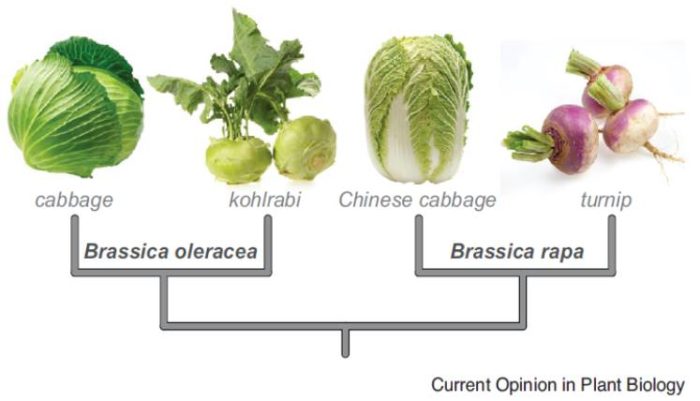
Review: Using mustard genomes to explore the genetic basis of evolutionary change ($)
0 Comments
/
Brassicaceae is one of the largest angiosperm families and provides many opportunities for studies of evolution. Of course, its most famous species, Arabidopsis thaliana is an important resource, but Brassicaceae also includes the very interesting Brassica crops (cabbage, turnip) that demonstrate the…
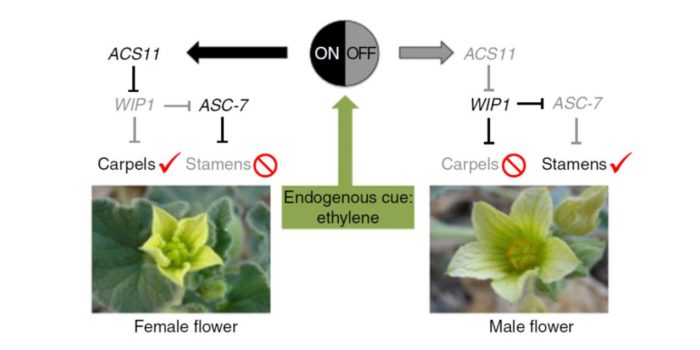
Review: Plant sex determination
Most angiosperms are hermaphrodites and produce flowers that have both male (stamens / sperm) and female (carpels / egg) parts. Pannell reviews the developmental and genetic programs that lead to these “perfect” flowers, as well as those that underlie reproductive structure development in dioecious…
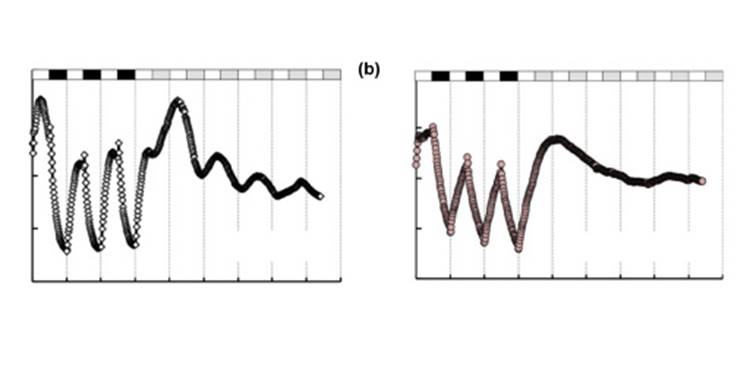
Early evolution of the land plant circadian clock
Clocks in green algae have been described as simple two-gene loops, while clocks in angiosperms have evolved to complex interlocked loops. This striking jump in complexity led Linde et al. to investigate the clocks in bryophytes and charophytes to shed light on this transition. First, through the sequence…
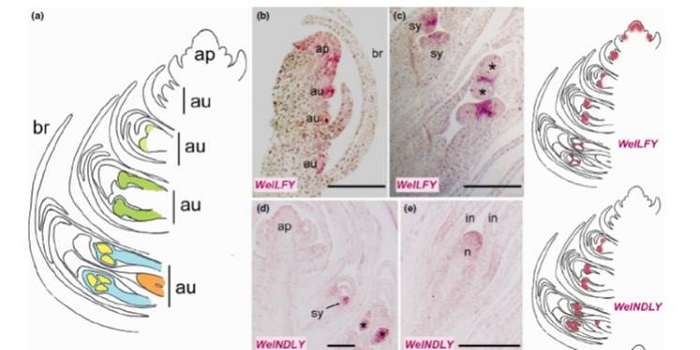
Welwitschia mirabilis sheds light on ancestral mechanisms prefiguring floral development ($)
In order to look at the origins of flowers, Moyroud et al. looked at reproductive controls in the gymnosperm Welwitschia mirabilis, which, as the authors say, is a good model because, “Although the plant body is famously bizarre, the reproductive structures are generalized.” Furthermore, its male…
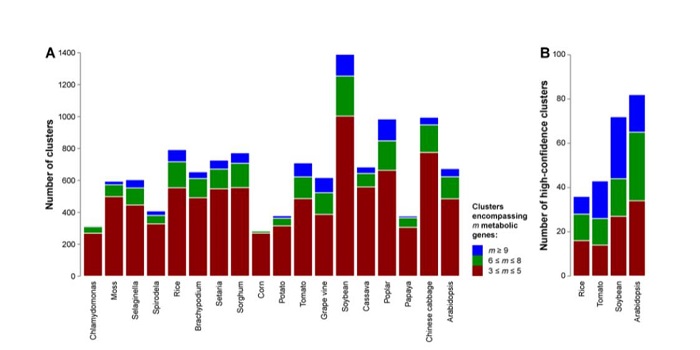
Genome-wide prediction of metabolic enzymes, pathways and gene clusters in plants
