
Breaking Water-wise Photosynthesis
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellBoxall et al. explore the effects of silencing phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in a Crassulacean acid metabolism species. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.19.00481
By Susie Boxall and James Hartwell
Background: Severe droughts and high temperatures are becoming more frequent due to climate…

Central clock components modulate plant shade avoidance by directly repressing transcriptional activation activity of PIF proteins ($) (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTORs (PIFs) are transcriptional factors that relay light signals from the phytochrome photoreceptors to regulate the expression of light-sensitive genes, but there is not a direct correlation between PIF binding and expression of the target genes. In this paper, Zhang Y et…
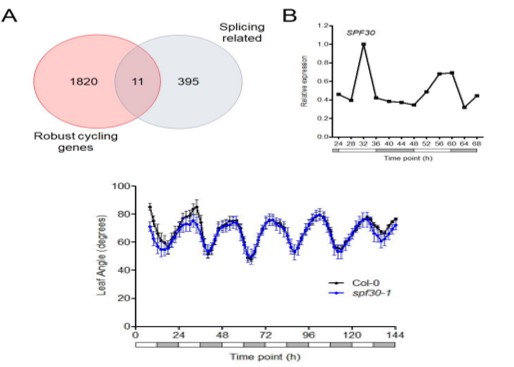
Global transcriptome analysis reveals circadian control of splicing events in Arabidopsis thaliana (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyDevelopmental programming, metabolism and plant growth are regulated by the circadian rhythm that integrates environmental signals and plant growth. In this paper, Romanowski et al. have used the RNAseq approach to determine post-transcriptional regulation in Arabidopsis thaliana, specifically alternate…
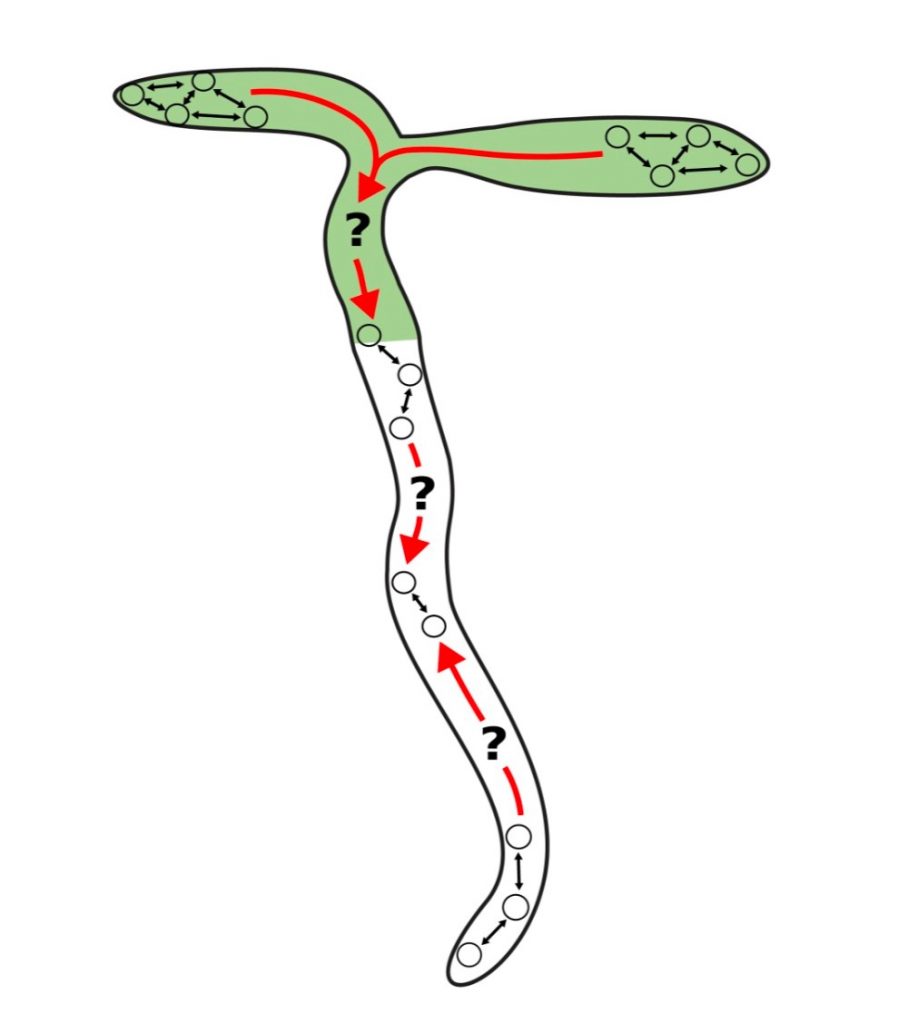
Coordination of circadian times in Arabidopsis seedlings (PLOS Biol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPrecise temporal control is crucial for plant developmental processes, e.g., photosynthesis, leaf movement, and flowering. In this work, Greenwood et al. studied how rhythms are coordinated at the whole-organism level. The authors monitored the activity of GIGANTEA (GI), a core clock gene, using a LUCIFERASE…

Glyphosate-based herbicide effectiveness can be maximized by considering plant circadian rhythms (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants’ internal circadian clocks regulate the timing of many physiological and developmental processes. This circadian clock also controls plant sensitivity to the herbicide glyphosate, which is maximally effective at dawn. Here, Belbin et al. showed that the minimum effective dose varies with time…
