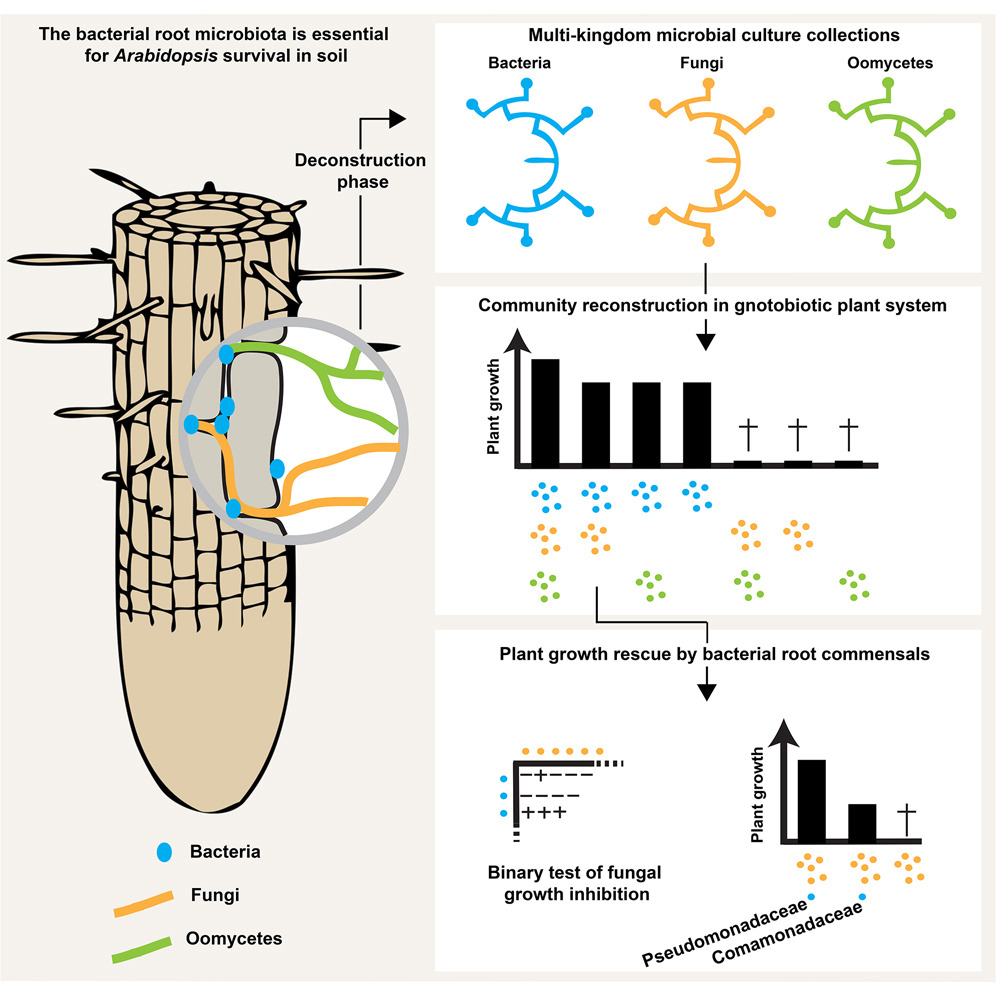
Microbial interkingdom interactions in roots promote Arabidopsis survival (Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant roots in soil are surrounded by different microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi and oomycetes. The impact of these organisms on plant health has been known f0r many decades. However, the interaction network between these organisms is not well understood. By using next generation sequencing as…
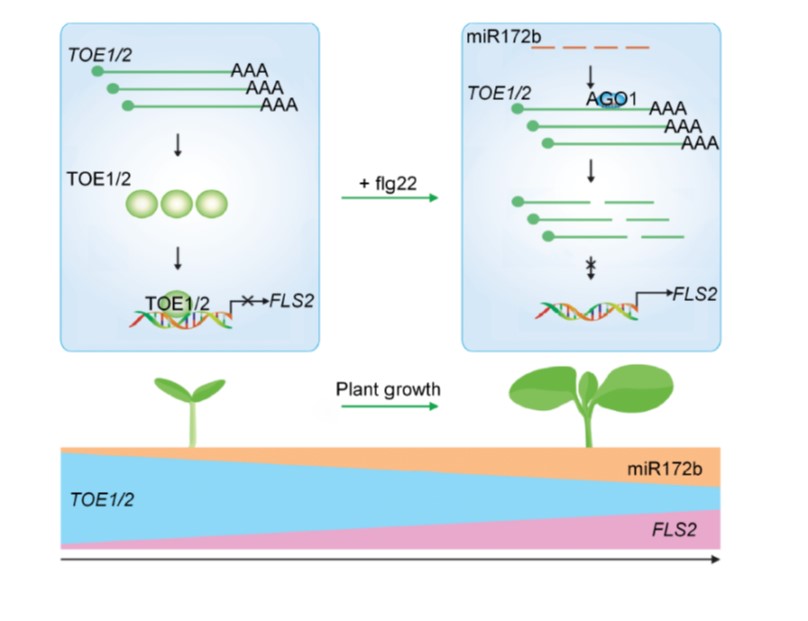
Transcriptional regulation of the immune receptor FLS2 controls the ontogeny of plant innate immunity (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyFLS2 is a well-known cell-surface receptor that triggers plant immune response. Zou et al. asked whether its expression level is age-dependent, and found that FLS2 is expressed at very low levels in newly-emerged seedlings. They identified two closely related transcription factors TOE1 and TOE2 that…
