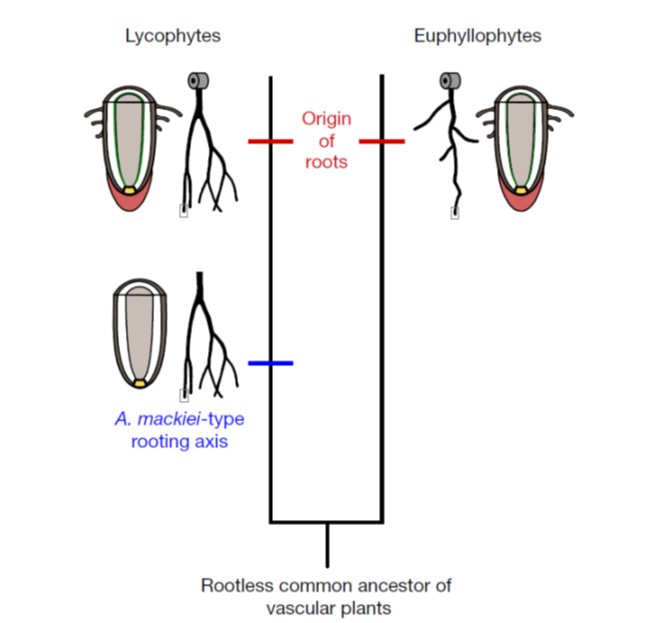
Stepwise and independent origins of roots among land plants (Nature)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe Rhynie chert (near the village of Rhynie, Scotland; chert is a type of sedimentary rock) is an important site for plant biologists as it holds some of earliest and best preserved land-plant fossils. Hetherington and Dolan examined more than 600 thin sections prepared from this site, specifically…

Evolution and diversification of the plant gibberellin receptor GID1 (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyGiberellins (GA) are plant hormones that have diverse role in plant growth and development. Although many GAs have been identified, only few of them show functional activity in plants. GAs are perceived by the GID1 receptor, which is widespread in vascular plants and structuraly similar to carboxylesterases…
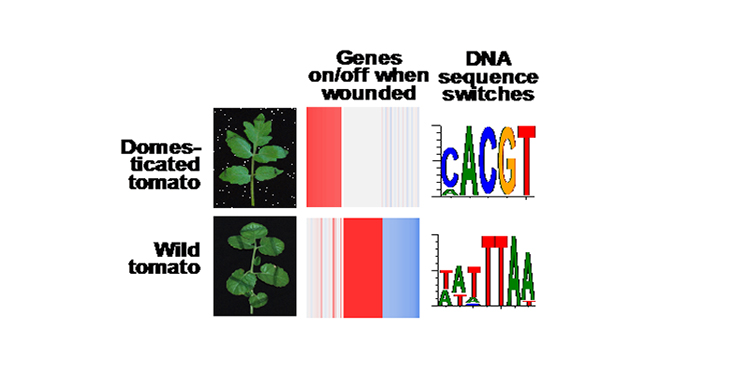
Evolution of Gene Regulation During Domestication
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellLiu, et al. examine how wound response and its control mechanism differs between domesticated and wild tomato. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00194.
By Ming-Jung Liu and Shin-Han Shiu
Background: Two related species accumulate differences between each other over time. If one of the…
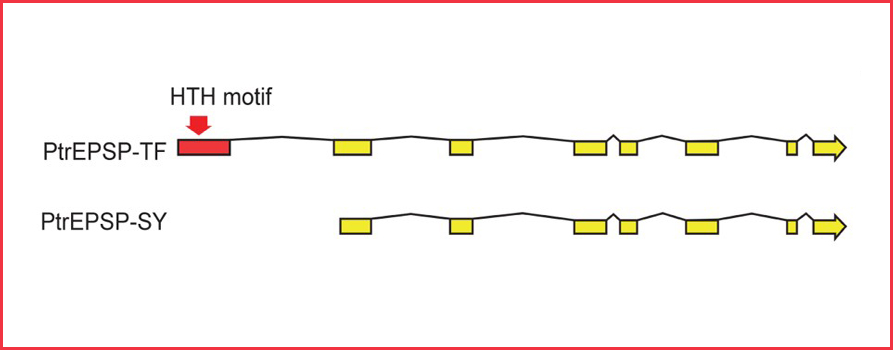
Old Gene, New Function
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellXie et al. discover an EPSP synthase gene involved in the transcriptional regulation of the phenylpropanoid pathway in Populus trichocarpa The Plant Cell (2018). https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00168.
By Meng Xie, Wellington Mechuro, Jin-Gui Chen, and Gerald A. Tuskan
Background: 5-enolpyruvylshikimate…
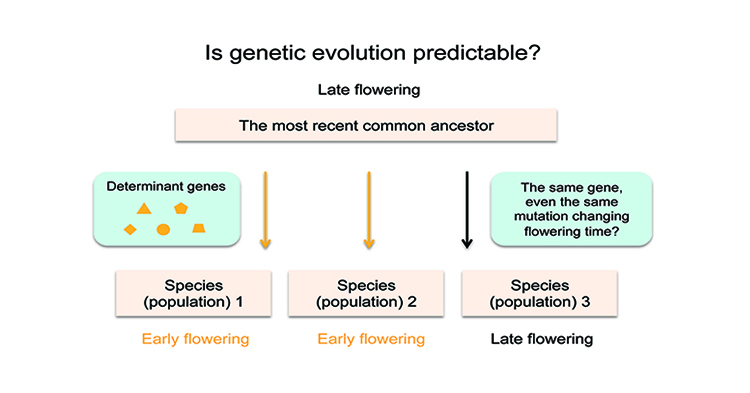
Is Genetic Evolution Predictable?
