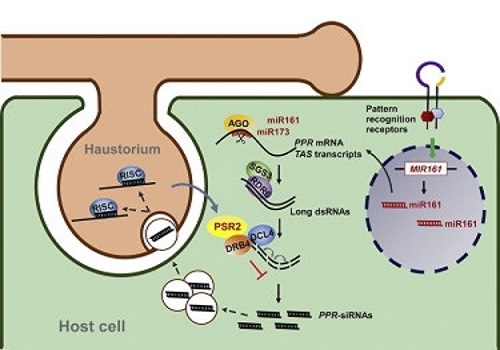
Plant-pathogen arms race: A pathogen effector protein inhibits trans-kingdom RNAi (Cell Host & Microbe)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhytophthora spp. are highly aggressive fungus-like pathogens that cause various blight and rot diseases in many crops. Upon invasion of host cells, Phytophthora delivers thousands of effector proteins. Some of these effectors suppress the host RNA silencing pathway, which is mediated by a diverse…
A smut fungus of Brassicaceae plants uses conserved and unique strategies to manipulate perennial hosts ($) New Phytol.
Plant Science Research WeeklyBiotrophic phytopathogens manipulate living hosts for the procurement of nutrients essential for growth and reproduction. It is therefore critical for invading biotrophs to evade or suppress immune responses without impacting overall plant function. In a recent study published in New Phytologist (2019),…
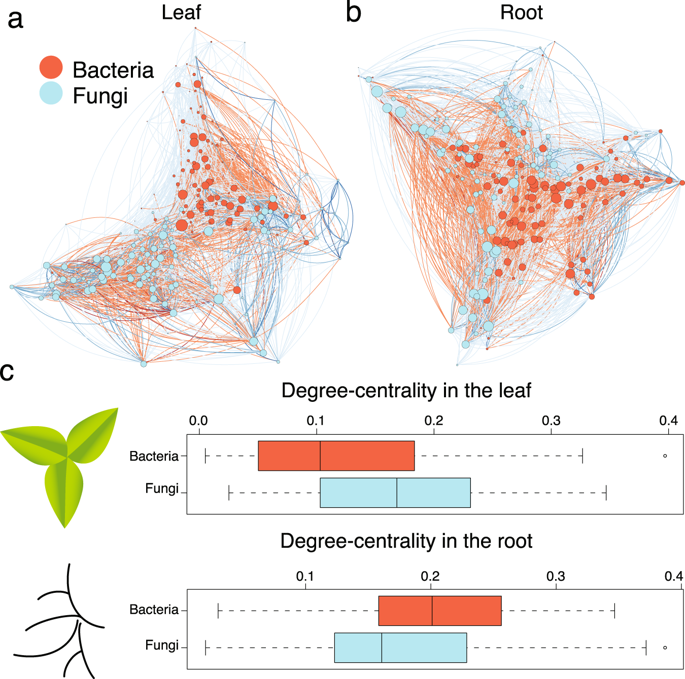
Characterizing both bacteria and fungi improves understanding of the Arabidopsis root microbiome (Sci Reports)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMicrobes that live in, on and near plants profoundly affect their growth and survival. Here, Bergelson et al. sequenced the bacterial and fungal microbiomes of Arabidopsis roots (previously they sequenced samples from leaves). The accessions are from all over the world but the sequenced samples are from…

Chloroplasts navigate towards the pathogen interface to counteract Phytophthora infection (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyChloroplasts have diverse roles in plant defense, including contributing to the production of defense compounds. Toufexi, Duggan et al. show new data indicating the dynamic relocation of chloroplasts to the contact point of the oomycete pathogen Phytophthora infestans. Infection also causes an increase…
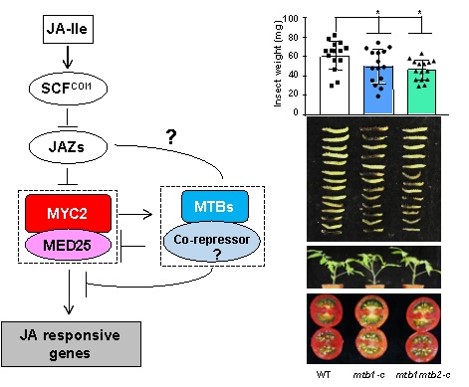
The mechanism by which MYC2 regulates the termination of jasmonic acid signaling
The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: News
Source: Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology Published: 2019-01-11. Translated from the original.
