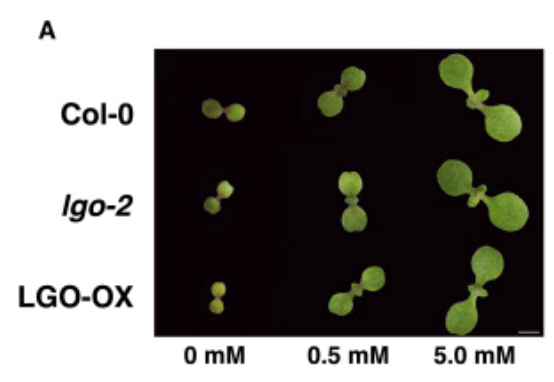
Nitrate defines shoot size through compensatory roles for endoreplication and cell division (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn this paper, Moreno et al. investigate how nitrate affects the balance between cell proliferation and cell expansion in shoots during early seedling development. They note that the cells in Arabidopsis cotyledons undergo considerable enlargement, and that the increase in cell size is correlated with…
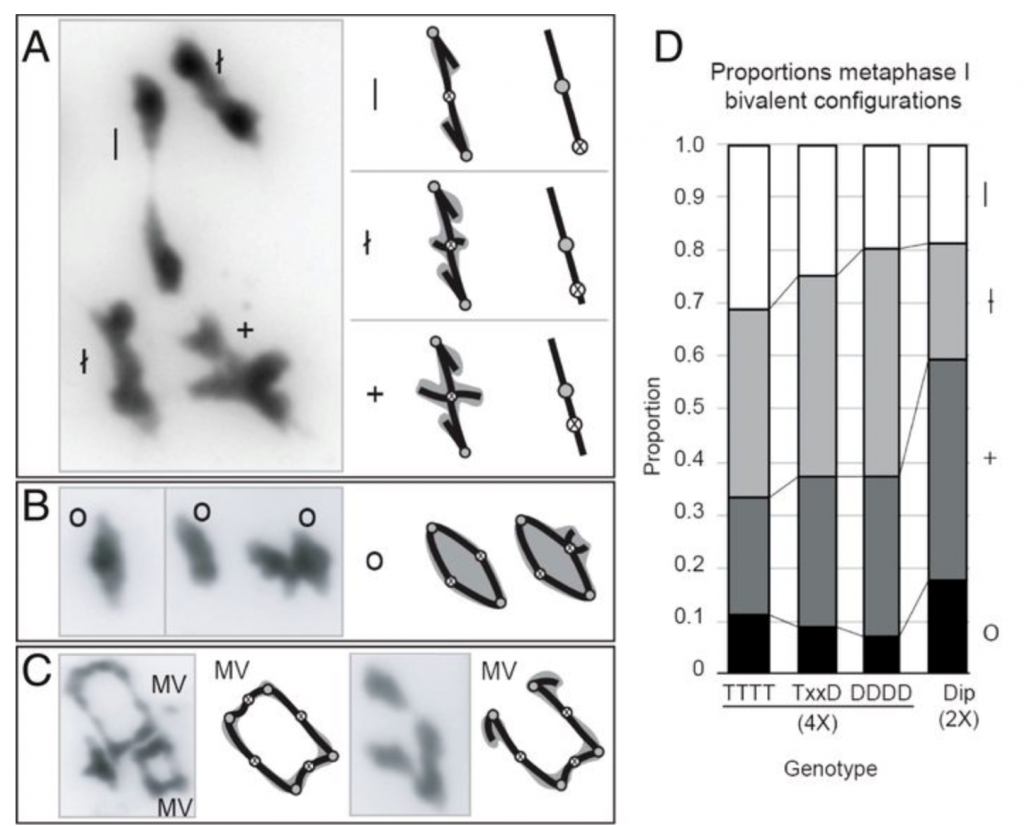
Evolution of tetraploid meiosis (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyGenome duplications are common in plants and thought to be an important contributor to evolutionary innovations, but the increase in ploidy that results from a genome duplication also presents challenges for reproduction. Because there are four sets of homologous chromosomes in the derived tetraploid…

How to transfer lipids from one membrane to another during thylakoid biogenesis (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe thylakoid membranes are located in the stroma of chloroplasts and house the machinery for the photosynthetic light reactions. They emerge largely de novo during the transition from pro-plastids into mature, photosynthesizing chloroplasts. Generating new thylakoid membranes requires a supply of lipids,…
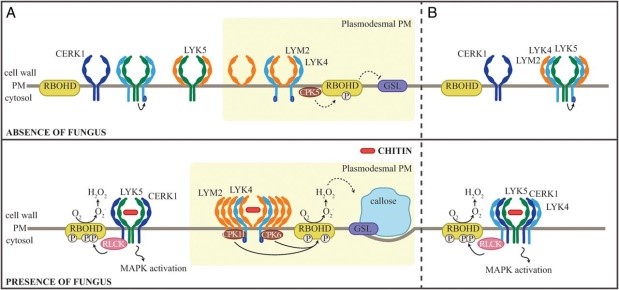
