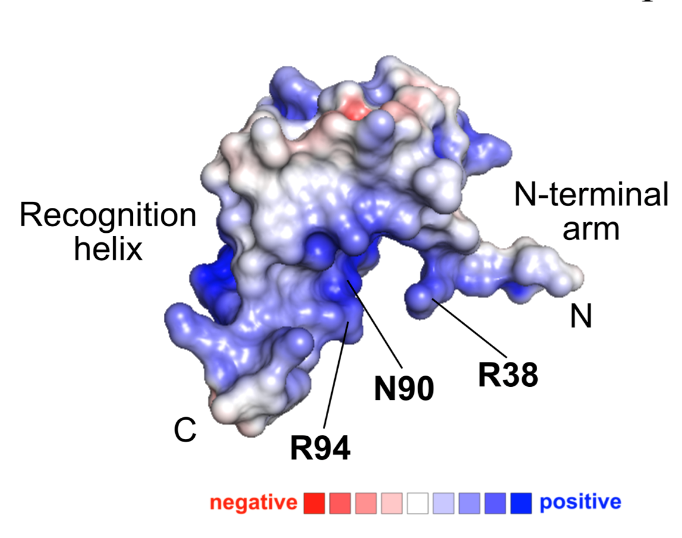
Structural basis for WUSCHEL binding (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe transcription factor WUSCHEL (WUS) plays a central role in organization of the shoot meristem. The three-helix bundle homeodomain in WUS can bind to several distinct DNA sequence motifs in many target genes promoters, but a structural view of these binding events has been lacking. Here Sloan et al.…
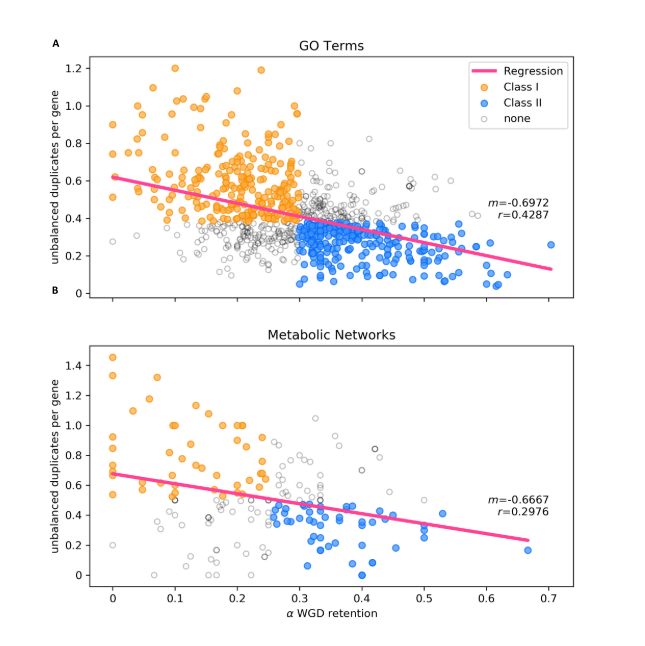
Gene balance predicts transcriptional responses immediately following ploidy change in Arabidopsis thaliana (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThroughout evolutionary time polyploidization events have occurred frequently, increasing the gene copy number (gene dosage) of multiple angiosperms. The gene balance hypothesis proposes that there is selection on gene copy number to maintain the stoichiometric balance between dosage-sensitive genes…
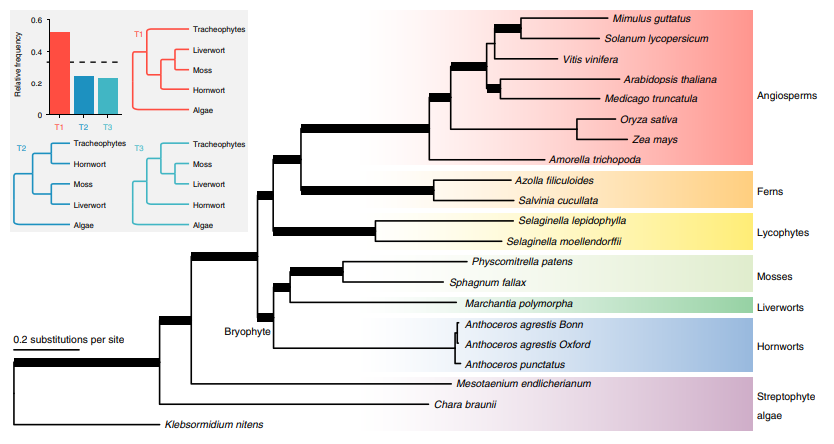
Hornwort genomes (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyA major update in plant genome information is taking place. Two independent groups have published genomes of hornwort species from the Anthoceros genus. Both papers arrive at similar conclusions supporting the model of a single “Setaphyta” clade, with hornworts sister to liverworts and mosses. These…
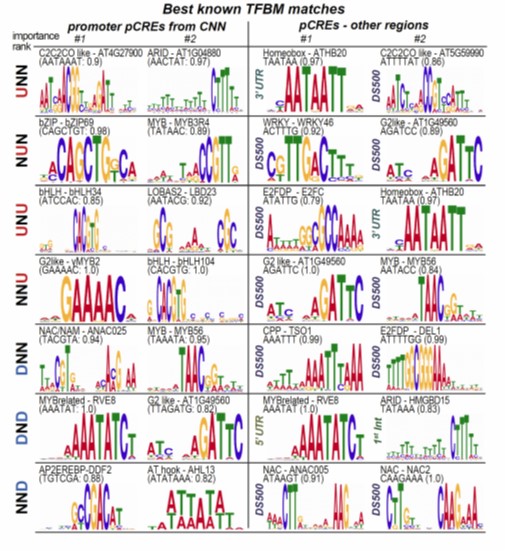
The cis-regulatory codes of response to combined heat and drought stress (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAs sessile organisms, plants must not only respond to a single stress, but multiple stresses at the same time. To understand the DNA regulatory elements that mediate the transcriptional response to heat, drought and combined heat and drought stress, Azodi et al. utilized the known transcription factor…