As an important plant hormone, jasmonic acid regulates plant defense responses and adaptive growth. When the plant is exposed to pests or other stresses, the active jasmonic…
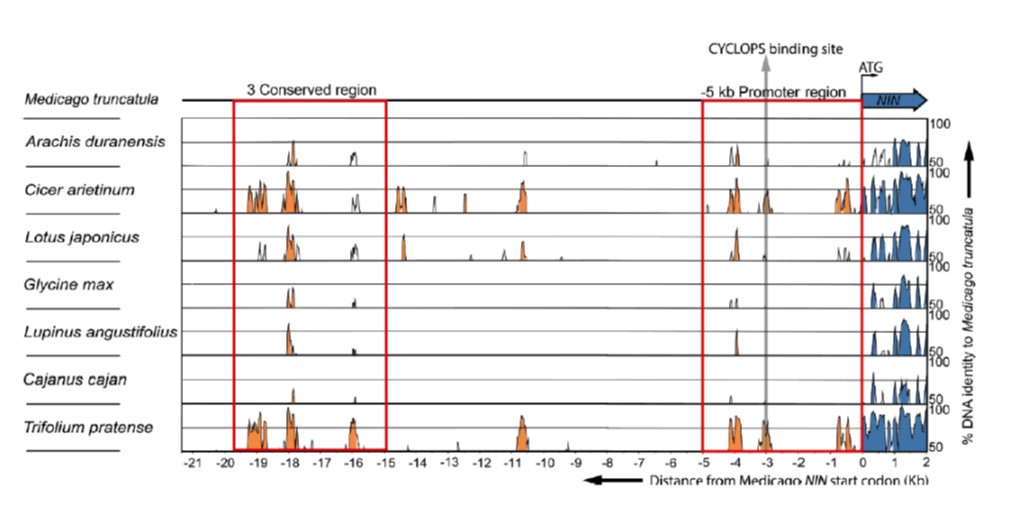
The secret of NIN (Nodule Inception) ($) (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyTwenty years ago, a genetic screen of Lotus japonicas identified NIN (NODULE INCEPTION), a transcription factor required for both early (infection thread) and late (nodule primordium development) stages of nodule formation. In daphne (a weak allele of NIN), infection threads form but not nodule primordia,…
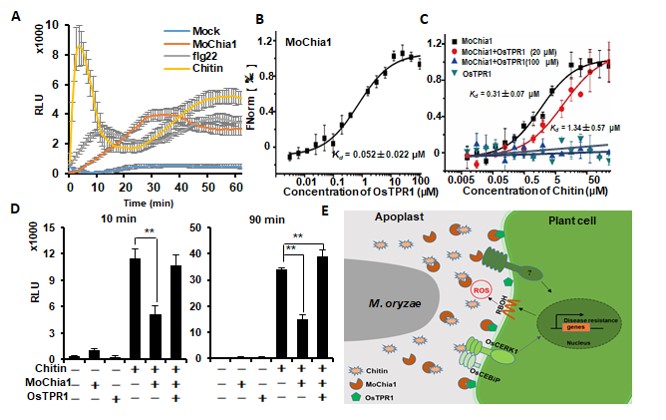
Mechanism of rice blast fungus recognition revealed
The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: NewsRice is an important food crop in China, but the damage of rice blast fungus is an important factor affecting the high and stable yield of rice. Liu Jun's research group of the Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences found in the previous study that when rice blast fungus infects rice,…
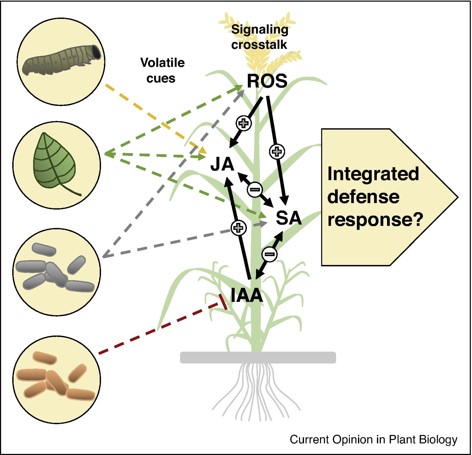
Volatiles as inducers and suppressors of plant defense and immunity — origins, specificity, perception and signaling (Current Opinion in Plant Biology)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWhen plants are under attack by herbivores and microbes, running away is not an option. As a defence, plants produce volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that repel herbivores, attract enemies of the herbivores, or alarm surrounding plants; VOCs have mostly been viewed as positive regulators in the plant…
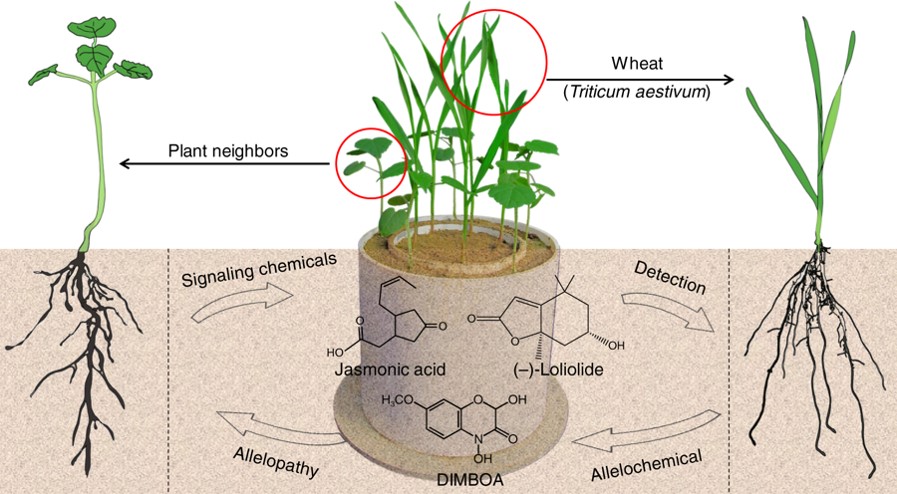
Plant neighbor detection and allelochemical response are driven by root-secreted signaling chemicals (Nature Communications)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants are not able to move out of their neighborhood if they are unhappy, but they are capable of recruiting and assembling a community in which they are able to thrive. Plants are also able to initiate defense when they sense that threats are near. To keep tabs on their neighbors, plants utilize both…

