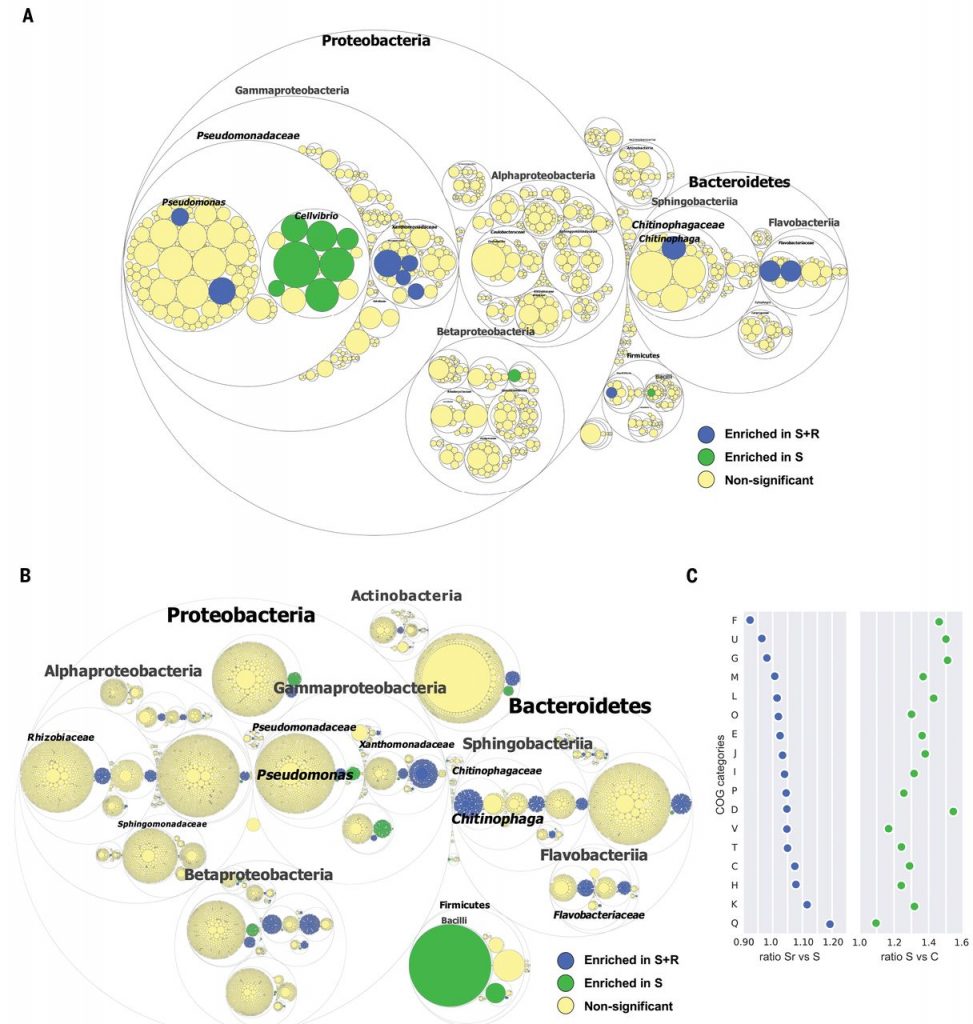
Pathogen-induced activation of disease-suppressive functions in the endophytic root microbiome ($) (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyDisease-suppressive soils have long been known, although it hasn’t always been clear how they function. Previous studies have suggested that soil microbes are responsible for disease suppression, because the suppressive property can be transferred to other soils and is lost when soil is sterilized.…
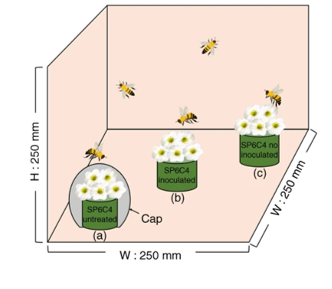
A mutualistic interaction between Streptomyces bacteria, strawberry plants and pollinating bees (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklySome species of Streptomyces bacteria produce antimicrobial compounds that have been shown to enhance plant resistance to pathogens. Kim et al. show that his protection can extend to a pollinator. The Streptomyces defends the plant against Botrytis cinerea and protects the bees against insect pathogens…
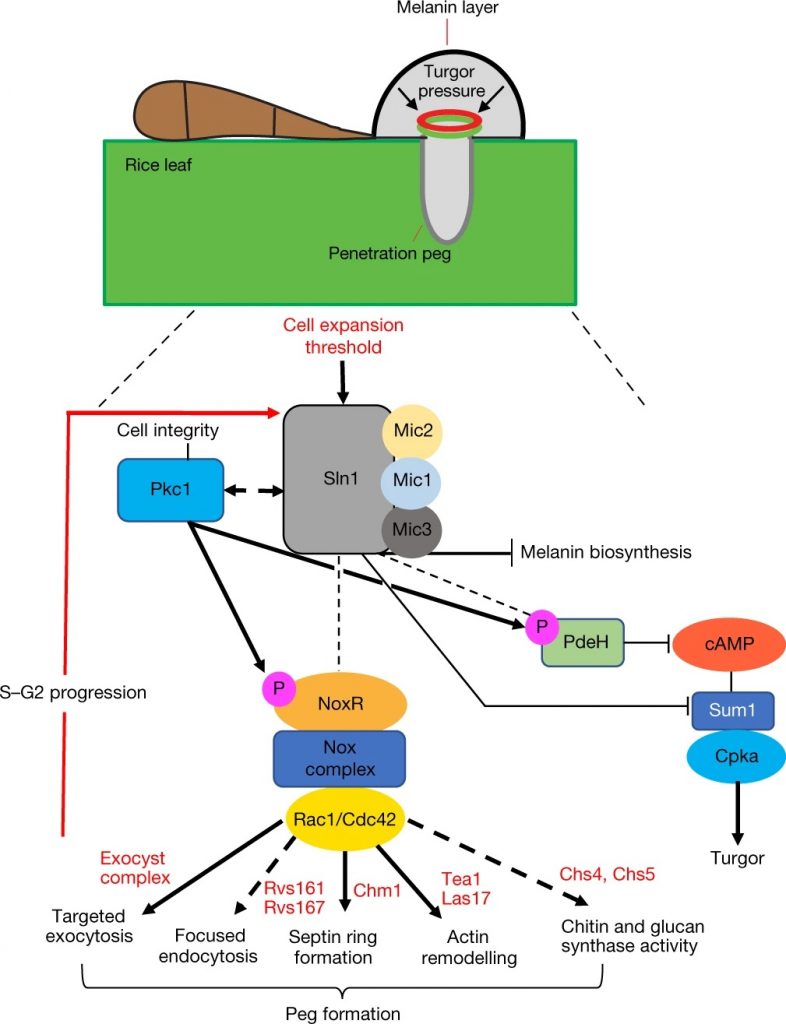
