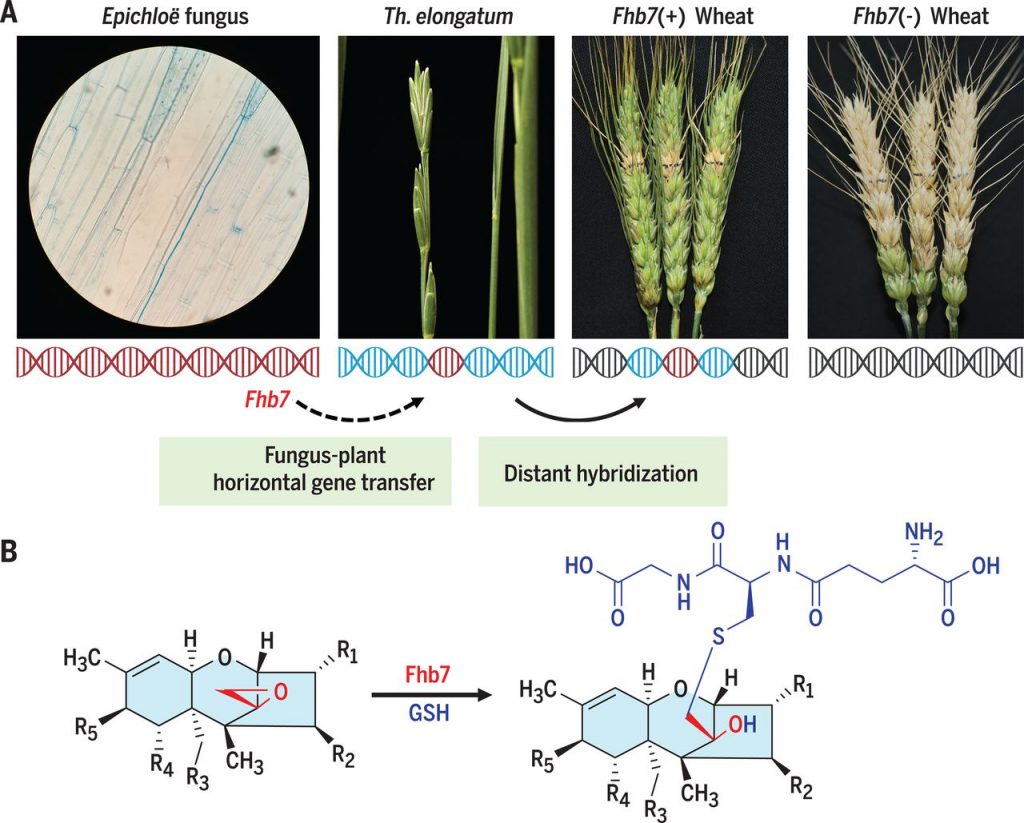
Horizontal gene transfer of Fhb7 from fungus underlies Fusarium head blight resistance in wheat (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMycotoxins are fungal toxins with harmful health effects on humans and other animals. Fusarium head blight is a fungal disease of wheat inflorescences that can contaminate the grain and harm its consumers. Previously, Fhb7 was identified in the wheat relative Thinopyrum elongatum as a quantitative trait…
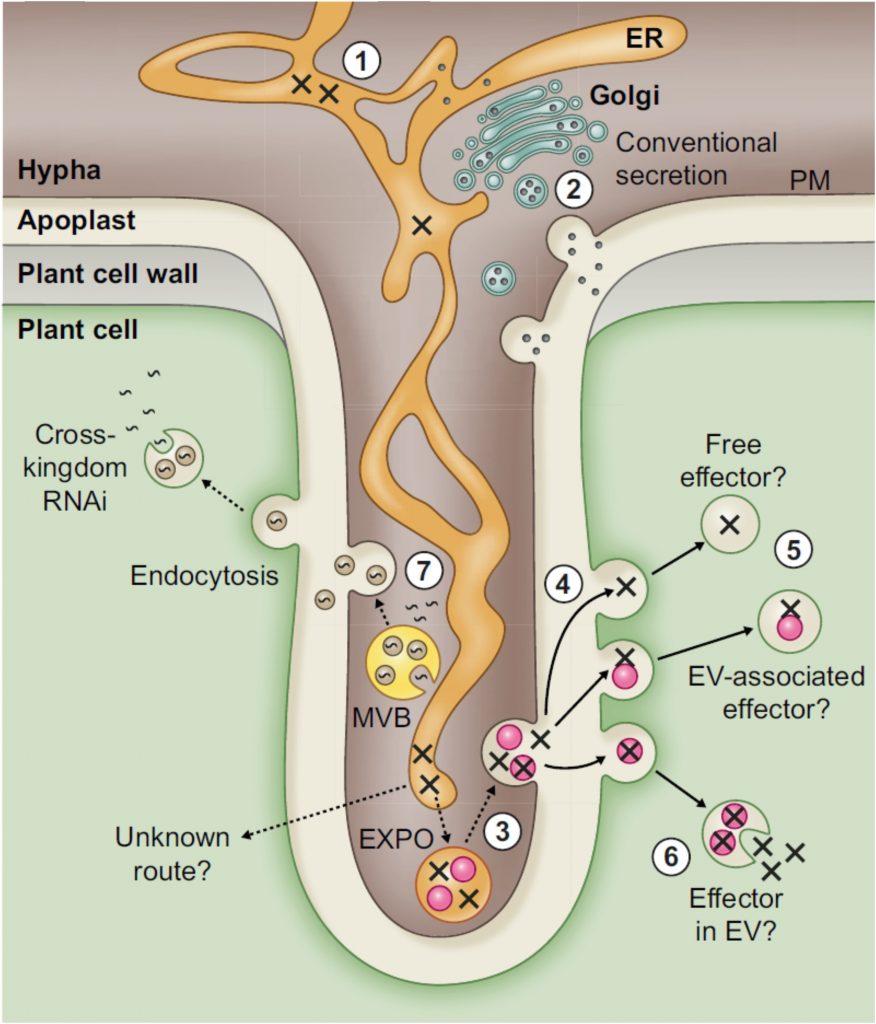
Review: Devastating intimacy: the cell biology of plant–Phytophthora interactions (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhytophthora are plant-destroying oomycetes. Within this genus are several infamous disease-causing agents: P. infestans of the potato late-blight fame, P. sojae of soybean root rot, P. ramorum of sudden oak death, and many other lesser-known species. This fine new review by Boevink et al. explores the…
