Division of labor during apical hook formation
The Plant Cell: In Brief0 Comments
/
Soon after dicots germinate, the hypocotyl arches into a hook-like structure that protects the shoot apical meristem as the seedling grows through the soil. Once the seedling emerges from the ground and senses light, the hypocotyl straightens. The asymmetric growth that results in apical hook formation…
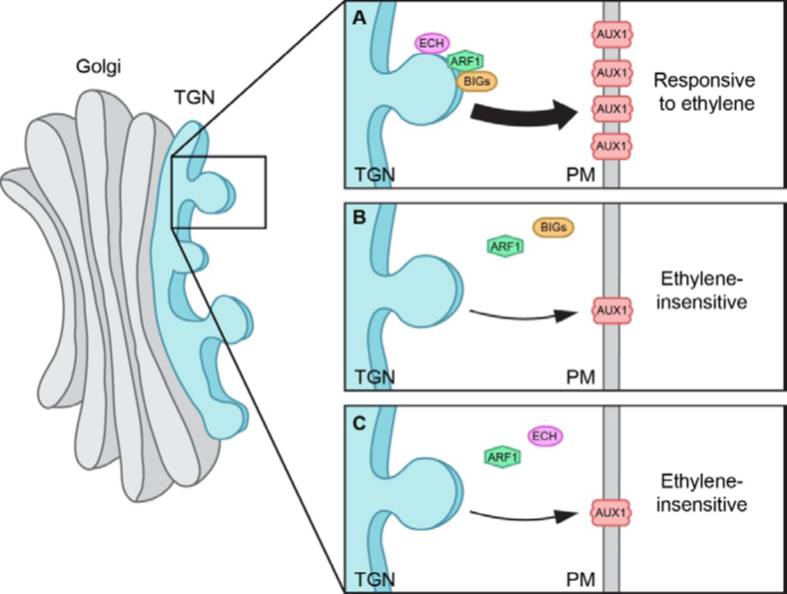
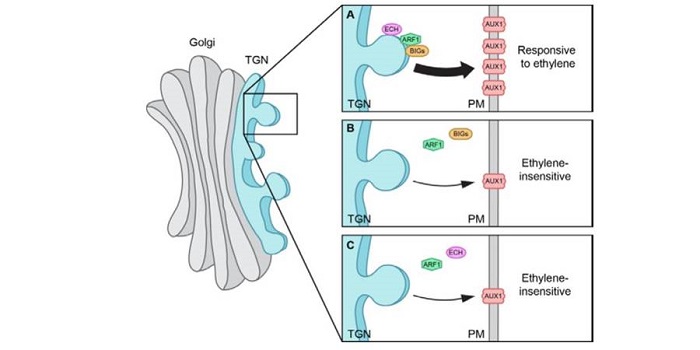
Ethylene regulates differential growth via BIG ARF-GEF-dependent post-Golgi secretory trafficking in Arabidopsis
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchRegulated movement to and from the plasma membrane (PM) has emerged as an important strategy for controlling the activity of plasma membrane proteins such as transporters and receptors. Jonsson et al. investigated the cellular machinery required for the insertion of the auxin-transport protein AUX1 into…

A Raf-like protein kinase BHP mediates blue light-dependent stomatal opening
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchHow do stomata open in response to blue light? Blue light is perceived by phototropin receptor kinases that activate BLUE LIGHT SIGNALING1 (BLUS1), type 1 protein phosphatase (PP1), and the plasma membrane (PM) H+-ATPase. Hayashi et al. screened a commercial kinase inhibitor library to identify the…

Nanoscale movements of cellulose microfibrils in primary cell walls ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchCell walls are complex mixtures of cellulose microfibrils, proteins and other materials. Their mechanical properties can be measured and modeled, but it is not always simple to translate these measurements to changes at the molecular level. Zhang et al. used atomic force microscopy to provide an unprecedented…
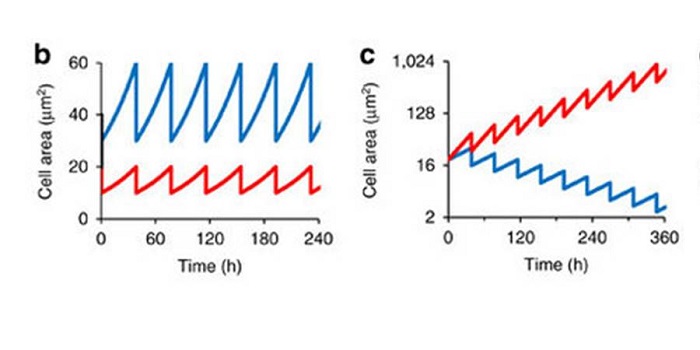
Cell-size dependent progression of the cell cycle for homeostasis and flexibility of cell size
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchCell size is determined by growth rate and frequency of division. Studies in yeast revealed mechanisms that coordinate these processes, as well as the crucial checkpoint controls that ensure the cell is “ready” to divide, but can models from single-celled organisms be applied to multicellular ones…
