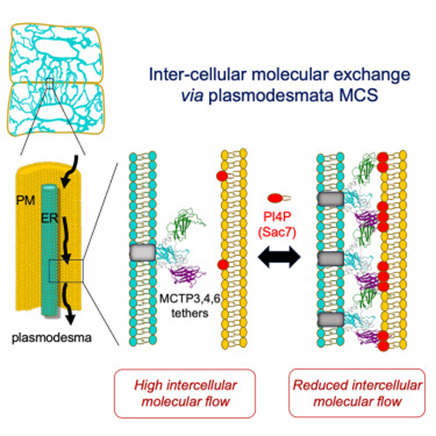
Plasmodesmata: A new frontier for membrane contact site intercellular communication
Plant Science Research WeeklyMembrane contact sites (MCSs) serve a critical role in intracellular communication, particularly between organelle membranes, enabling direct molecular transfer. Less clear is the role MCSs play in intercellular communication. New evidence from Pérez-Sancho et al. implicates plasmodesmata in this function…
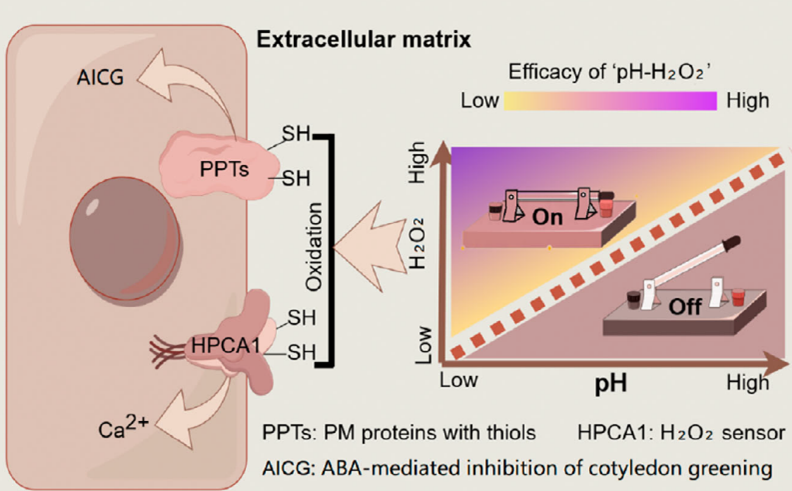
Apoplastic pH acts as a chemical switch in plants by modulating H2O2 redox potential
Plant Science Research WeeklyEnvironmental stimuli, such as drought and salinity, alter cellular conditions including apoplastic pH (pHApo) in plants. These stimuli often lead to an elevation in pHApo which is closely associated with cell functions and plant growth. However, the mechanism behind is largely unexplored. A recent study…
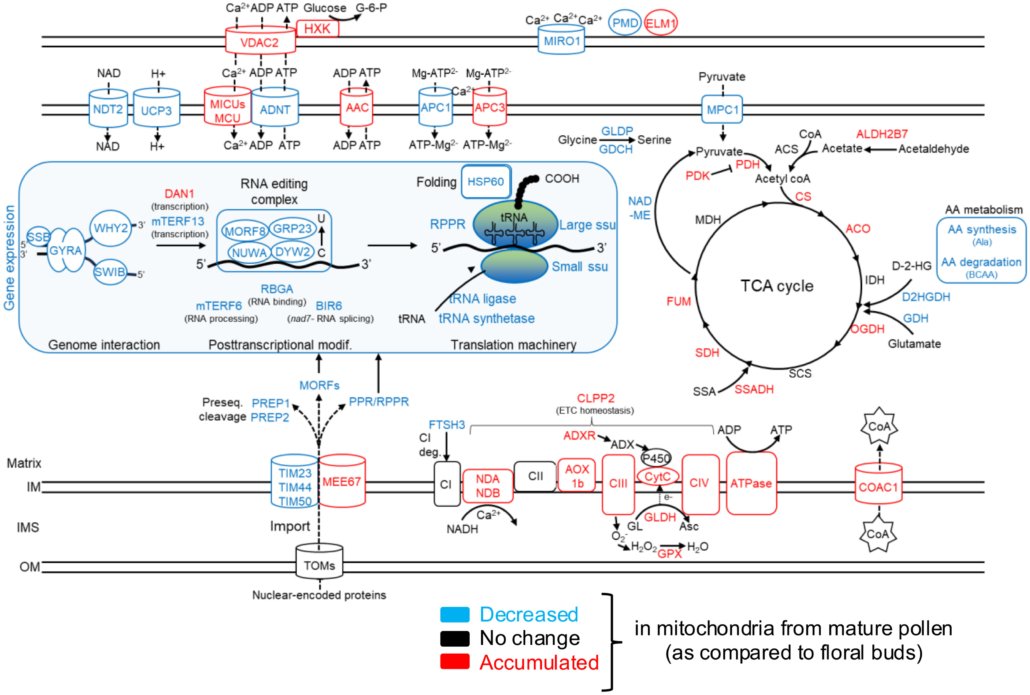
High-energy requiring pollen grains have specialized mitochondria
