
Cones structure and seed traits of four species of large‐seeded pines: Adaptation to animal‐mediated dispersal (Ecol. Evol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyDifferent studies show that animal-dispersed pines have particular cone and seed structures to match their dispersers. However, most research has either addressed the changes in cone and seed traits in a single species over an environmental gradient or the differences between wind-dispersed and animal-dispersed…
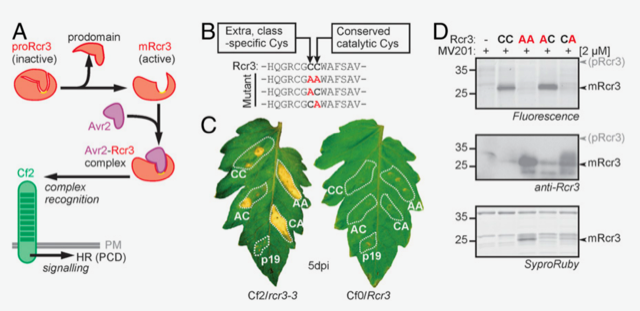
Extracellular proteolytic cascade in tomato activates immune protease Rcr3 (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe plant apoplast is a sea of immune-related proteins that facilitate robust defense against pathogens. Rcr3 is a tomato secreted apoplastic protease that contributes to both basal defense and gene-for-gene resistance against pathogens. Rcr3 is activated by the cleavage of its autoinhibitory prodomain,…
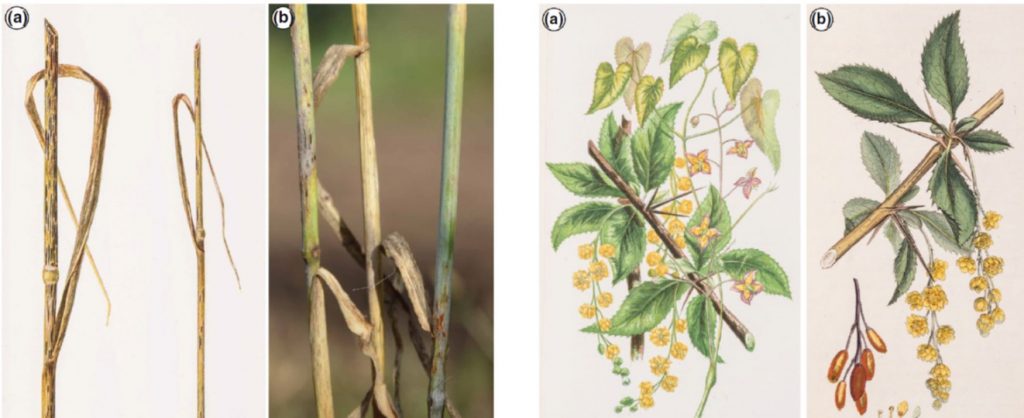