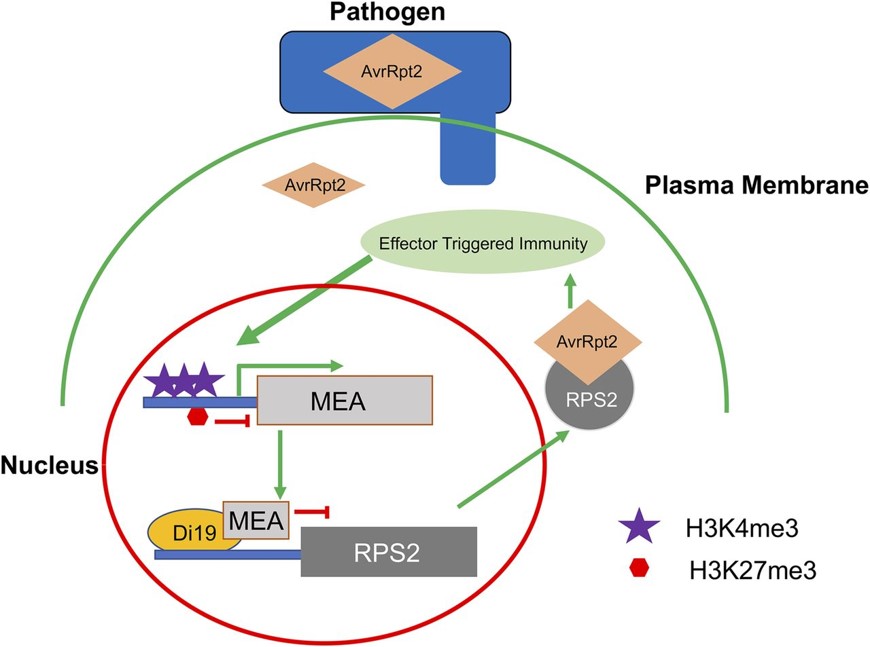
Polycomb Group Transcriptional Repressor: Suppress to Sustain
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and ViewsEvidence of epigenetic gene regulation in plant immunity was first reported in 1975 (Guseinov et al., 1975) with the demonstration that cytosine methylation is altered in response to pathogen infection. Since then, it has been established that pathogen infection influences DNA methylation and histone…
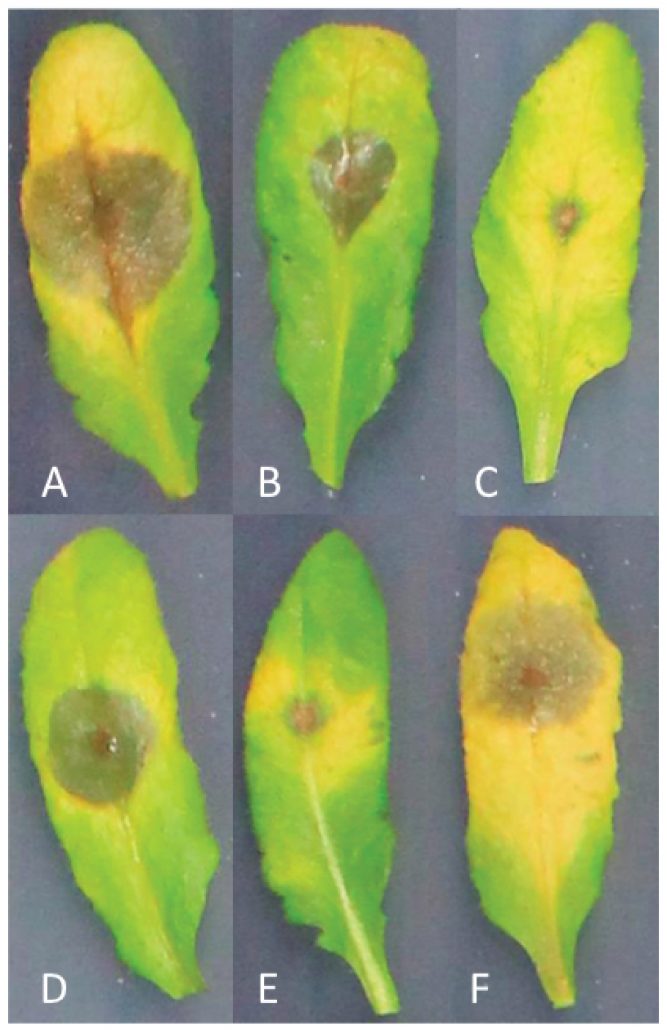

Digital imaging combined with genome-wide association mapping links loci to plant-pathogen interaction traits (Plant Phys.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyResistance to plant pathogens is often studied as a qualitative trait than quantitative, focusing on the lesion size and pathogen