
Rapid customization of Solanaceae fruit crops for urban agriculture ($) (Nature Biotech)
Plant Science Research WeeklyNumerous genes have been identified that modify shoot architecture, which has allowed breeding of varieties for specific purposes and environments. Here, Kwon et al. describe how they have used gene editing to modify several of these genes to produce tomatoes and groundcherries that are compact and rapid…
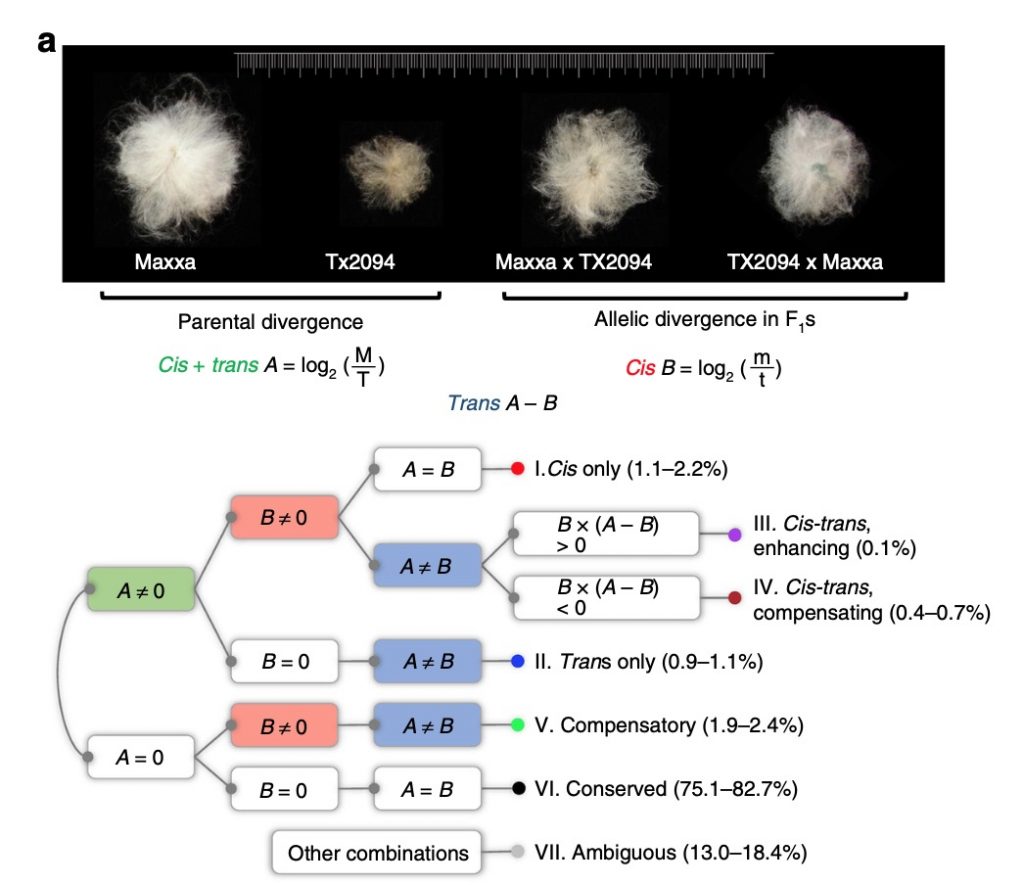
Unraveling cis and trans regulatory evolution during cotton domestication (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPolyploidization leads to a myriad of changes in gene expression and organization of genomes and can supply the material for speciation, adaptation, and morphological innovation. The most cultivated cotton species, Gossypium hirsutum, is an allotetraploid species (AD genome) containing two subgenomes…
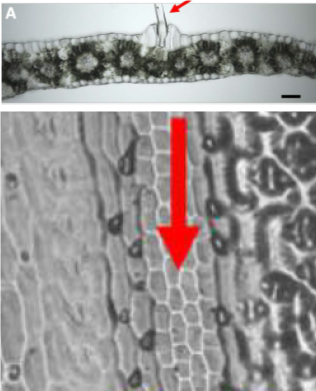
Machine learning enables high-throughput phenotyping for analyses of the genetic architecture of bulliform cell patterning in maize (G3)