Review: Banishing barberry: The history of Berberis vulgaris prevalence and wheat stem rust incidence across Britain (Plant Pathology)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPuccinia graminis f. sp. tritici (Pgt) has a strange life strategy in that it requires two hosts to complete its sexual life cycle; wheat and barberry. In the absence of barberry, it reproduces clonally; clonal reproduction limits its ability to generate diversity and therefore its ability to evade plant…
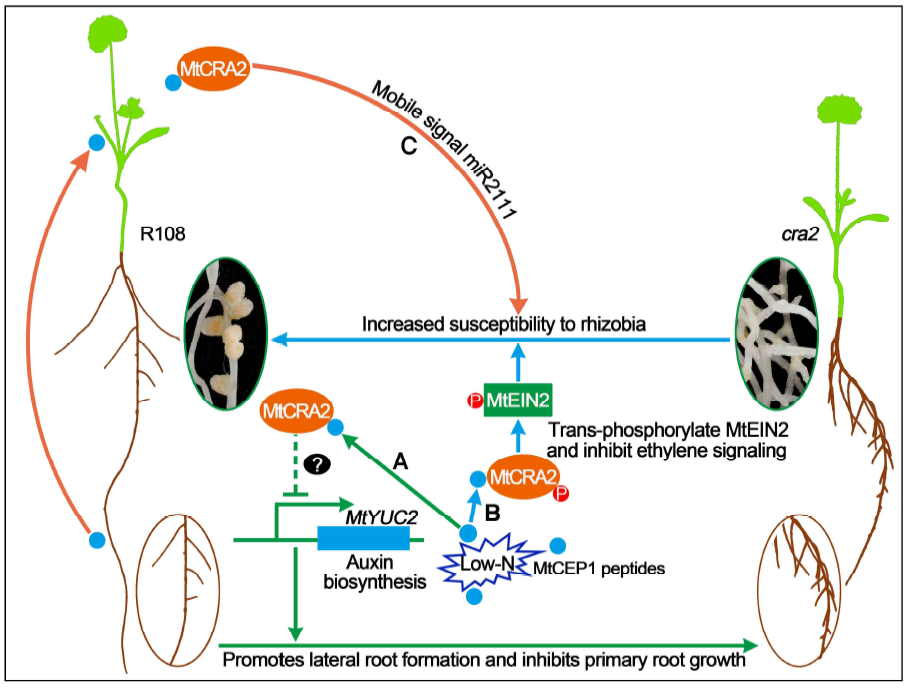
A CEP Peptide receptor-like kinase regulates root growth and symbiotic nodulation (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyUnder low N condition, plants form more lateral roots to facilitate N-uptake efficiency, and legumes such as Medicago truncatula develop more nodules to fulfill plant nitrogen requirements. Since both lateral root formation and nodulation are energy-consuming processes, plants balance these developmental…
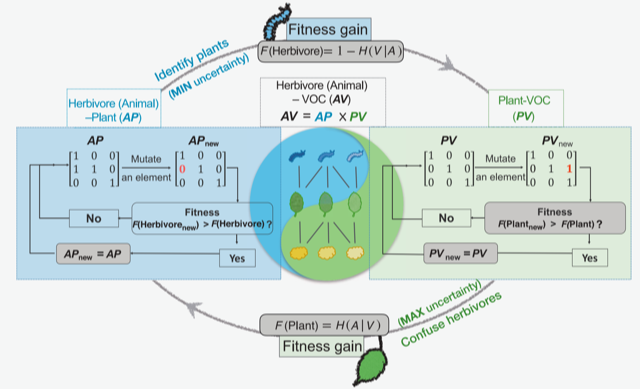