Plant Science Research WeeklyImagine you’re on a quest to deliver a package, racing against the competition. How do you prepare? Pollen grains and the pollen tubes that they form are essentially package-delivery systems. Their purpose is to deliver genetic information (sperm cell nuclei) to the ovule. Once the task is completed,…
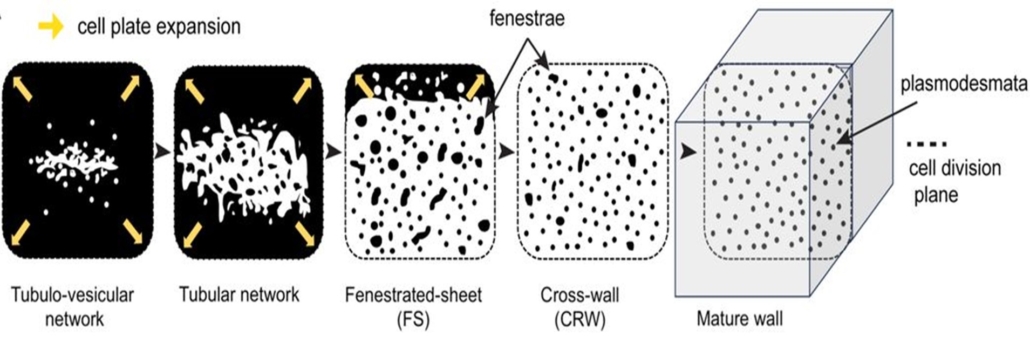
Formation of plasmodesmata bridges through ER-dependent incomplete cytokinesis
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlasmodesmata are important for intercellular communication in plants. They are formed through incomplete cytokinesis during which there is no “final cut” of the communication between daughter cells. Unlike animal cells that have a single bridge between cells, plants create several hundreds of plasmodesmata…
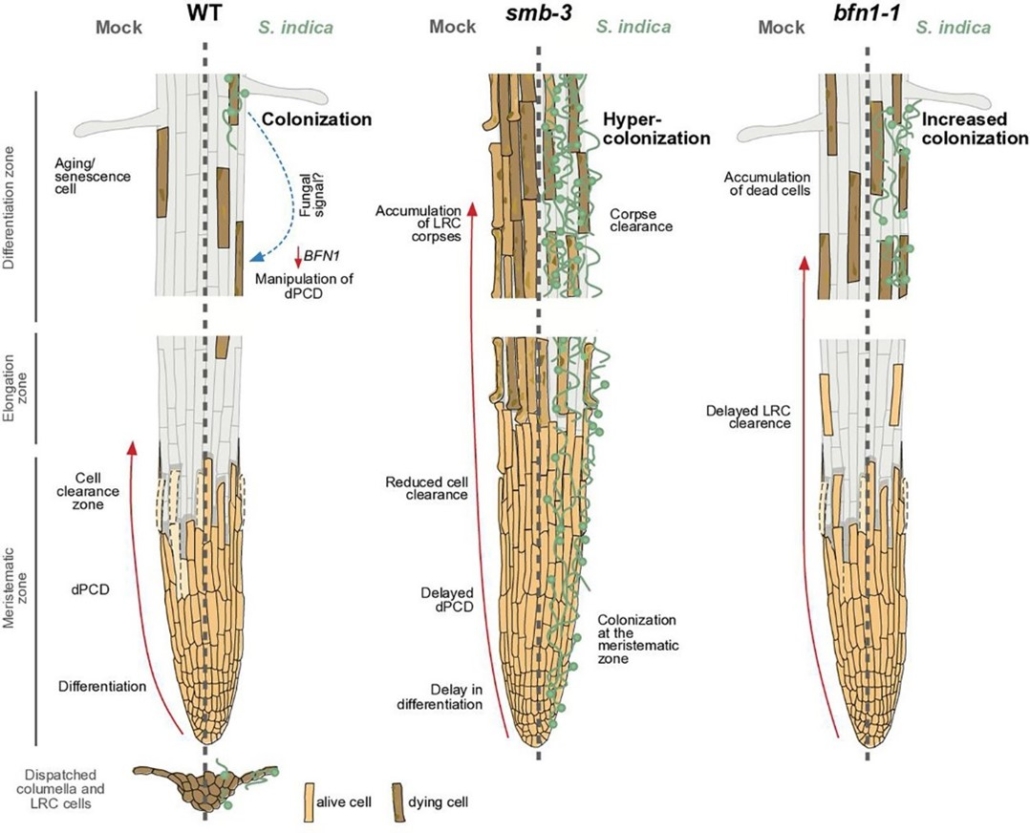
Capping your occupancy: programmed cell death as a mechanism to restrict microbial colonization of the root tip