Plant Science Research WeeklyBulliform cells lie in rows along the upper (adaxial) surface of the maize leaf, and through changes in volume contribute to leaf-rolling, which is a response to water deficit. Several mutants have been identified that affect bulliform cell formation and function, but as yet their occurance in natural…
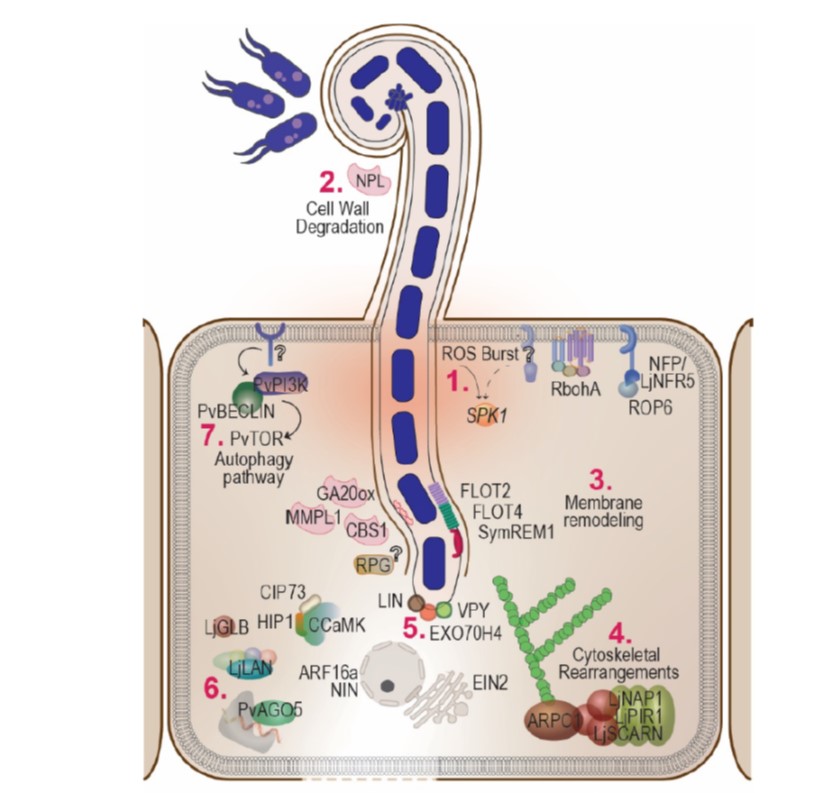
Review: Celebrating 20 years of genetic discoveries in legume nodulation and symbiotic nitrogen fixation (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLegumes are important crops because they are protein-rich, as a consequence of symbiotic nitrogen fixation (SNF). In the past 20 years, through forward and reverse genetics more than 200 genes have been identified that are involved in this process, from recognition through nodule differentiation and…
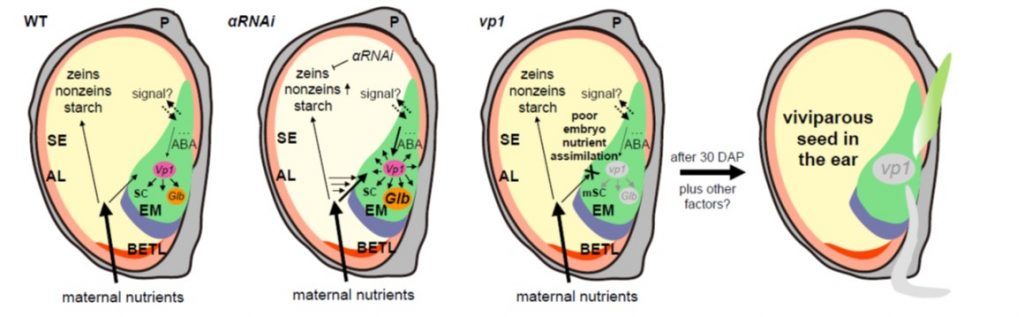
VP1 regulates intra-kernel protein reallocation (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMaize kernels have a triploid endosperm and a diploid embryo. Storage reserves move from the endosperm to the