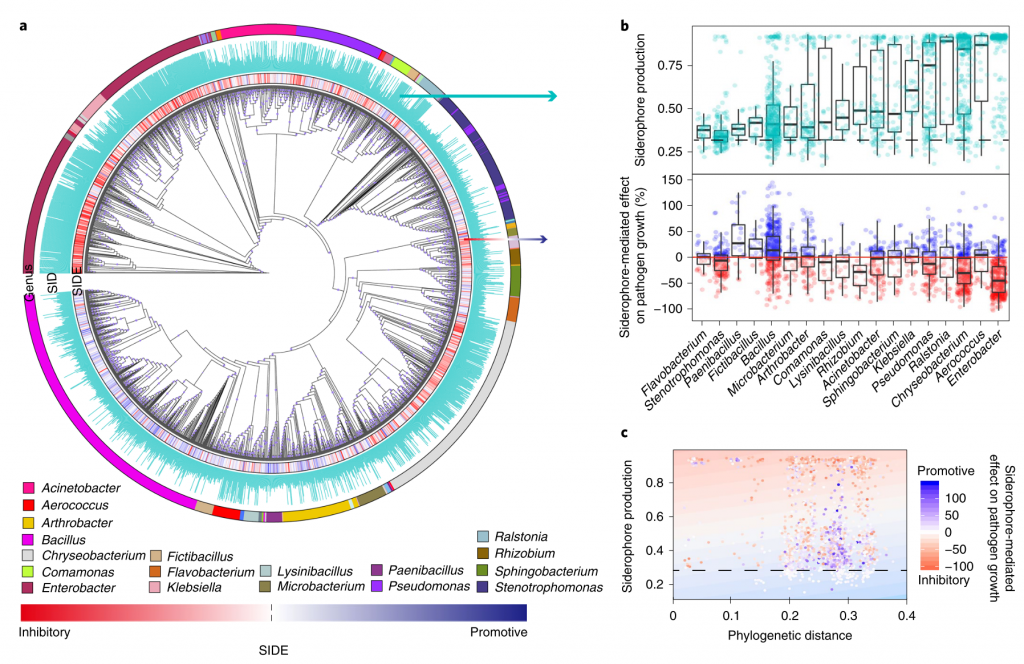
Rhizosphere microbiome protects plants from a pathogen via iron competition (Nature Microbiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIron is an essential element for most living organisms, including plant-associated bacteria. As iron is insoluble in most soils, many soil-borne bacteria scavenge iron using siderophores, a chemically diverse group of secondary metabolites with a high affinity for iron. Siderophores are known to drive…
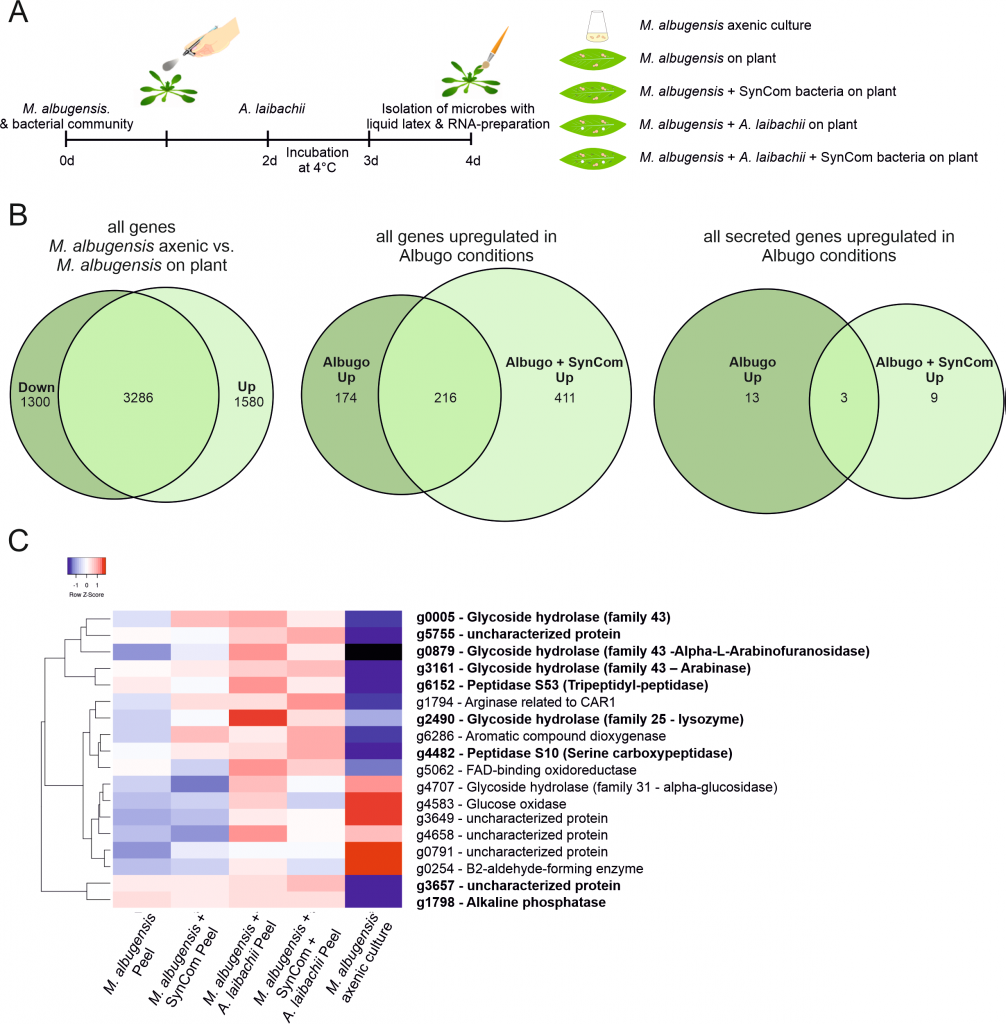
Fungal antagonism of Arabidopsis oomycete infection requires a previously uncharacterized secreted hydrolase (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAntagonist interactions between microbes of the phyllosphere stabilize the