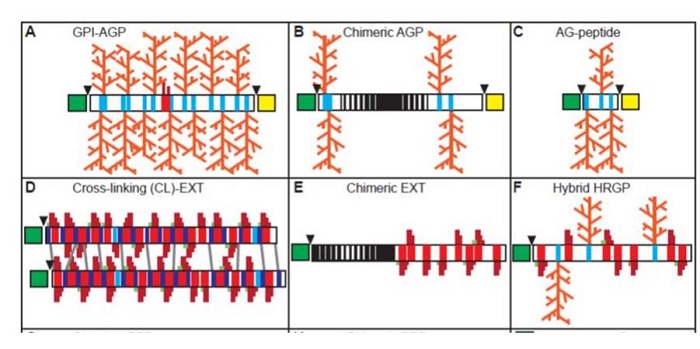
Breakthrough Technologies: Hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins – bioinformatics and evolution
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchA pair of Breakthrough Technology papers in Plant Physiology discusses new tools to identify hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins and insights into their evolution. Hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins (HRGPs) are repeat-rich cell wall proteins that have been described as falling into three large families:…
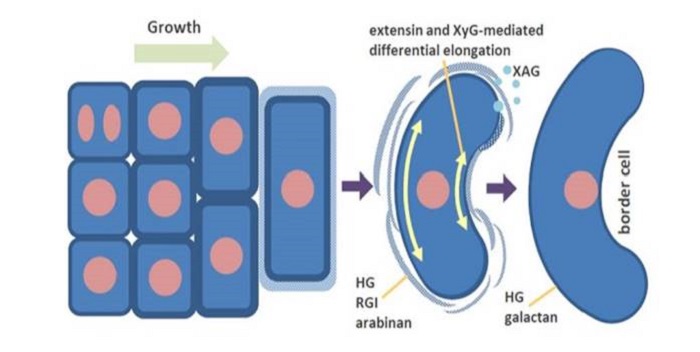
Pea border cell maturation and release involve complex cell wall structural dynamics
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchBorder cells form at the root tip and are shed during growth, protecting the sensitive root apex from damage as it pushes through the soil. Mravec et al. investigated the cell wall chemistry, carbohydrate distributioion and expression of cell-wall modifying genes to determine the mechanism by which border…
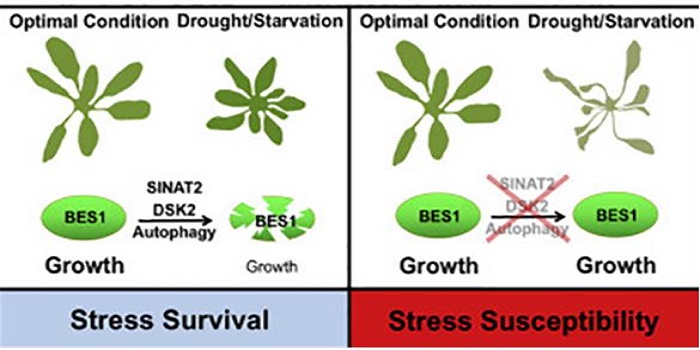
Selective autophagy of BES1 mediated by DSK2 balances plant growth and survival
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchBrassinosteroid (BR) signaling promotes growth and development by regulating gene expression through the BES1 and BZR1 transcription factors. Nolan et al. show how plants balance growth and stress tolerance by cross-talk between the BR and autophagy pathways. Under environmental stresses, BES1 is targeted…
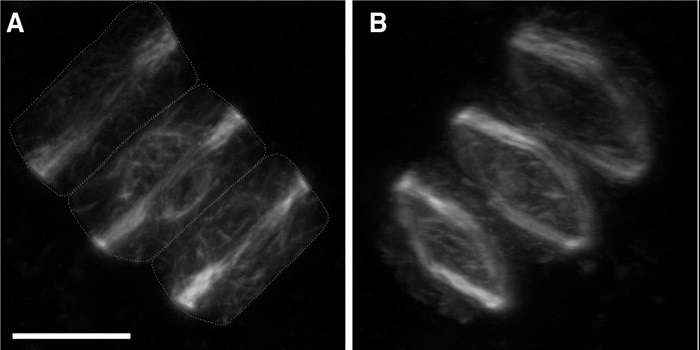
The preprophase band of microtubules controls the robustness of division orientation in plants ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchEvery student of plant cell biology learns that the future plane of cell division is marked very early in mitosis by the preprophase band (PPB), a band of microtubules that forms around the periphery of the cell. Prior experimental studies have suggested that the PPB is necessary for proper placement…