Plant-herbivore chemical communication decoded (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyChemical communications between species are prevalent in nature. For instance, herbivorous insects can spot their host plants by sensing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted by plants. Despite our knowledge about interactions between individual plant and herbivore species, little is known about…
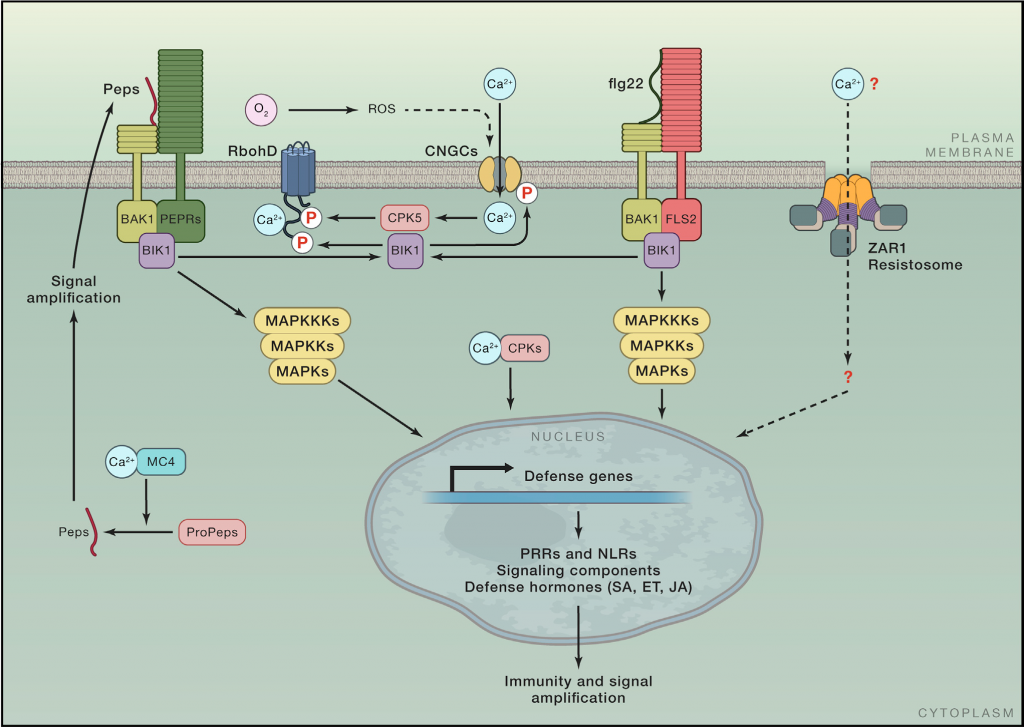
Review. Plant immunity: Danger perception and signaling (Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyResearch from the last three decades has discovered many genes and pathways involved in plant immunity and how they are connected. Here, Zhou and Zhang highlight new research regarding activation and signaling of cell surface pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) and intracellular nucleotide-binding,…
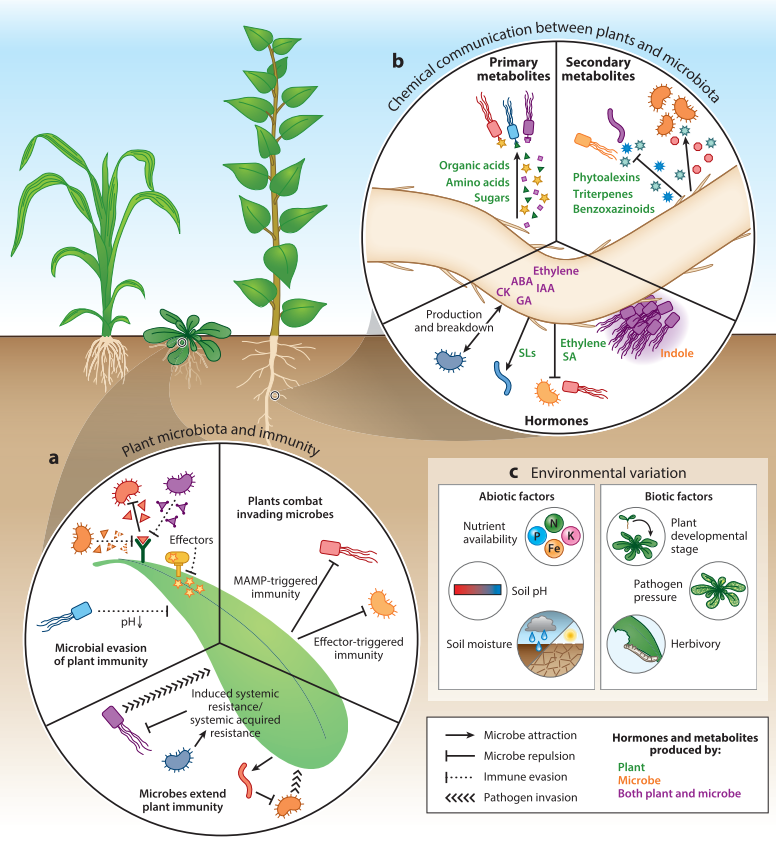
Review. The plant microbiome: From ecology to reductionism and beyond (Annu. Rev. Microbiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe last two decades have witnessed tremendous progress in our understanding of plant microbiota. Fitzpatrick, Salas-González et al. highlight recent discoveries from culture-dependent and culture-independent approaches and discuss the future path towards integrating these approaches. Culture-independent…