Self-isolation to the rescue – how plasmodesmata initiate signaling in response to chitin (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant cells are known to initiate local and systemic signaling in response to certain stressful conditions to safeguard cells in the immediate vicinity as well as that are far from the site of stimuli. In this study, Cheval and co-workers have characterized a pathway in plant cells for sensing and responding…
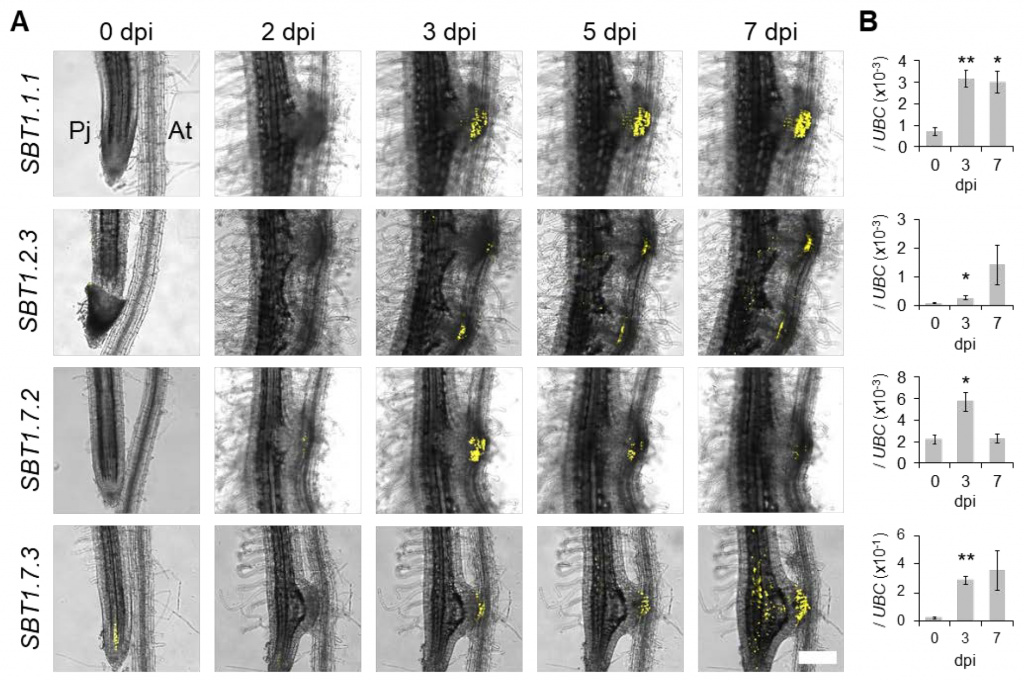
Subtilase activity in intrusive cells mediates haustorium maturation in parasitic plants (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyParasitic plants develop unique structures called haustoria that penetrate into the host plant vasculature, from which they take nutrients. During this process, haustorial epidermal cells differentiate into specialized cells called intrusive cells, which eventually re-differentiate into a xylem bridge…
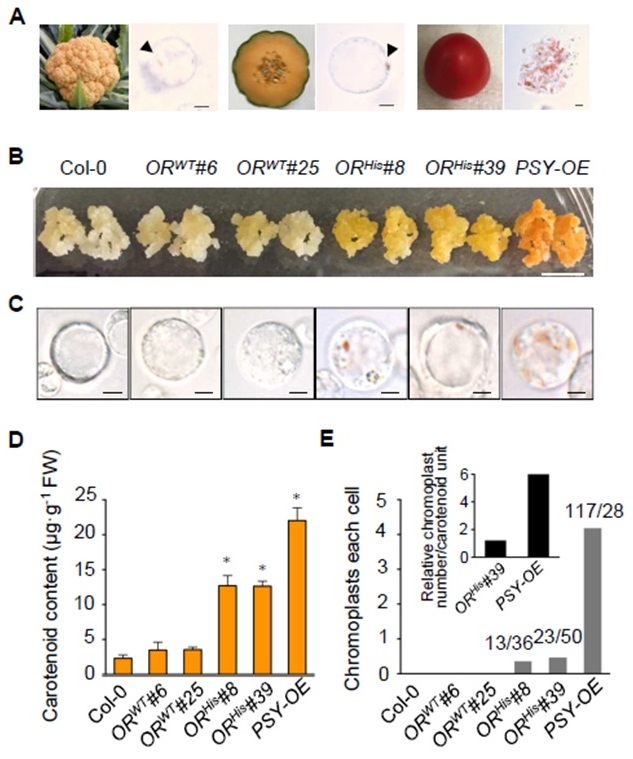
A natural variant of ORANGE interacts with plastid division factor ARC3 to regulate chromoplast number and carotenoid accumulation (Mol. Plant)
Plant Science Research WeeklySome “superfoods” have high nutritional value due to the presence of carotenoids, which prevent degenerative diseases like cancer. In plants, these pigments are biosynthesized and stored by plastid organelles called chromoplasts. Chromoplast number and size define total carotenoid accumulation. ORHis,…