Plant Science Research WeeklyThanks to the continued shedding and renewal of root cap cells, plant roots are able to extend into further reaches within the soil column overcoming physical barriers and potential microbial attacks, or so we assumed. Charura et al. explored the latter hypothesis showing that timely programmed cell…
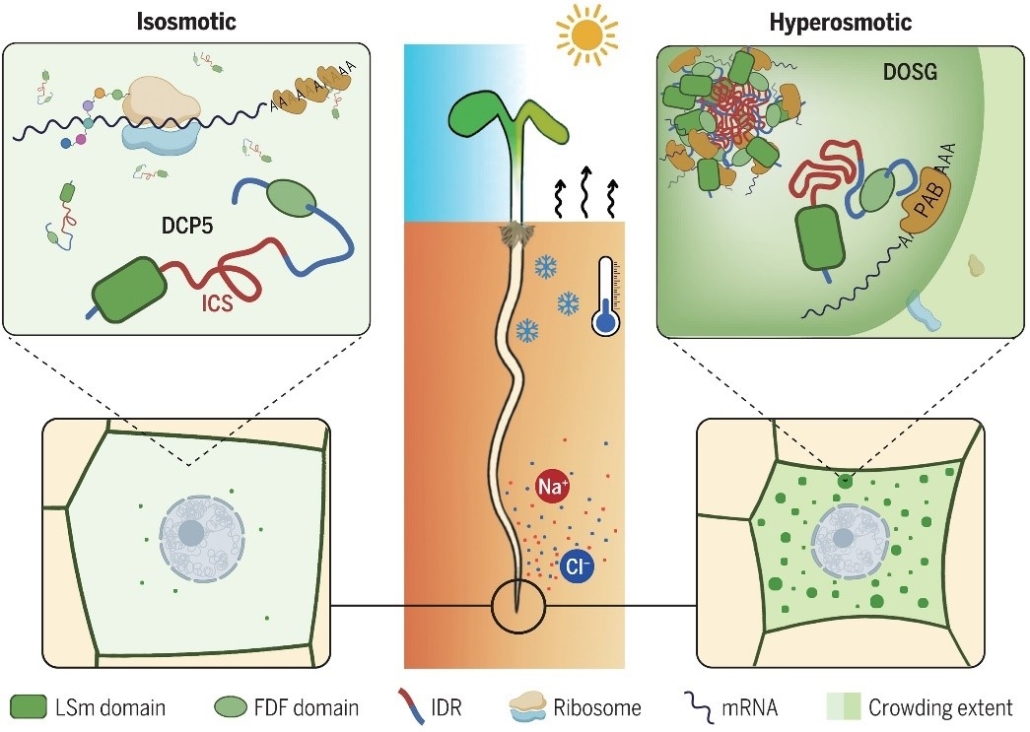
Crowd control by DCP5 - a new cytoplasmic osmosensor
Plant Science Research WeeklyOsmosis, driving water uptake and transport, is crucial for plants. It supports nutrient uptake, turgidity, and overall plant health. In hyperosmotic conditions, caused by drought, salinity, and cold stress, water loss triggers osmotic responses. A key question is: what sensors detect osmotic changes?…
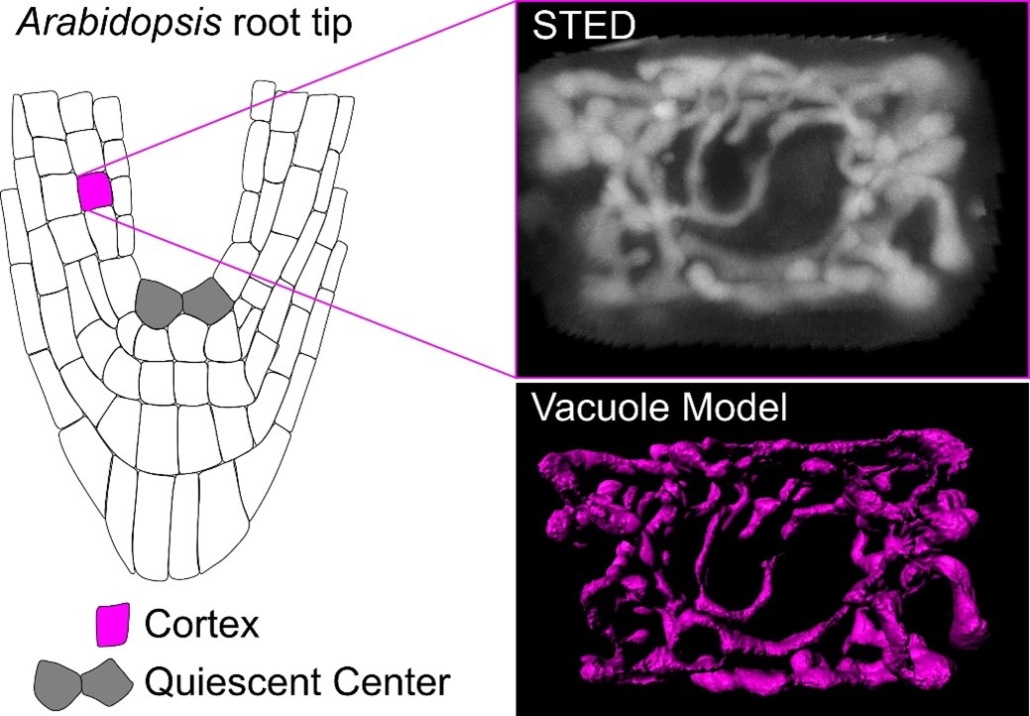
Unveiling vacuole biogenesis: Tubular networks are present in plant meristem cells
Plant Science Research WeeklyA recent paper by Scheuring and colleagues investigates vacuole biogenesis in meristematic cells of Arabidopsis thaliana, challenging earlier models of vacuole formation. Vacuoles are crucial organelles responsible for various cellular functions, yet their formation has remained puzzling for quite some…