numbers. However, resistance to generalist plant pathogens, such as Botrytis cinerea, is known to involve multiple genes. Fordyce et al. used high-throughput phenotyping…
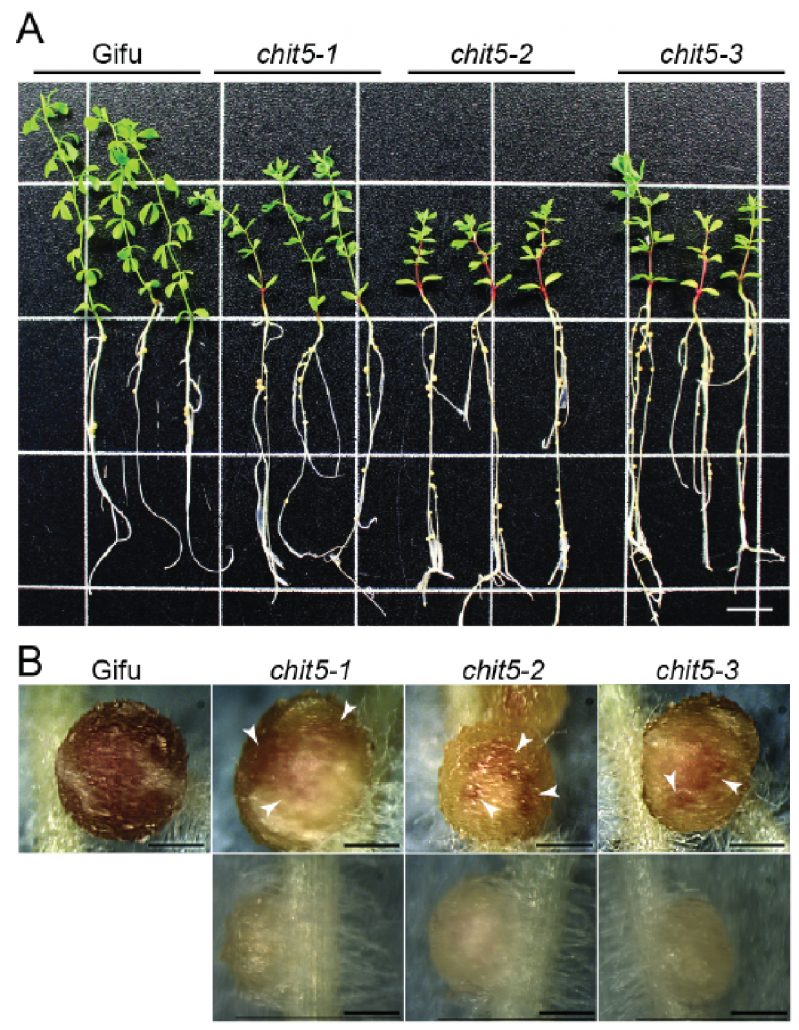

A plant chitinase controls cortical infection thread progression and nitrogen-fixing symbiosis (eLIFE)
Plant Science Research WeeklyNitrogen-fixing bacteria produce species-specific chitin-like molecules, Nod factors, which induce nodule development and infection thread formation in the host plant, aiding microbial infection. Malolepszy et al. performed a detailed study of symbiotic defective mutants in lotus (chit5), where the nodule…
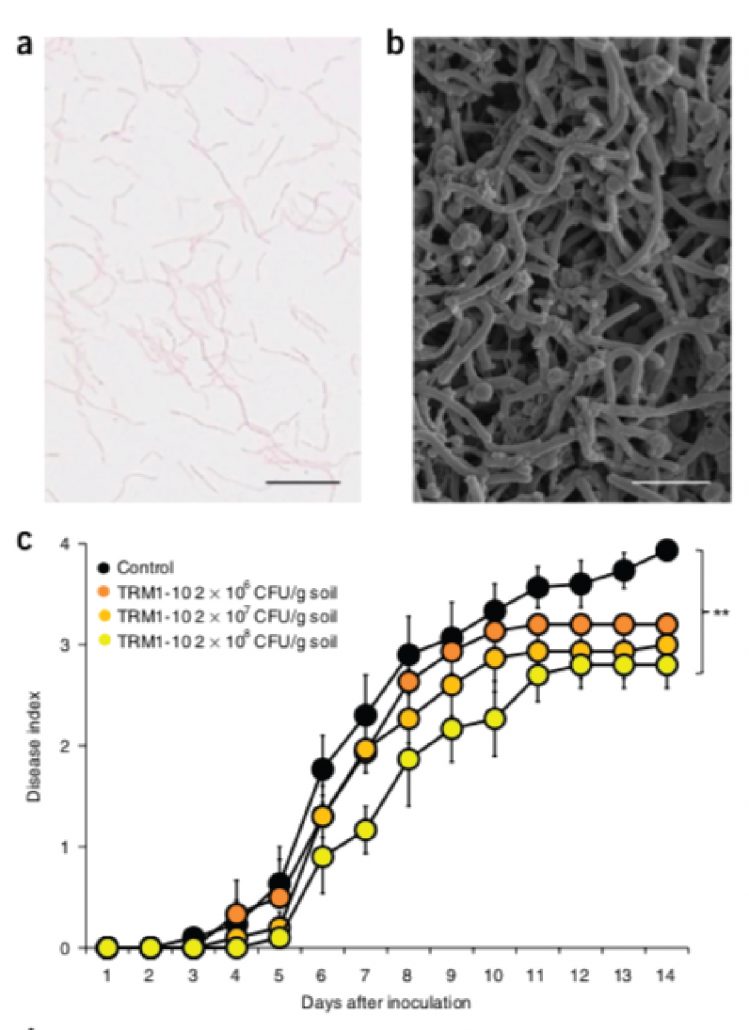
Rhizosphere microbiota structure alters to enable wilt resistance in tomato (Nature Biotech. - $)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants are frequently attacked by pathogens, but the pathogen-resistance