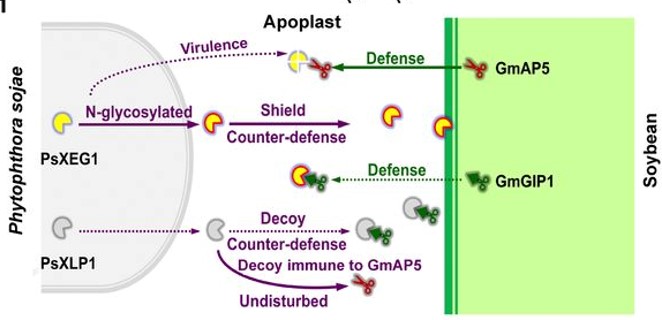
N-glycosylation shields Phytophthora sojae apoplastic effector PsXEG1 from a specific host aspartic protease (Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Physicists say “for every reaction there is an equal and opposite reaction,” an expression that applies to the interactions between plants and pathogens as well. Here, Xia et al. have uncovered another layer in the “arms race” between soybeans and the oomycete pathogen Phytophthora sojae.…

Identification of a unique ZIP transporter involved in zinc uptake via the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal pathway (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLast week, PSRW presented two review papers regarding host plant interactions with microbial populations, particularly for plant nutrient intake. Watt-Williams et al. utilize such knowledge for their paper, performing an RNA-seq dataset to identify a novel zinc transporter in Medicago truncatula. Zinc…
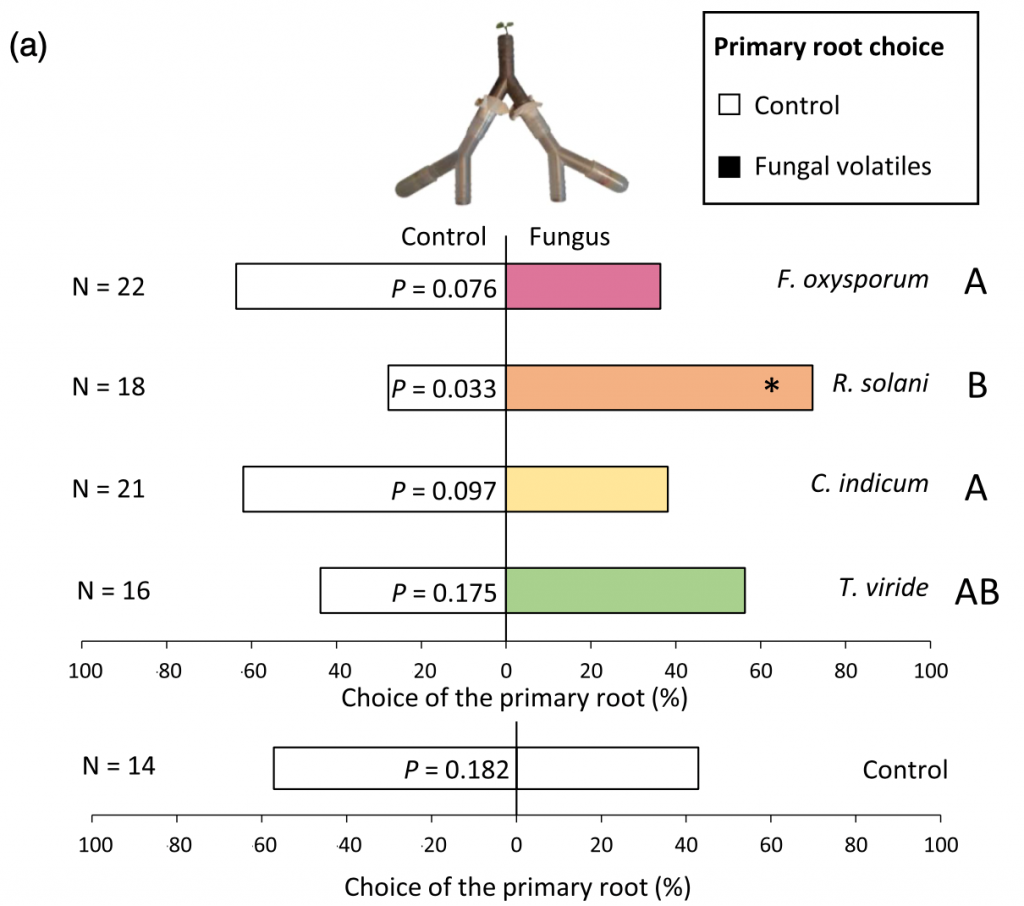
The love potion made by soil-borne fungi (Plant Cell Environ.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe basic requirements for plant growth are water, nutrients, and light. There are many other factors contributing to plant growth, including the interactions between plants and soil microorganisms. Soil microorganisms produce a large array of volatiles that can affect root architecture (e.g., some volatiles…
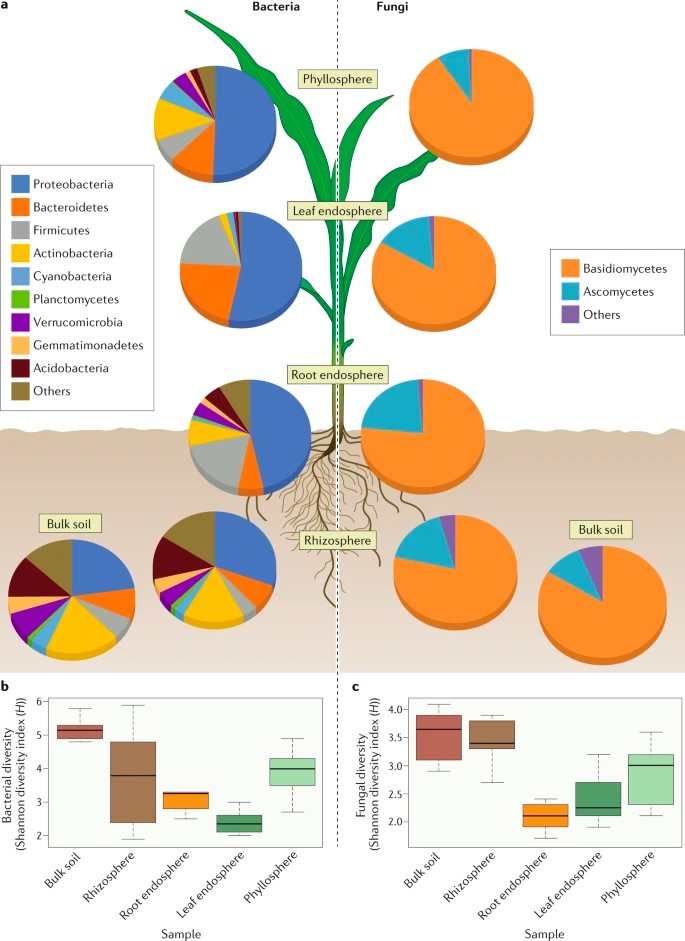
Review: Plant–microbiome interactions: from community assembly to plant health (Nat. Rev. Microbiol)
Plant Science Research Weekly
The association of plants with communities of beneficial microbes, called plant microbiota, has a positive effect on growth and proliferation of both organisms. Recent findings in plant microbiota research uncovered the role of individual microbes and associated genes during plant-microbe interaction…