Review: Guidelines for studying and naming plant plasma-membrane domains
Plant Science Research WeeklyNumerous studies have highlighted the critical importance of plasma membrane heterogeneities in regulating cell functions, leading to a proliferation of overlapping and contradictory terminologies. Here, Jaillais and others in the field propose a new system of nomenclature. It really is a must-read for…
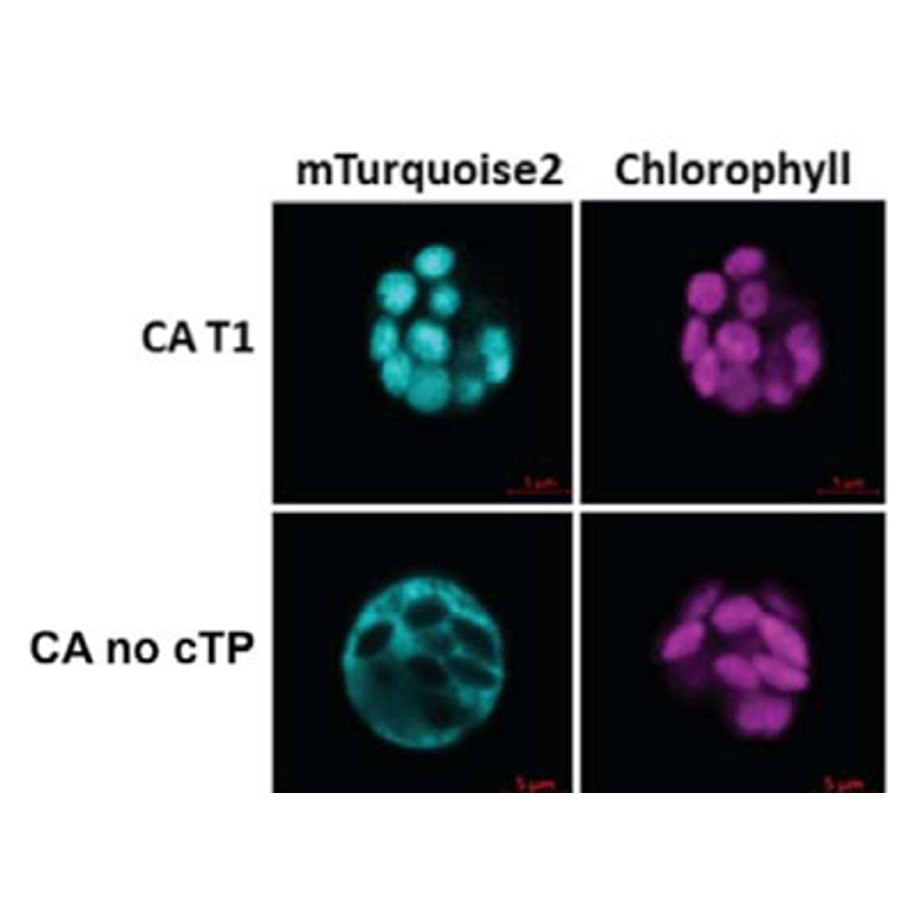
Engineering cytosolic carbonic anhydrase to establish C4 photosynthesis in rice
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn mesophyll cells, carbonic anhydrase is mainly located in the chloroplast, however it is in the cytosol in plants with a C4 carbon concentrating mechanism. There is interest in relocating carbonic anhydrase to the cytosol of C3 plants as a first step in the introduction of a carbon concentrating mechanism.…