is often attributed to the host. While interactions between the plant and its microbiota are recognized for their role in plant growth, their role in pathogen resistance is unknown. Kwak et al. studied the effect of soil-borne pathogen Ralstonia…
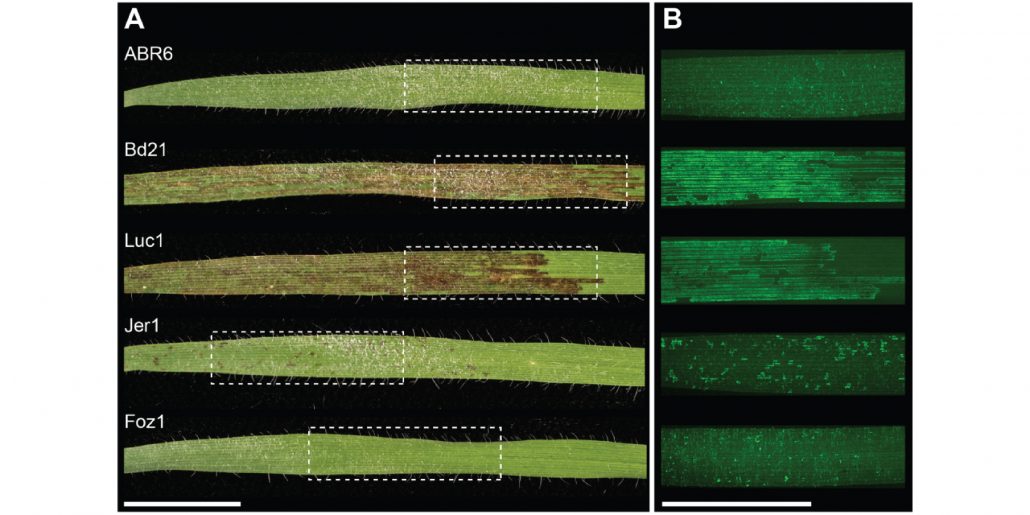
The genetic architecture of colonization resistance in Brachypodium distachyon to non-adapted stripe rust (Puccinia striiformis) isolates (PLOS Gen.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe host range of a pathogen depends on its ability to overcome various plant defense barriers and successfully complete its life cycle. Although host “jumps” are considered rare, the pathogens are able to infect plants other than their usual host with varying degree of success. Yellow stripe rust…
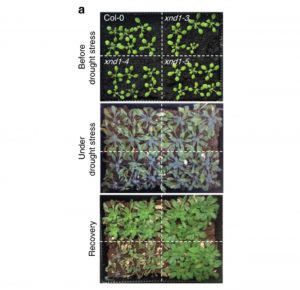