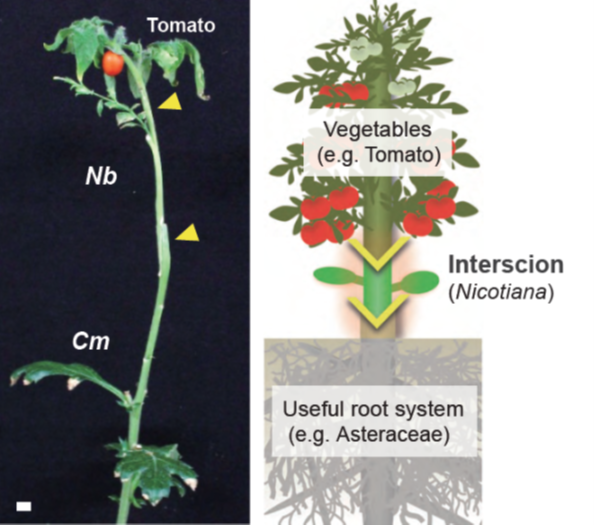
Unlocking interspecies grafting (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant grafting is an agricultural technique that joins plant tissues (e.g., the shoot and root) to confer beneficial traits from one plant to another. Although interfamily grafting is difficult in general, Notaguchi et al. found that Nicotiana benthamiana (Nb) has a strong potential to graft with phylogenetically…

A plant-specific protein, COST1, mediates autophagy to promote drought tolerance (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMuch remains to be learned about the sensing and signaling mechanisms controlling growth in response to drought. To dissect how plants control drought via autophagy, Bao et al. found a plant-specific protein, COST1 (CONSTITUTIVELY STRESSED 1) containing a DUF641 (domain of unknown function 641) domain,…
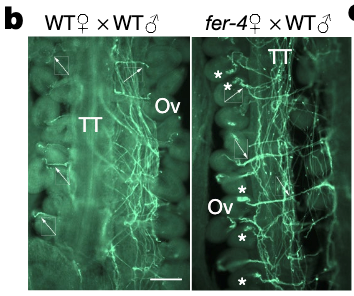
FERONIA controls pectin- and nitric oxide-mediated male–female interaction (Nature)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn flowering plants, fertilization occurs when a pollen tube, growing down the transmitting tissue, arrives at the ovule, ruptures, and releases its content of sperm cells. The pollen tube is guided towards the ovule by LUREs, small cysteine-rich secreted peptides. Timely rupturing and sperm release…