embryo as it grows. Mutants have been identified with abnormal embryos but normal endosperms, although usually a defective endosperm prevents normal embryo formation. Here Zheng and Li et al.…
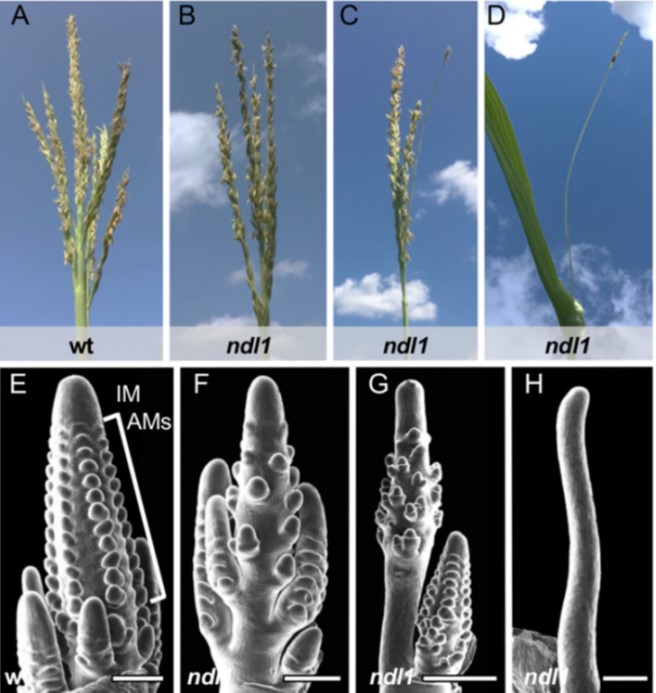

NEEDLE1 encodes a mitochondria localized ATP-dependent metalloprotease required for thermotolerant maize growth ($) (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPreviously, the needle1 (ndl1) maize mutant was identified as showing a variable phenotype mainly affecting the tassel. Here, Liu et al. showed that this variability arises due to its temperature sensitivity, with strongest effects at warmer temperatures. In some cases, the plants arrest before reaching…
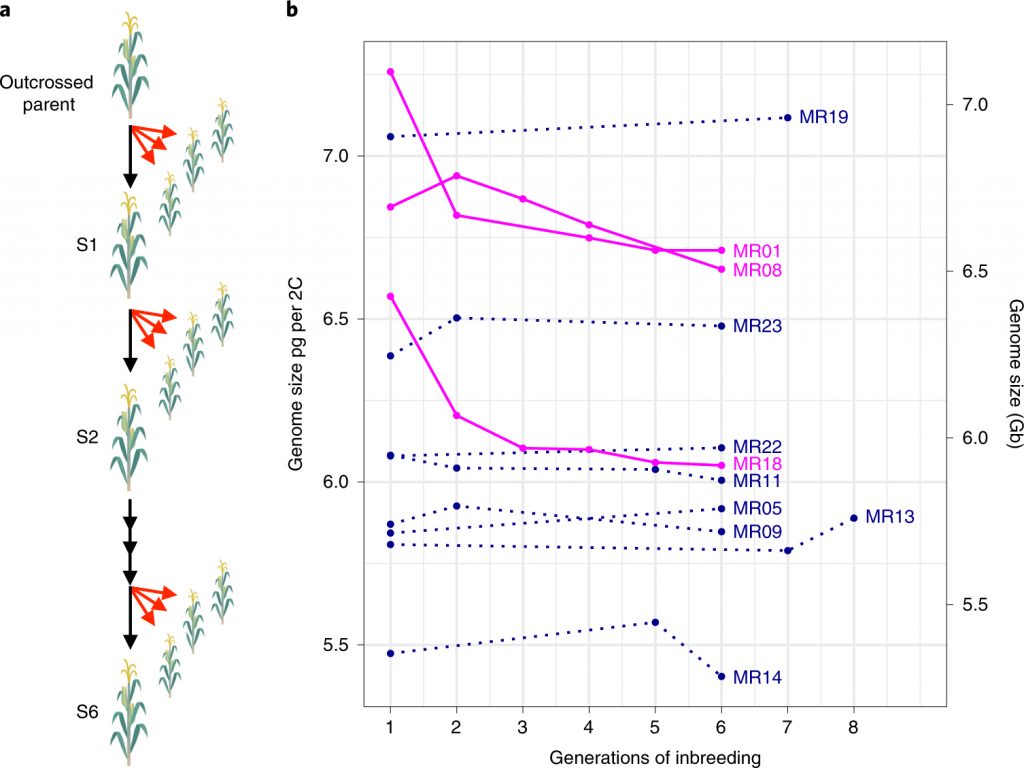
KonMari for Maize - keeping genomes clutter-free during selfing ($) (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyJust like years of hoarding can end up cluttering our homes, years of self-fertilization or selfing can also accumulate harmful mutations in plant genomes. By removing such harmful alleles from the genome (i.e., purging) plants can reduce the mutational load and prevent fitness loss due to selfing. Roessler…