microbiome and some “hub” organisms can exert strong effects on community structure. The yeast family Ustilaginales contains several apathogenic species that are microbial antagonists that can inhibit infection from diverse…
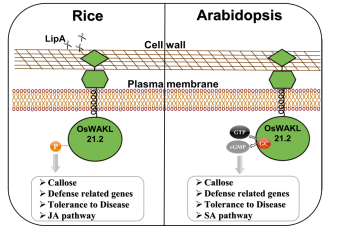
A moonlighting kinase induces immune responses in rice and Arabidopsis ($) (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyBacterial infections are a serious issue for crop plants and it is thus imperative to understand the mechanisms employed by plants to develop resistance against pathogens. Malukani et al. have identified a receptor kinase in rice, WALL-ASSOCIATED KINASE-LIKE 21 (OsWAKL21.2) that perceives pathogen-induced…
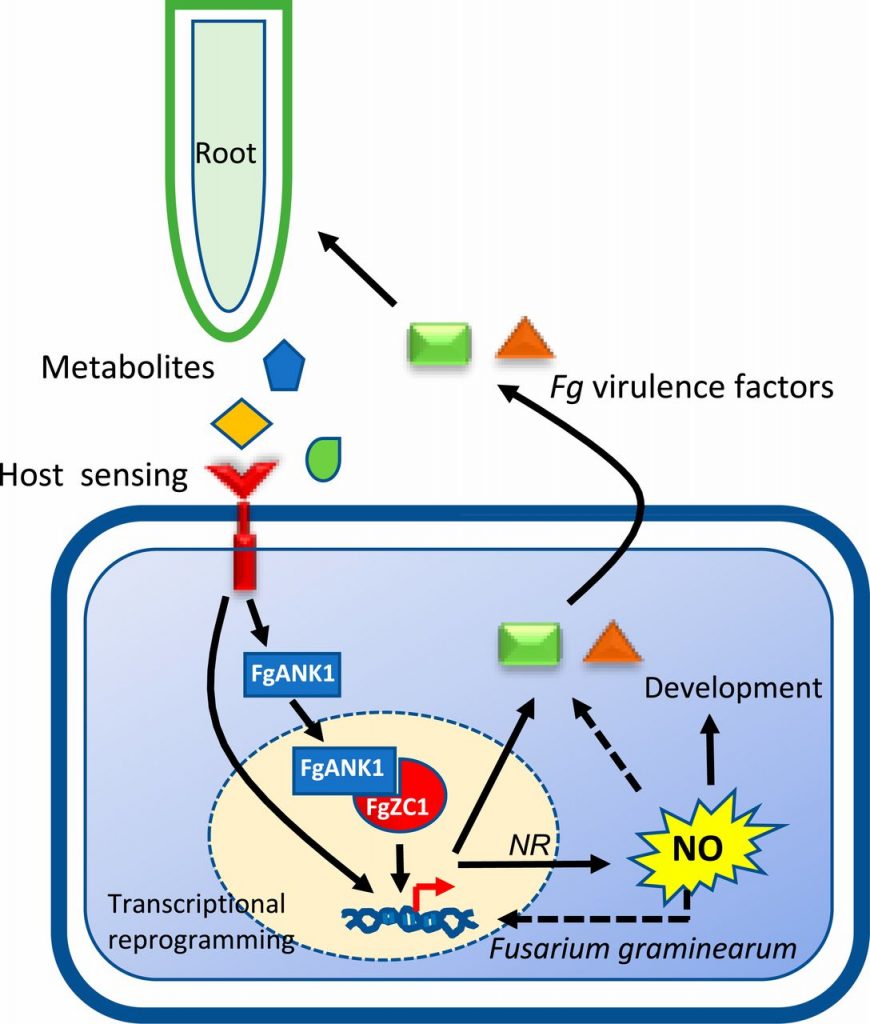
Mechanistic insights into host perception by a fungal pathogen (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyHost perception