A sensor kinase controls turgor-driven plant infection by the rice blast fungus ($) (Nature)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMagnaporthe oryzae, the causal organism of blast disease in rice and wheat, is the most devasting pathogen in rice production. During infection, it develops a germ tube that forms an infection structure called the appressorium. Through septin-mediated reorganization of the cytoskeleton, a high amount…

Insect herbivory selects for volatile-mediated plant-plant communication ($) (Current Biology)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in response to insect herbivory. The potential for VOCs to serve as diffusible signals has long been recognized. For example, VOCs can signal neighbors to prime for defense, signal distant parts of the emitting plant, and even attract predatory insects…
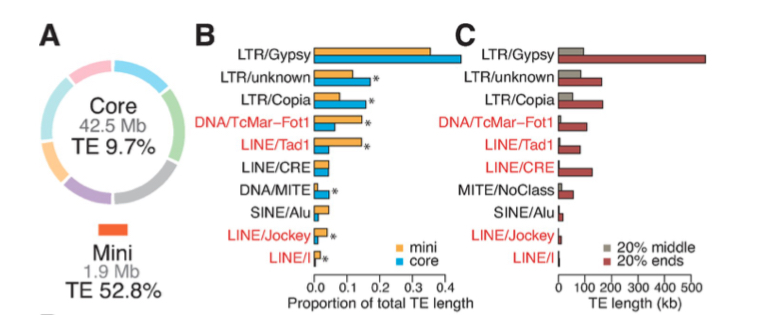
Effector gene reshuffling involves dispensable mini chromosomes in wheat blast fungus (PLOS Genetics)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe emerging disease wheat blast is devastating and has the capacity to cause 