
Out of Uganda: An Aggressive Crop Killer That Threatens Global Food
Blog, Research, Research BlogFungal disease in wheat crops has been a serious but controllable problem, but a newer strain of what’s called “stem rust” has scientists worried.
January 8, 2018 by Kerstin Hoppenhaus & Sibylle Grunze
The video below is the first part in a six-part series examining the scourge of Ug99,…

Ash leaf metabolomes reveal differences between trees tolerant and susceptible to ash dieback disease
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogOver the last two decades, Ash dieback (ADB) has been sweeping through Europe killing or damaging a large proportion of European common ash trees (Fraxinus excelsior). ADB results from infection by wind borne spores of the fungus Hymenoscyphus fraxineus. As ADB spread and the scientific research…
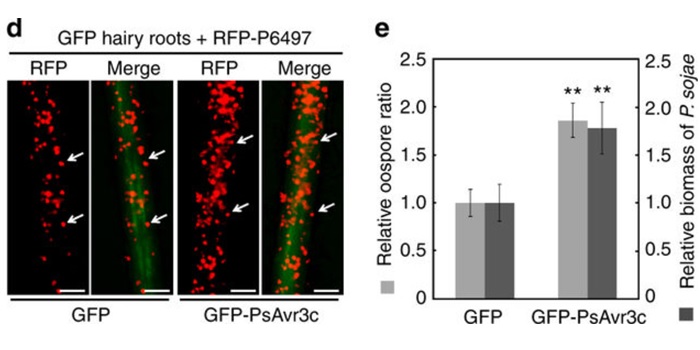
An oomycete plant pathogen reprograms host pre-mRNA splicing to subvert immunity
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPhytopthora sojae poses a serious threat to soybean production world-wide. This oomycete pathogen has a wide arsenal of effector proteins, some of which have been functionally characterized for their virulence role. Huang et al. characterized and demonstrated the functional role of an avirulence effector…

Oh, the places they’ll go! A survey of phytopathogen effectors and their host targets ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogAll phytopathogens encode for a toolbox of secreted proteins called ‘effectors’ that promote disease formation in the best possible way. Effectors are either acting in the apoplastic space or are translocated to the host cell to target diverse processes and modulate the host using enzymatic activities.…
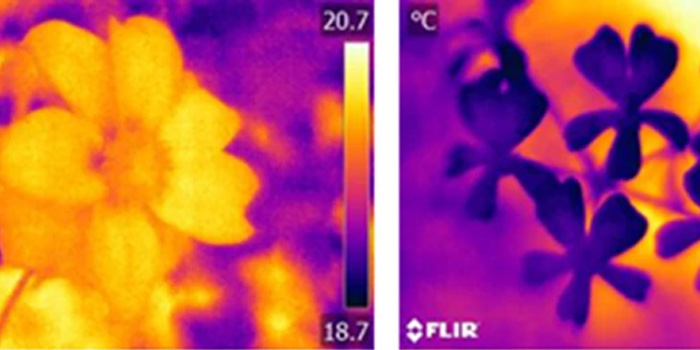
The diversity of floral temperature patterns, and their use by pollinators
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogBees and other pollinators experience the world in a different way to humans. They use different strategies in order to identify their surroundings, including their preferred flower species. Among these strategies, floral temperature. These differential “floral warming” happens due to floral thermogenesis…
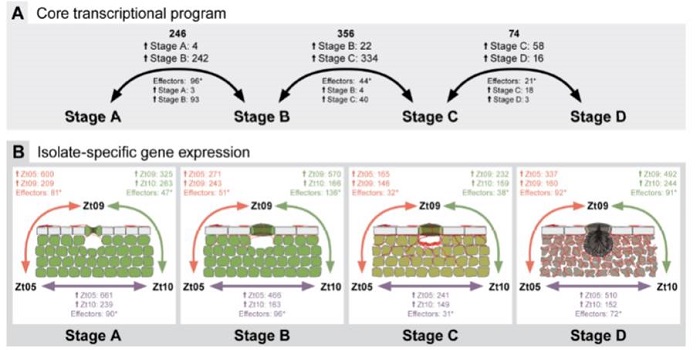
Extremely flexible infection programs in a fungal plant pathogen
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogFilamentous plant pathogens have developed an extra-ordinary level of dynamic genome architecture that adapts to changing host environment in the best possible way to promote infection. There are very limited studies describing the impact of this genome plasticity on phenotypic variation. Haueisen et…
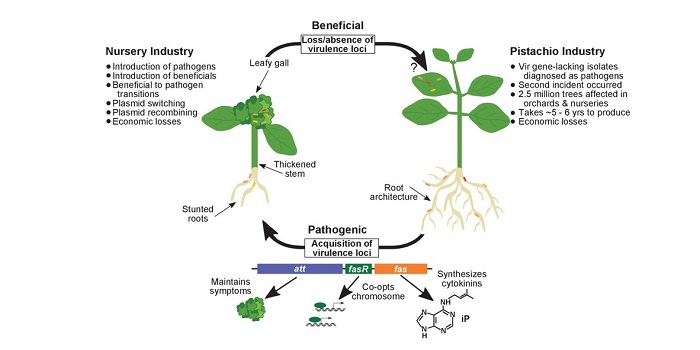
Evolutionary transitions between beneficial and phytopathogenic Rhodococcus
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogRodococcus bacteria are often identified as causal agents in disease outbreaks. Savory et al. analyzed 60 isolates from diseased plants. By comparing these new isolates and previous isolates, they found that 64 of 66 pathogenic isolates carry a linear virulence plasmid, and that all but four carried…
Broad-Spectrum Disease Resistance in Tomato
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellBroad-Spectrum Disease Resistance in Tomato
Zhu et al. examine how a plant receptor protein confers broad-spectrum resistance to various tospovirus pathogens https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00180
By Min Zhu, Savithramma P. Dinesh-Kumar, and Xiaorong Tao
Background: Highly evolved microbes cause…
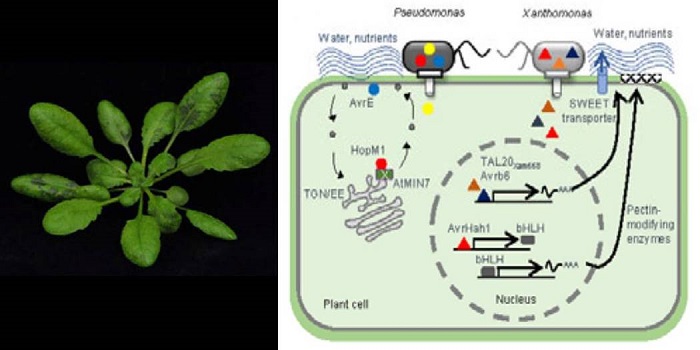
Review: The role of water in plant-microbe interactions ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogWater, a principal component on earth has also a fundamental role in maintenance of plants, microbes and the disease that is shaped by such interaction. Pathogenic disease outbreaks occur only in favorable environmental conditions, and atmospheric humidity is essential for pathogenesis. This review by…

