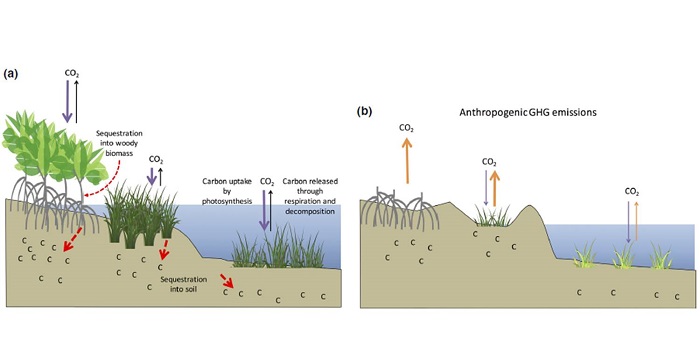
Review: Coastal wetland blue carbon
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research0 Comments
/
Coastal wetlands (mangroves, tidal marshes and seagrasses) are important carbon sinks, in both biomass and soils. Howard et al. describe and quantify the carbon flow through these different coastal ecosystems, and their potentials as long-term carbon sinks. Unlike the open ocean, these coastal ecosystems…
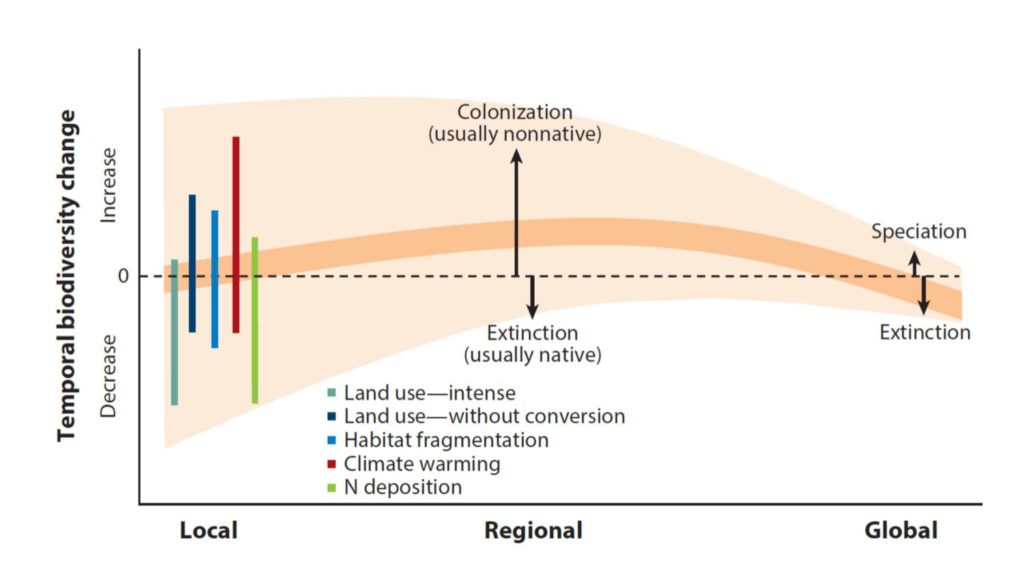
Review: Plant diversity change across scales during the Anthropocene ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchWe’re living in the Anthropocene, a term that reflects the profound impact of human activities on Earth’s geology and ecology. A hallmark of the Anthropocene is a decrease in biodiversity due to an increase in the rate of extinctions. Vellend et al. examine the plant diversity has been affected…

Response of US crops to elevated temperatures
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchClimate change could affect agricultural productivity by increasing the number of days with temperatures above 30°C that staple crops like soybean, maize and wheat will experience during a given growing season. Schauberger et al. used nine statistical models to assess future threats to US crops. They…

Alistair Fritter. People, plants and planet
CSVL Research, Curated Webinars / Video Lectures, WebinarsFilmed at Gatsby Summer School, 2011
Abstract: Population issues are receiving renewed attention from both scientists and policy-makers and well-founded predictions of likely global population growth have given new urgency to concerns about food security and loss of ecosystem services. Plant science…