100% yield loss. Wheat blast is caused by the fungus Magnaporthe oryzae pathotype Triticum (MoT). This pathotype is distinct from most of the pathotypes that causes disease in other plants such as M. oryzae Oryza (MoO) in rice.…
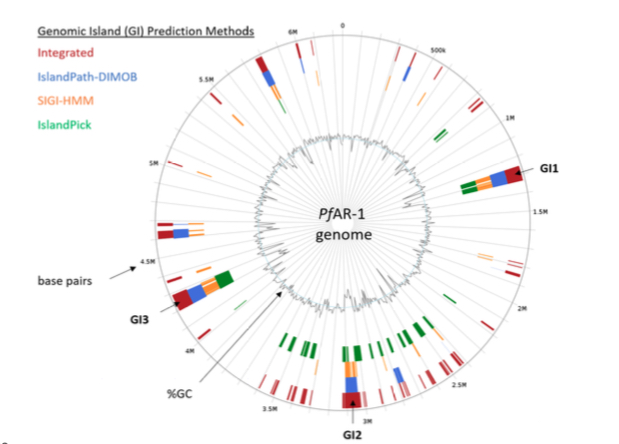
Plant microbe co-evolution: Allicin resistance in Pseudomonas fluorescens (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyGarlic (Allium sativum L.) produces allicin (diallylthiosulfinate), which is an antibiotic defense substance. It can oxidize thiols in celular targets such as cysteines and glutathione. Because allicin has multiple sites and mechanisms of action, it is difficult for an organism to become resistant.…
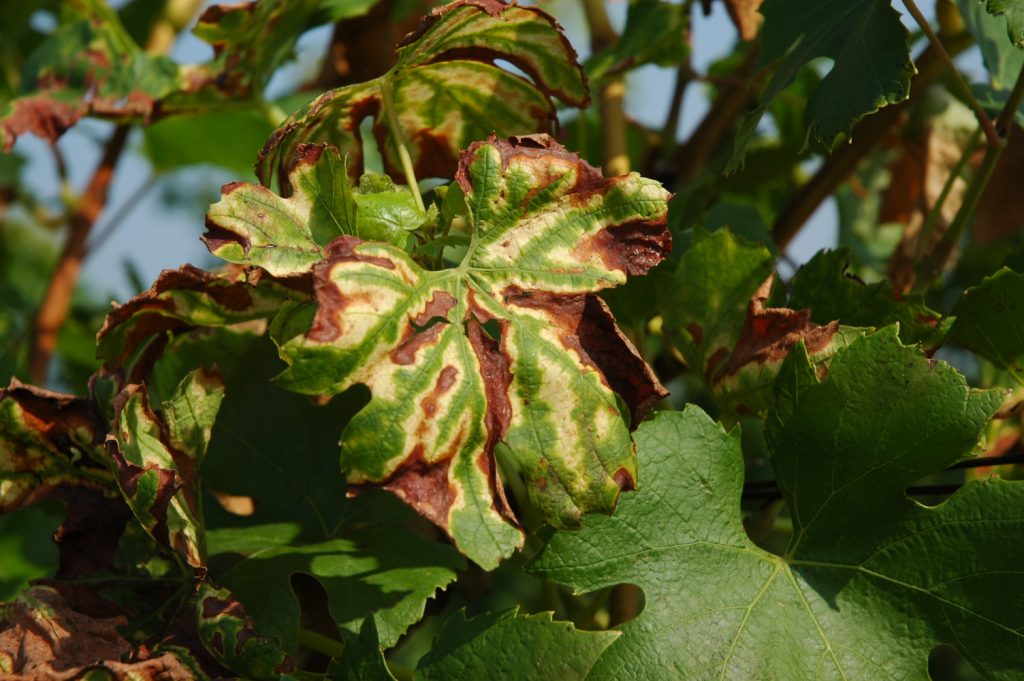

Exploring the hydraulic failure hypothesis of esca leaf symptom formation (Plant Phys)
Plant Science Research WeeklyEsca is a leaf scorch (necrosis) disease of grapevine that causes tremendous yield losses. Bortolami et al. have investigated the etiology of this condition, which is known to be a consequence of fungal pathogen infection. But how exactly does the fungal infection contribute to the observed symptoms?…
