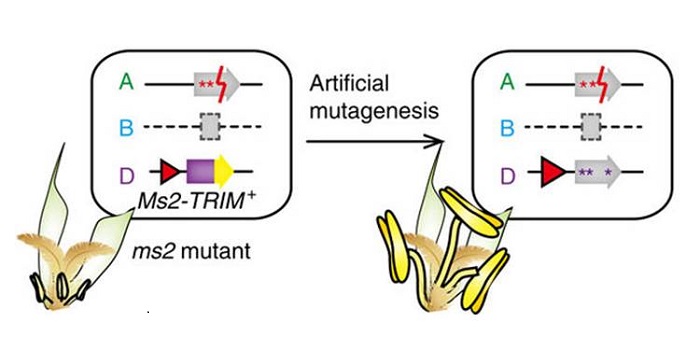
A TRIM insertion in the promoter of Ms2 causes male sterility in wheat
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe first dominant male-sterile mutant in wheat, ms2 was identified more than 40 years ago, and Xia et al. have now identified the molecular basis for this trait. They find that the mutation is caused by a transposon (a terminal-repeat retrotransposon in miniature, or TRIM) insertion into the promoter…
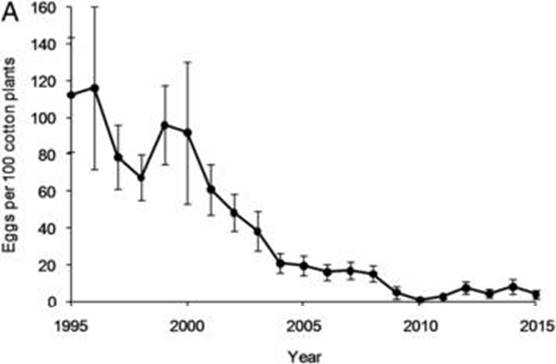
Hybridizing transgenic Bt cotton with non-Bt cotton counters resistance in pink bollworm
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research0 Comments
/
Biotic interactions are complex; any effort by the prey/host to defend against the predator/pathogen provides selective pressure towards overcoming those defenses. As new herbivore control methods are developed they quickly lose effectiveness as the pests evolve resistance; this is true whether the control…

Root hydrotropism is controlled via a cortex-specific growth mechanism ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchHydrotropism is the curvature of a plant root towards water. Previous work showed that the hormone abscisic acid (ABA), but not the auxin transporters AUX1 and PIN, is required for hydrotropism, demonstrating that the mechanisms of hydrotropism and gravitropism are distinct. Previous work also showed…
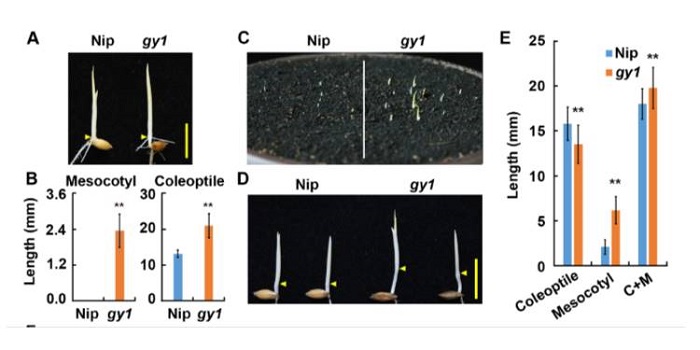
Ethylene-inhibited jasmonic acid biosynthesis promotes elongation of etiolated rice seedlings
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchDuring germination, the rice shoot is protected by the coleoptile, which is a highly light and hormone-sensitive tissue. While searching for genes involved in ethylene responses, Xiong et al. identified a mutant with an elongated coleoptile, in which the subtending mesocotyl is also elongated; they named…
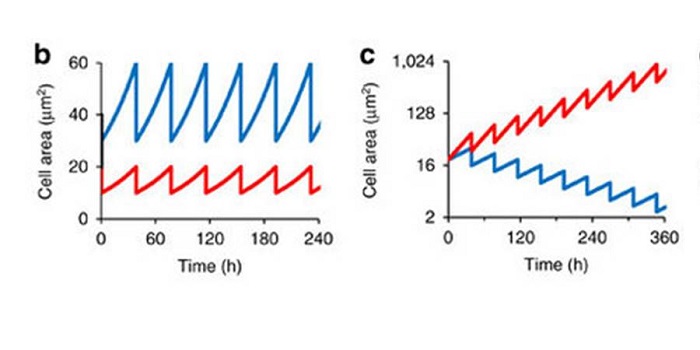
Cell-size dependent progression of the cell cycle for homeostasis and flexibility of cell size