The Arabidopsis negative regulator of root hydraulics XND1 is involved in abiotic and biotic stress responses (Nature Comm.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyProper uptake and management of water is essential for plant growth and adaptation to stress. However, there are gaps in the understanding of the genetics of root hydraulics, including the regulatory components. Tang et al. used a genome-wide associate analysis approach to identify XYLEM NAC DOMAIN 1 (XND1),…
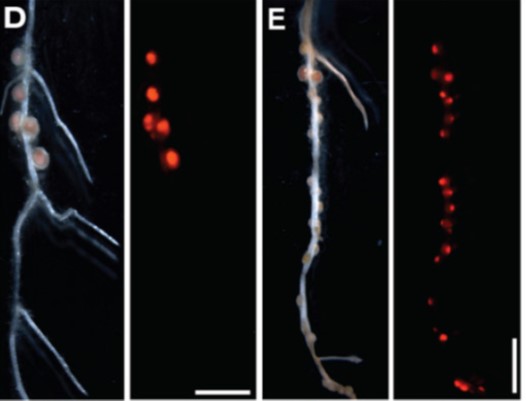
A shoot-derived miRNA ensures susceptibility to beneficial rhizobacteria in legumes (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyNitrogen-fixing rhizobacteria and leguminous plants engage in a tightly controlled root symbiosis resulting from bacteria-to-plant as well as (plant) shoot-to-root communication. This interplay controls the initiation and maintenance of root nodule development while preventing the over-production of…