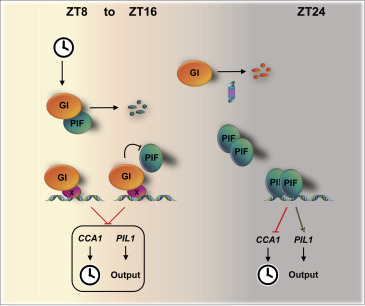
Multi-level modulation of light signaling by GIGANTEA regulates both the output and pace of the circadian clock ($) (Devel Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe daily cycle of light and dark controls many facets of plant growth and development, but these cycles depend on and are most efficient when integrated with the rhythms of the circadian clock. Nohales et al. have identified a key mechanism that directly links the regulation of light-responsive genes…
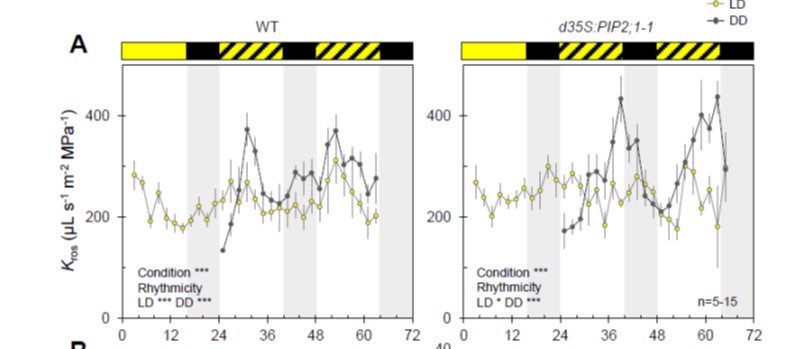
Oscillating aquaporin phosphorylations and 14-3-3 proteins mediate circadian regulation of leaf hydraulics (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant activities change drastically between the light and dark times of day. Many of these different activities can be observed through transcriptional studies, which show that gene expression goes up and down over the course of the day. Many of these transcriptional changes are driven by the circadian…
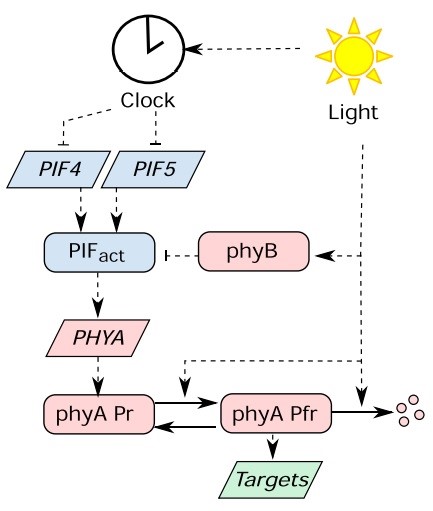
Dawn and photoperiod sensing by phytochrome A ($) (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants perceive the change of seasons based on measuring the duration of daylight. Flowering is a major seasonal response that depends on photoperiod. In this study, Seaton et al. looked at the role of phytochrome A (phyA) in photoperiod sensing. PHYA is the direct target of PIF4 and PIF5 transcription…
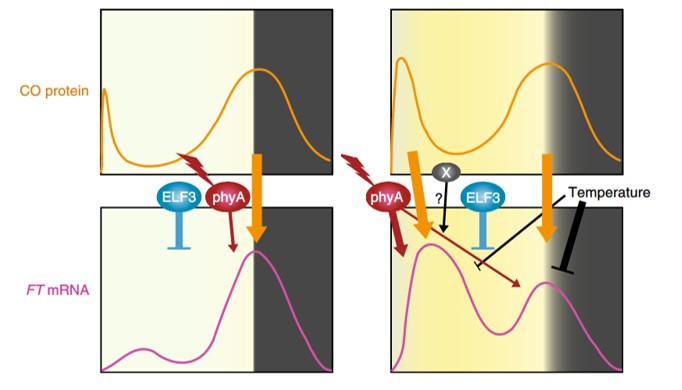
Flowering time in the real world (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThere are pros and cons to growing plants in controlled conditions. On the one hand, controlling light, temperature, humidity and other environmental factors should aid reproducibility between experiments and labs. But what if the conditions used profoundly and unexpectedly affect the process you are…