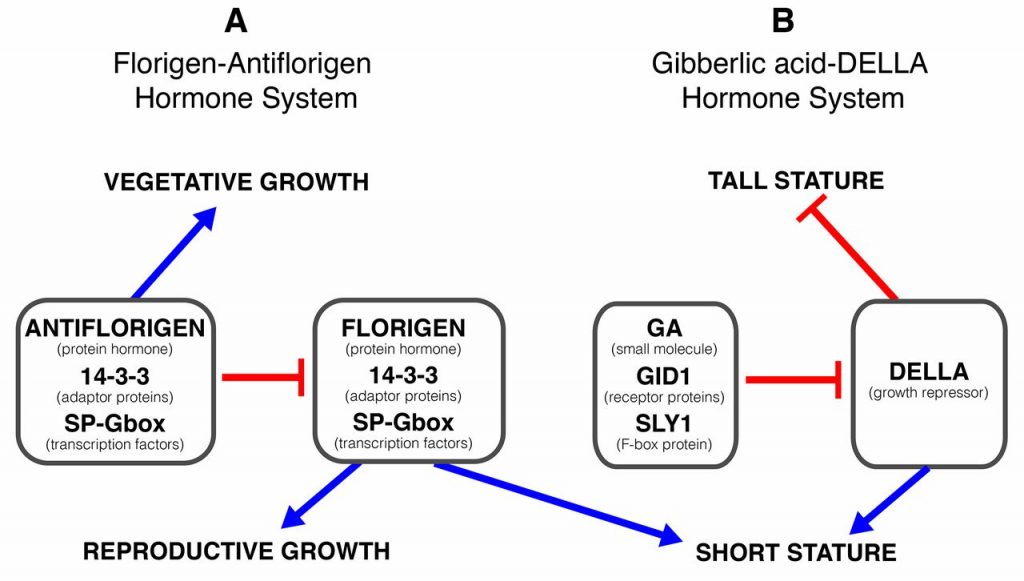
Review: Revolutions in agriculture chart a course for targeted breeding of old and new crops ($) (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyA few traits are associated with domestication across many species. Eshed and Lippman provide an overview of the changes to plant stature and flowering time that have been repeatedly selected by our ancestors. By comparing the molecular underpinnings of these traits across crops, it becomes clear that…
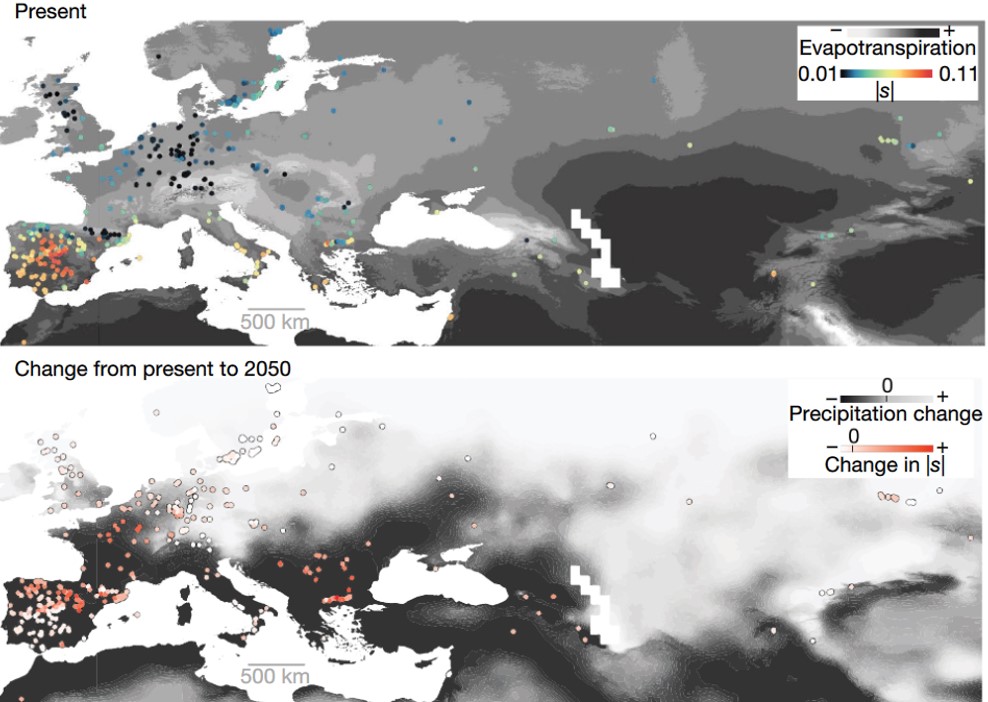
Natural selection on the Arabidopsis thaliana genome in present and future climates (Nature)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe rapidly changing climate will have profound effects on Earth’s ecosystems, but as yet it is difficult to determine exactly what these effects will be. Exposito-Alonso et al. have set up a large experiment to try to identify how a population’s genetic diversity will enable it to survive a future…

