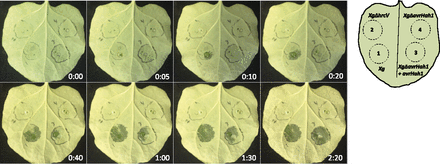
A pectase lyase that is an indirect target of a Xanthomonas TAL effector promotes susceptibility
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research0 Comments
/
One of the many ways that Xanthomonas bacteria manipulate their host plants is by the production of transcription activator-like (TAL) effectors, which the bacterium introduces into the host cell where they alter gene expression in the host nucleus. Schwartz et al. investigated the targets of the TAL…

Regulation of tulip flowering by temperature ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchCultivation of Tulipa gesneriana (tulip), an economically important species due to its ornamental value, can be affected by warming winters, leading to low quality flowers produced out of season. Leeggangers et al. have sequenced RNA and used top-down and bottom-up approaches in tulips grown in two contrasting…
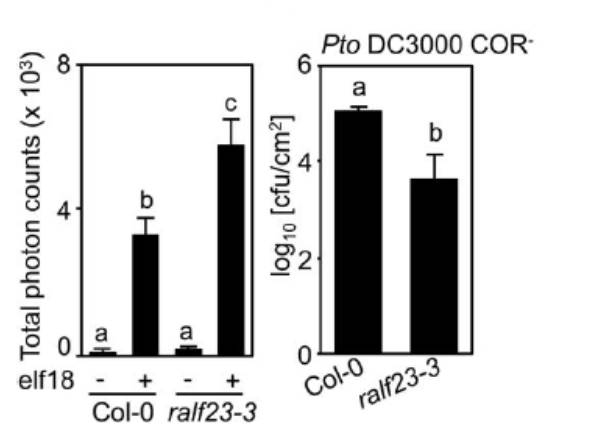
Peptide-mediated regulation of receptor scaffolding in plant immune signaling ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchContinuing the theme of peptide signaling, Stegmann et al. showed that a subset of the RALF (RAPID ALKALINIZATION FACTOR) family of plant peptides can negatively regulate plant immune responses. When plants are treated with flg22, a peptide epitope of bacterial flagellin, they produce reactive oxygen…

Review: Dark signaling in plants ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchPlants use light as a source of energy and information; however, they are also sensitive and respond to light/dark diurnal cycling, with many processes happening during the dark phase of the diurnal cycle. In this review, Seluzicki et al. emphasize the importance of studying and understanding what…

Review: The sexual advantage of looking, smelling and tasting good, the metabolic network that produces signals for pollinators ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe interaction between angiosperms and their pollinators provides an excellent system to study co-evolution, and underpins the evolution of the biosynthesis of numerous interesting and useful specialized metabolites, from pigments to fragrances. Borghi et al. review the metabolic pathways that produce…

CATchUP: A web database providing information on spatiotemporal specific gene expression
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchNakamura et al. have created a searchable database, CATchUP (http://plantomics.mind.meiji.ac.jp/CATchUP) that allows the user to explore the spatiotemporal expression of genes across eight plant species (monocots and dicots) using data from publically available databases of large-scale RNA-Seq data.…

Water deficit-induced changes in transcription factor expression in maize seedlings ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchUnderstanding plant responses to water deficit is crucial for the development of drought-reliance, but complicated by the different ways plant researchers induce water deficit. Starting with the premise that transcription factors are important coordinators of water-deficit responses, Seeve et al. carried…
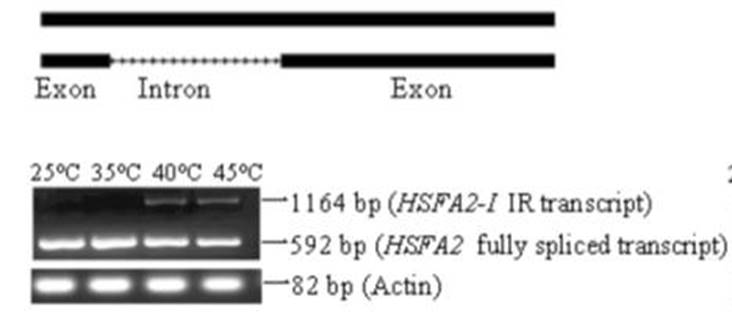
Integrating omics reveals insights into grape response to high temperature
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchHeat stress is one of the main abiotic stresses plants encounter. Jiang et al. used combined transcriptomic and proteomic data to explore the responses of grape leaves to elevated temperatures (35, 40, 45°C). Using high-throughput sequencing and the iTRAQ (isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation)…

UV-B perceived by the UVR8 photoreceptor inhibits plant thermomorphogenesis
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchAmbient temperature can influence plant architecture, an effect termed thermomorphogenesis. In A. thaliana, thermomorphogenesis phenotypes include stem elongation and changes in leaf elevation angles. Increased auxin biosynthesis involving the transcription factor PIF4 is required for thermomorphogenesis,…

