
Harnessing the hidden genetic diversity for improving multiple abiotic stress tolerance in rice
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research0 Comments
/
Ali et al. describe a rice breeding strategy to improve abiotic stress tolerance as well as to accelerate the speed to achieving homozygosity. The researchers named this particular technique as “Green Super Rice” (GSR) breeding technology. They use a backcross (BC) breeding approach to fix breeding…

Root traits confer grain yield advantages under terminal drought in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThis study by Ramamoorthy et al. showed that survival of plants under drought conditions is not a sufficient goal for breeding. Rather, yield for biomass and food production under water deficit is a better target. Chickpea genotypes having better root growth and higher root density showed better grain…
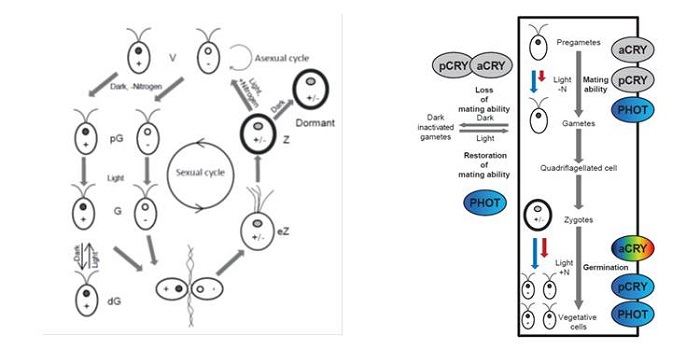
A plant cryptochrome controls key features of the Chlamydomonas circadian clock and its life cycle
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchAnimals and plants have divergent sets of blue light receptors, called Cryptochromes. However, green alga Chlamydomonas has both animal-like and plant cryptochrome (pCRY). The presence of multiple cryptochrome suggests specific roles in different pathways in respective organisms. In this paper, Müller…
BASS Fishing: Genetic Screen Uncovers a New Transporter in Photorespiration
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellSouth et al. discover a new transporter involved in photorespiration http://www.plantcell.org/content/29/4/808.abstract.
Photosynthesis uses solar energy to convert carbon dioxide in the atmosphere into sugars that provide the energy and chemical building blocks for plant growth. A key enzyme in photosynthesis…

Natural allelic variation of FRO2 modulates Arabidopsis root growth under iron deficiency
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchIron is an essential nutrient that plants assimilate from the soil. Moderate iron deficiency induces an increase in primary root length and lateral root production. Satbhai et al. examined natural variation of root responses and showed a correlation between root length and allelic variation at the FRO2…
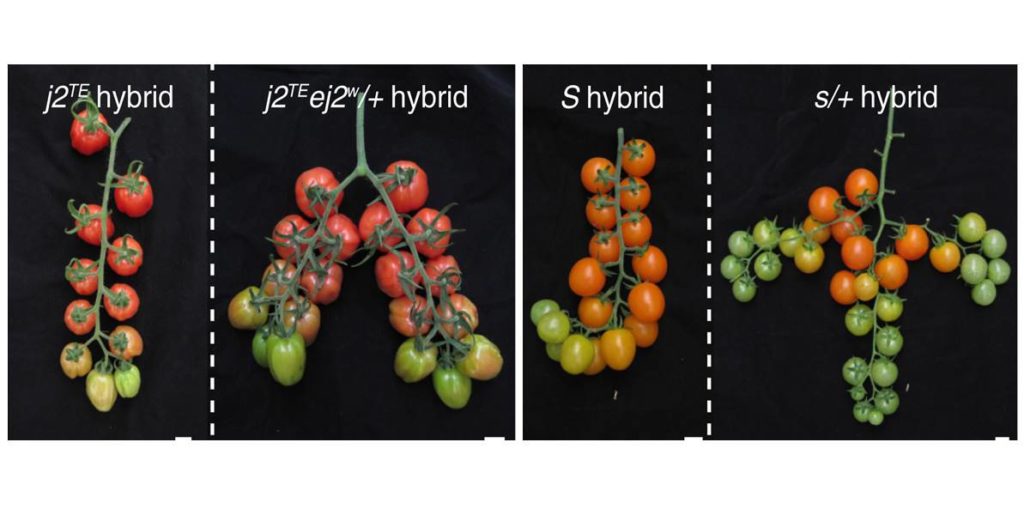

Bypassing negative epistasis on yield in tomato imposed by a domestication gene
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchTomatoes normally grow as multiple flowers along a single branch. Soyk et al. explored a large collection of wild and domesticated accessions to identify those with branched inflorescences, which should be able to produce more fruit per plant. They identified a few related branchy mutants which they…
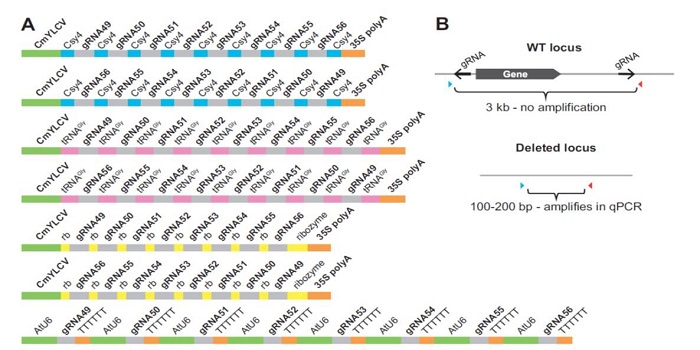
A multi-purpose toolkit to enable advanced genome engineering in plants
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchPrecise genome editing holds tremendous promise for meeting future food security needs and sustainable agriculture. Čermák et al. describe a set of reagents that facilitate genome editing in plants, based on both TALEN (Transcription Activator-Like Effector Nucleases) and CRISPR/Cas technologies. Precise…

Review: Enhancing genetic gain in the era of molecular breeding ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchYield is determined by the crop’s genetic potential and the realization of that potential as affected by agronomic practices and environmental factors. Xu et al. address how yields can be improved through enhancing genetic gain, which they define as “the amount of increase in performance that is…
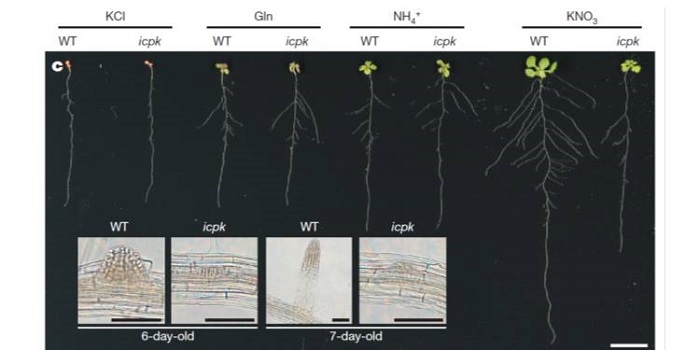
Discovery of nitrate–CPK–NLP signalling in central nutrient–growth networks ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchNitrate acts as a potent signal as well as a source of nutritional nitrogen, but key players in the nitrate response have been missing from our understanding. Liu et al. identified a unique calcium signal stimulated by nitrate in mesophyll cells. They then found that in vitro kinase activity of Ca2+-sensor…