Beverley Glover. Flowering plant diversity: development, function and evolution
CSVL Research, Curated Webinars / Video Lectures, WebinarsFilmed at the Gatby Summer School, University of York, 2013
http://www.tree.leeds.ac.uk/tree.2.0/view_lecture.php?permalink=MTA2Nw
Abstract: The enormous species diversity of the flowering plants has puzzled evolutionary biologists since Darwin’s day. The rapid radiation of the flowering plants…

Low Phytate Rice Grains
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchPhosphorus (P) is an important macronutrient for crop productivity. In cereal crops like rice, about 60-85% of total plant P is allocated to grains and therefore removed from fields at harvest. Furthermore, the major form of P in the grains is phytate (C6H18O24P6), which cannot be digested by humans…
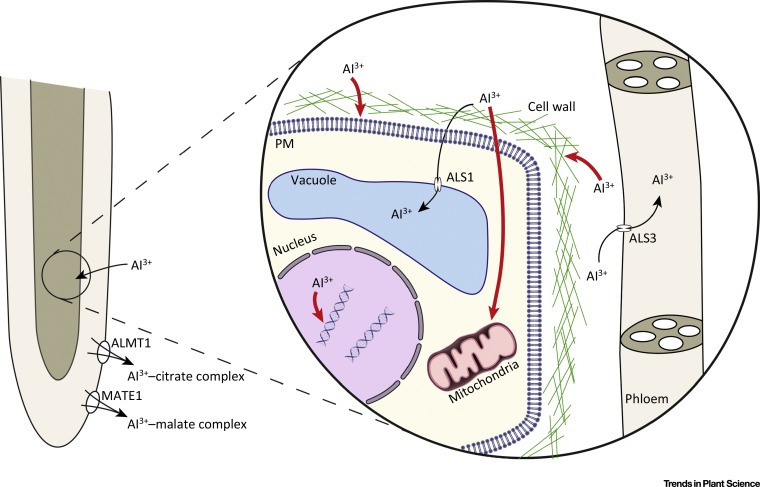
Review: DNA Checkpoints and Aluminum Tolerance ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchAluminum (Al) toxicity is an important agricultural problem, limiting crop production globally. Al toxicity causes a reduction in nutrient uptake, resulting in nutritional deficiency and leading to an overall reduction in shoot biomass and crop yield. Eekhout et al. discuss Al toxicity and strategies…

Edge effects enhance vulnerability to climate change in temperate forests
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchMuch of the data used to predict forest responses to climate change comes from unfragmented forests, but much of the world’s forests are highly fragmented. Reinmann and Hutyra examined edge effects in a temperate forest in New England, and observed both an increase in biomass with proximity to the…
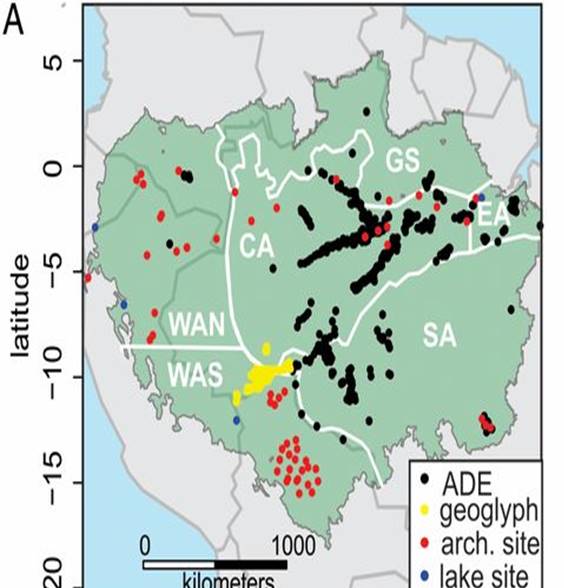
Ancient human disturbances may be skewing our understanding of Amazonian forests ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe Amazonian forest is an enormous and crucial ecosystem that encompasses a huge proportion of Earth’s biodiversity and stored carbon. By overlaying maps showing forest inventory plots and sites of ancient human impact, McMichael et al. observe that the inventoried plots from which we draw conclusions…