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellYang et al. investigate the evolution of flowering time in the young species Capsella rubella. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00124
Background: Flowering time is an important adaptive life-history trait in plants. Capsella rubella, a close relative of Arabidopsis thaliana and—in evolutionary time—a…
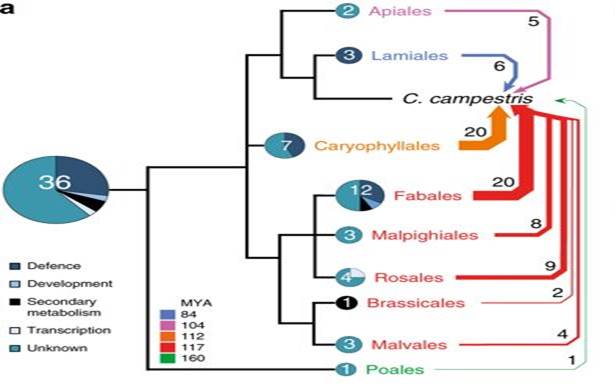
Footprints of parasitism in the genome of the parasitic flowering plant Cuscuta campestris (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyEven without knowing a lot about parasitic plants, you can probably guess some of the insights that come from the first parasitic plant genomic sequence. Because parasitic plants get their nutrients from another organism (functionally, they become heterotrophic), you might expect they would gradually…

Genome assemblies of maize lines Mo17 and W22: Extensive intraspecific variation, and resource for functional biology (Nature Genetics)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe maize genome is largely composed of transposable elements, which is one reason maize has been such a powerful genetic model. However, these transposons also mean that there is a great deal of genetic variability between inbred lines, which can contribute to heterosis (hybrid vigor). In a pair of…
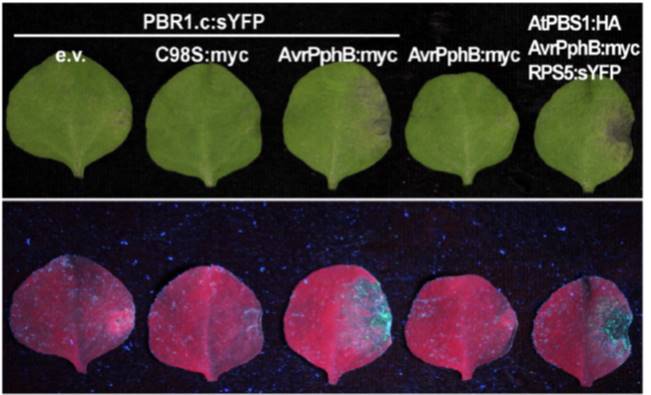
Convergent evolution of effector protease recognition by Arabidopsis and barley (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPathogenic bacteria Pseudomonas syringae produce an effector protein, AvrPphB. The indirect interaction between this bacterial effector and the Arabidopsis resistance (R) protein RPS5 has been characterized previously; AvrPphB is a cysteine protease that targets another plant protein, PBS1, causing it…
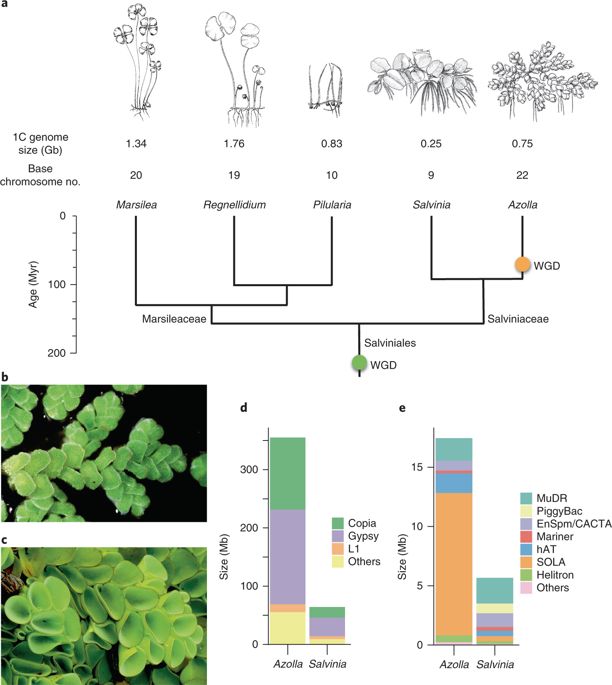
Aquatic fern genomes provide insight into land plant evolution and symbiosis (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLand plants evolved from freshwater charophytic algae over ~450 million years ago and have since diverged into the plethora of embryophyte genera that we see today. Genomics efforts have classically focused on key angiosperm species representing experimental model systems and/or agriculturally important…