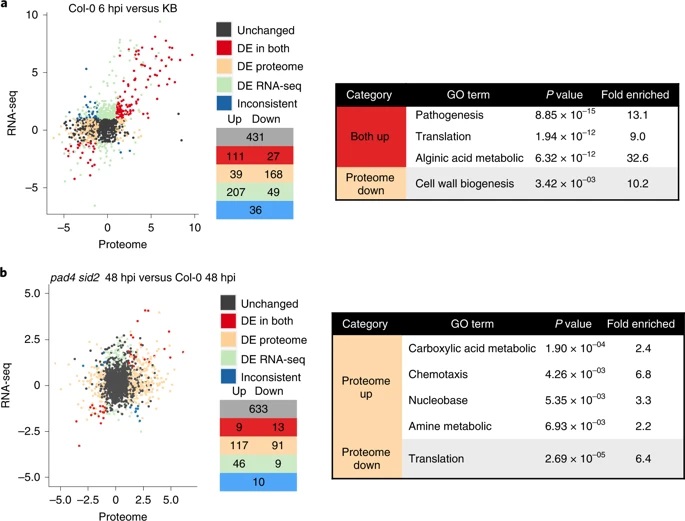
Multidimensional gene regulatory landscape of a bacterial pathogen in plants (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe outcome of a plant-bacteria interaction is determined by the bacterial virulence and plant immune systems. Individually, these systems, and to an extent their interactions, have been well studied. However, certain aspects of their interactions remain elusive, particularly how plant immunity affects…
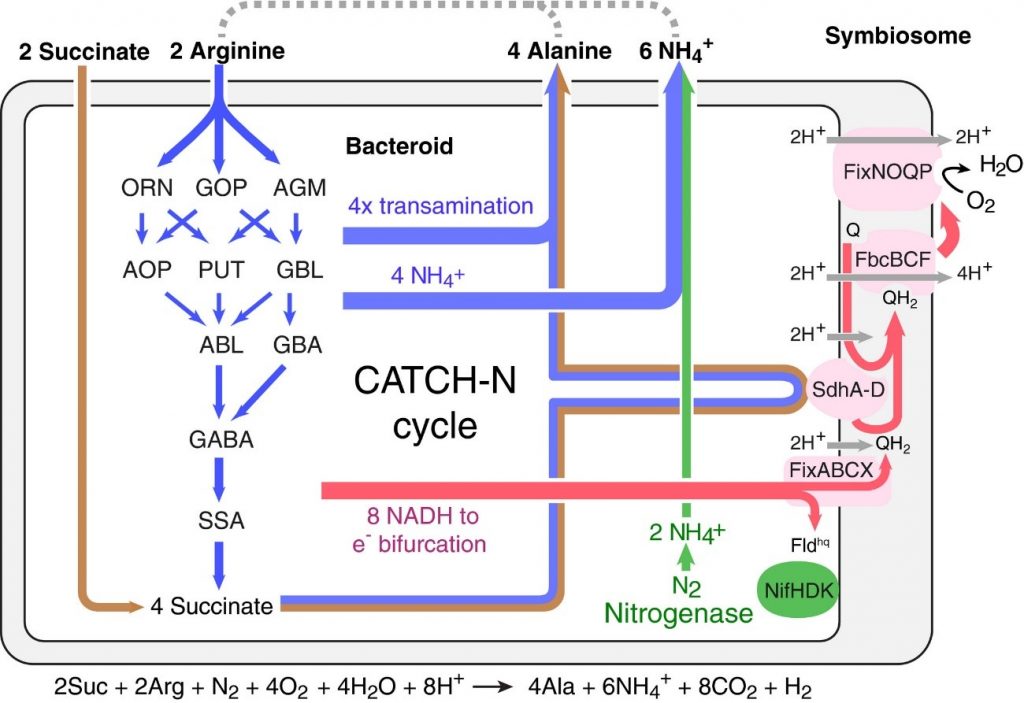
Co‐catabolism of arginine and succinate drives symbiotic nitrogen fixation (Mol Sys Biol)
Plant Science Research WeeklySymbiotic nitrogen fixation is a mutualistic relationship between plants and microbes in which plants supply fixed carbon to bacteria in exchange for nitrogen. During this process, the microbes use nitrogenase enzyme to convert atmospheric nitrogen into a plant-usable form, but the metabolic interaction…