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchCell size is determined by growth rate and frequency of division. Studies in yeast revealed mechanisms that coordinate these processes, as well as the crucial checkpoint controls that ensure the cell is “ready” to divide, but can models from single-celled organisms be applied to multicellular ones…
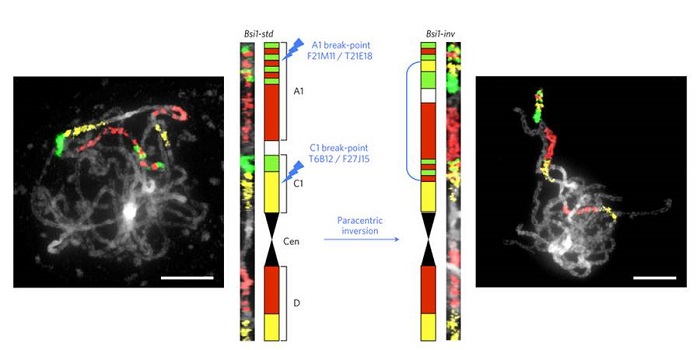
Young inversion with multiple linked QTLs under selection in a hybrid zone
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchChromosomal inversions are chromosomal rearrangements that can span several Mb and have been described in several organisms from Drosophila to maize. Inversions suppress recombination and can favor local adaptation and speciation if they capture favorable alleles. It’s not clear though if favorable…

Brassica oilseeds transporter gene mutations decrease antinutritional glucosinolates
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchGlucosinolates are sulfur-containing defense compounds produced by brassica plants. Brassica napus (canola) is an important oilseed crop because a low-glucosinolate variety has been developed. Brassica juncea is more stress tolerant, but has not been developed as a crop due to its high levels of glucosinolates.…
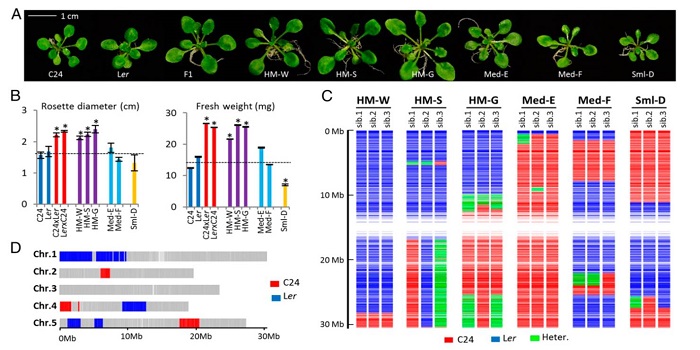
PIF4-controlled auxin pathway contributes to hybrid vigor in Arabidopsis thaliana
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchHybrid vigor is a well-known but still poorly understood phenomenon in which the F1 hybrid progeny of a cross often show enhanced growth as compared to either parent. True-breeding lines that retain this enhanced growth, known as hybrid mimics, have been developed and are important tools for understanding…
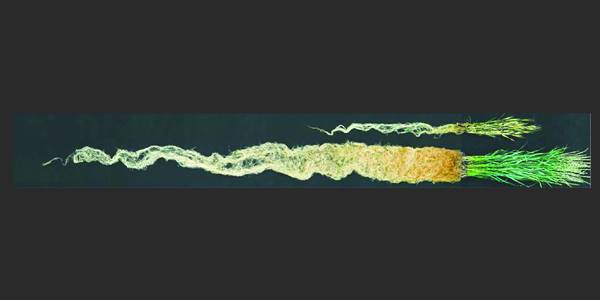
Review: Can modern agriculture be sustainable? Perennial polyculture holds promise
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchMost of our major food crops are annuals, started from seed each year and fully harvested to collect the seeds at the end of their short growing season. By contrast, perennial crops are longer lived, and only partially harvested, so their biomass can increase from year to year. The larger root system…