A considerable knowledge gap remains between the plant genome and the plant metabolome. To address this, Schläpfer et al. have developed a computational pipeline to identify metabolic enzymes, pathways, and gene clusters. Although metabolic genes are known to cluster in bacteria and fungi, until recently…
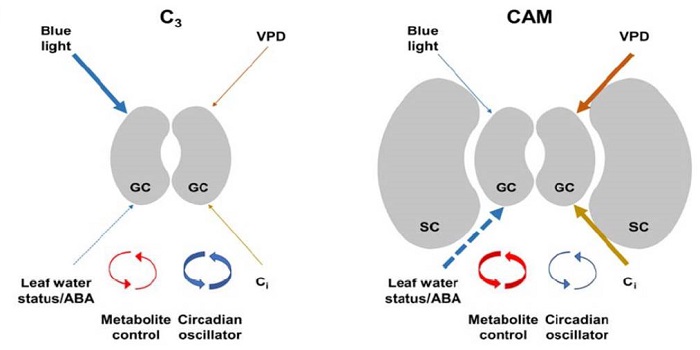
Update: Stomatal biology of CAM plants
Crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) plants open their stomata at night, decreasing water loss and increasing water-use efficiency as well as drought tolerance. Males and Griffiths review the stomatal biology of CAM plants as compared to C3 plants. For example, CAM stomata are relatively insensitive to…
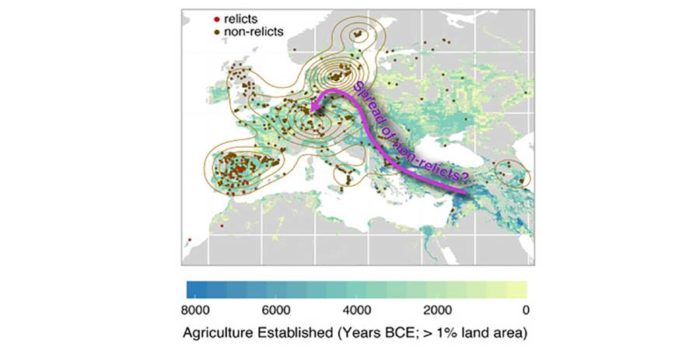
1135 Arabidopsis genomes reveal global pattern of polymorphism
There are many accessions of Arabidopsis thaliana beyond the ecotypes predominantly used in research laboratories. In this article, The 1001 Genomes Consortium describe a resource based on whole-genome sequencing of 1,135 A. thaliana genomes from Europe, North Africa, and North America. This data…
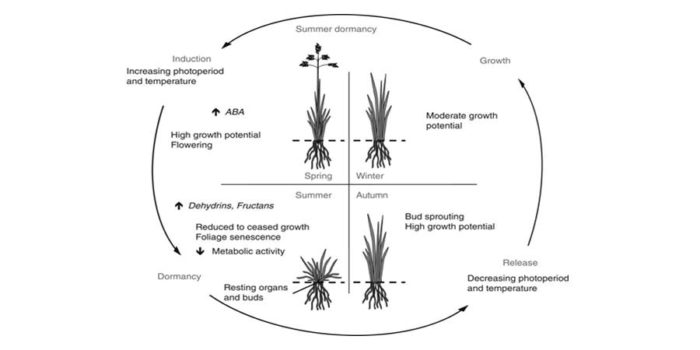
Review: Winter and summer dormancy: similar adaptive strategies?
Dormancy (growth arrest) is a state by which seeds and plants can survive harsh conditions. Seasonal dormancy is a strategy to survive seasonally unfavorable conditions. Plants can display winter and summer dormancy. Although woody species are the main study systems for winter dormancy, herbaceous species…
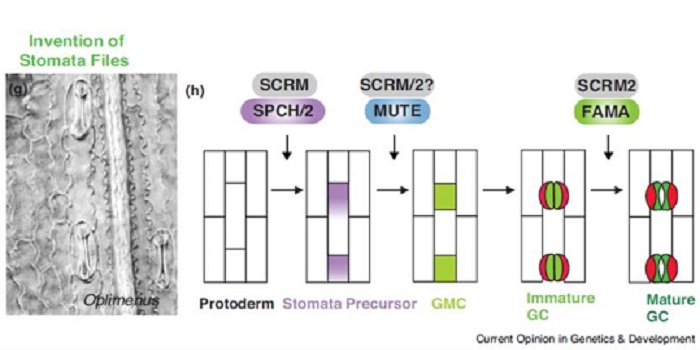
Review: Stomatal development in time: the past and the future ($)
Stomata, epidermal pores for gas exchange, first appeared about 400 million years ago. Since then, there has been functional and structural diversification. Qu et al. synthesize the developmental genetics underpinning diverse stomata, spanning from bryophytes through monocots and the astomatous (without…