is crucial for soil-borne microbes to successfully colonize plant roots. Ding et al. conducted transcriptome analysis of the fungal pathogen Fusarium graminearum (Fg) in the presence of its host plant Brachypodium distachyon (Bd), either without direct contact (precontact) or during colonization.…
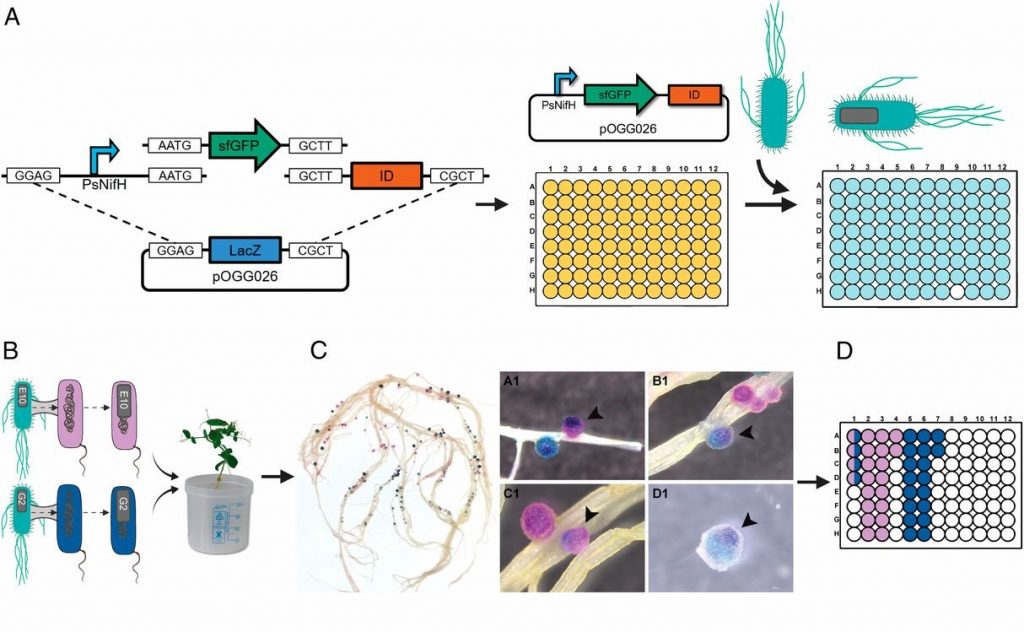
A molecular toolkit for screening elite rhizobia (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyN2-fixing rhizobia bacteria are able to establish symbiotic interactions with legumes in specialized organs called root nodules. Identifying elite rhizobia that are both competitive for nodule occupancy and effective in N2 fixation in agricultural environments is crucial for maximizing the yield of legumes.…
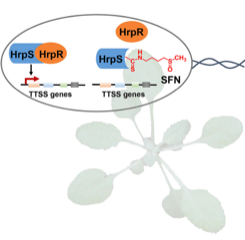