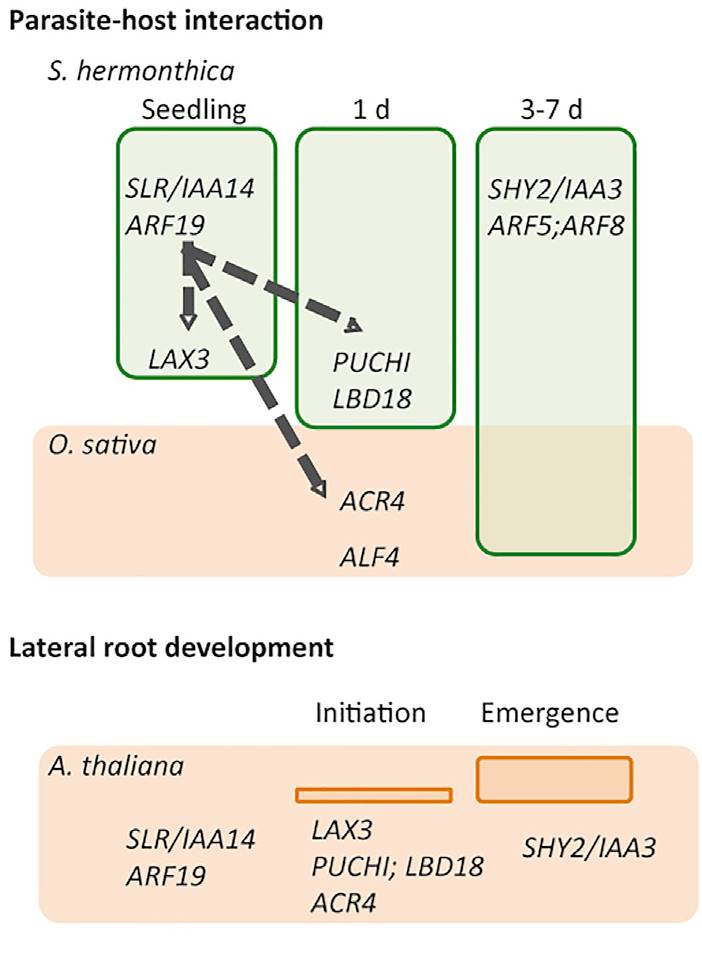
Genome sequence of Striga asiatica provides insight into the evolution of plant parasitism (Curr Biol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe parasitic plant Striga asiatica is both a serious agricultural pest and a fascinating plant oddity. Yoshida et al. report its genome sequence, which provides a glimpse into how a plant becomes an obligate parasite. Three key findings are the tremendous expansion of receptors for strigolactones (host-released…
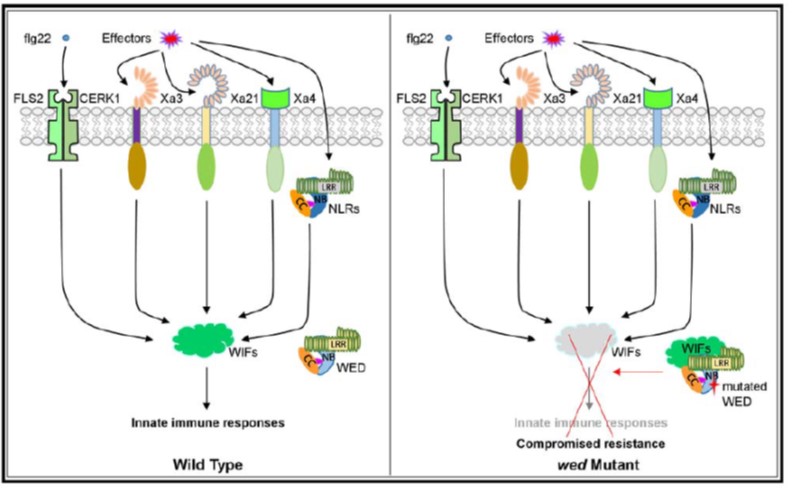
A single amino-acid substitution impairs PTI and ETI in an SA-dependent manner in rice ($) (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants possess two immune strategies to prevent invasion by pathogens called pattern-triggered immunity (PTI, typically mediated by cell-surface receptors) and effector-triggered immunity (ETI). During ETI, intracellular resistance (R) proteins perceive specific pathogen effectors. Tang et al. describe…