A plant secondary metabolite selectively targets bacterial pathogenicity (Cell Host Microbe)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants have a variety of secondary metabolites that are associated with defense against pathogens, but the mode of action of such metabolites is poorly understood. Wang et al. revealed that the Arabidopsis secondary metabolite sulforaphane (SFN), which is derived from aliphatic glucosinolate, suppresses…
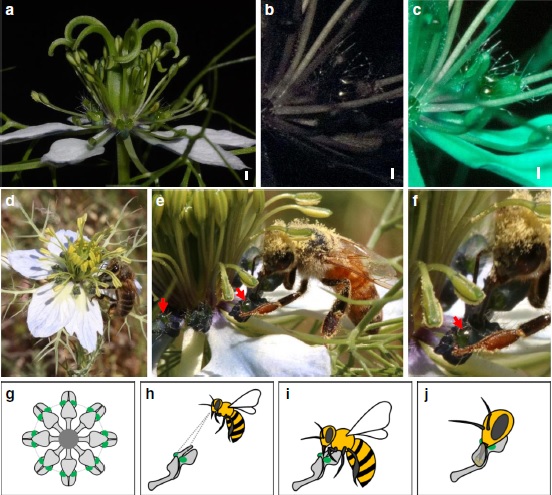

Morphology, molecular development and ecological function of pseudonectaries on Nigella damascena petals (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPseudonectaries do not secrete nectar like nectaries. So, what are their ecological functions? Are there any morphological and anatomical differences between them and true nectaries? How do they develop and evolve? Liao et al. examined pseudonectaries of Nigella damascene to answer these questions. The…