Cuscuta australis (dodder) parasite eavesdrops on the host plants’ FT signals to flower (PNAS)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Plants sense environmental cues, such as day length, to induce flowering and successfully reproduce. An important mobile regulator of flowering is FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT). Upon floral induction, FT is transported from the leaves to the shoot apical meristem where it triggers flower development. Dodders…

Review: Compartmentalization drives the evolution of symbiotic cooperation (Proc. Roy. Soc.)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Many plants take advantage of microbial symbionts to boost their nutrient uptake, with classic examples provided by mycorrhizal fungi and the legume/Rhizobia partnership. Similar symbiotic partners are found in other domains of life, including the coral/dinoflagellate symbiosis, and the symbiosis…
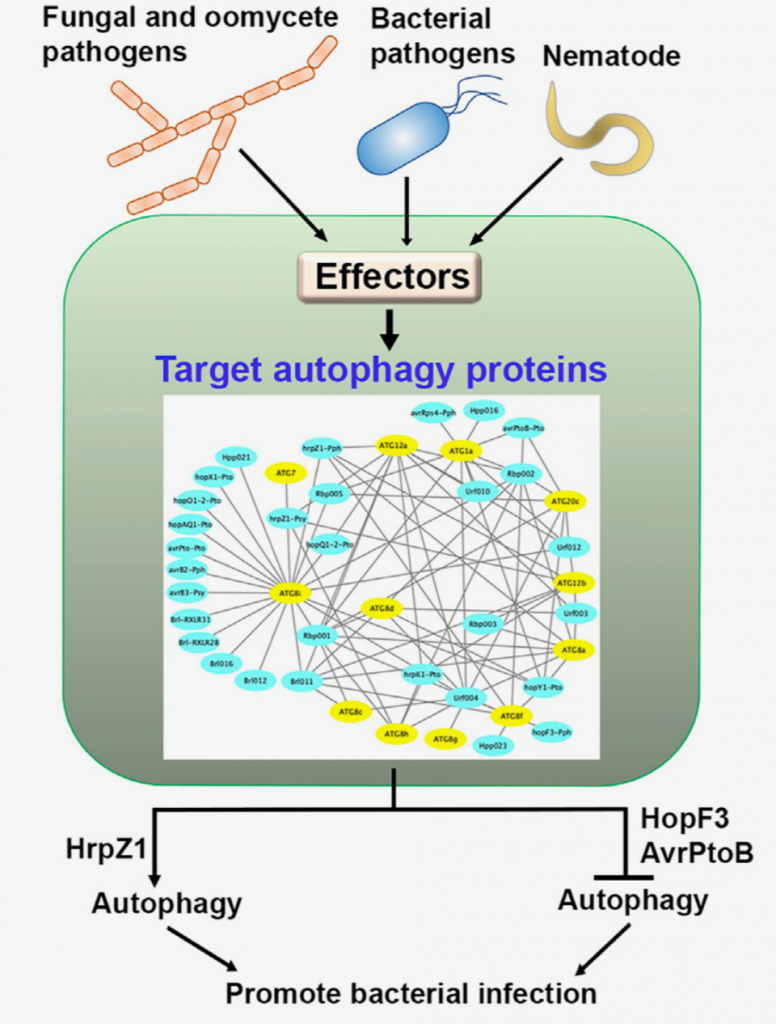
An interactome of plant autophagy proteins and pathogen effectors (Cell Host Microbe) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAutophagy is a regulated process whereby select cytoplasmic components are degraded. It is involved in a variety of biological processes, including defense against pathogens. As such, plant pathogens have evolved mechanisms to target host autophagy machinery to gain virulence. However, we still lack…
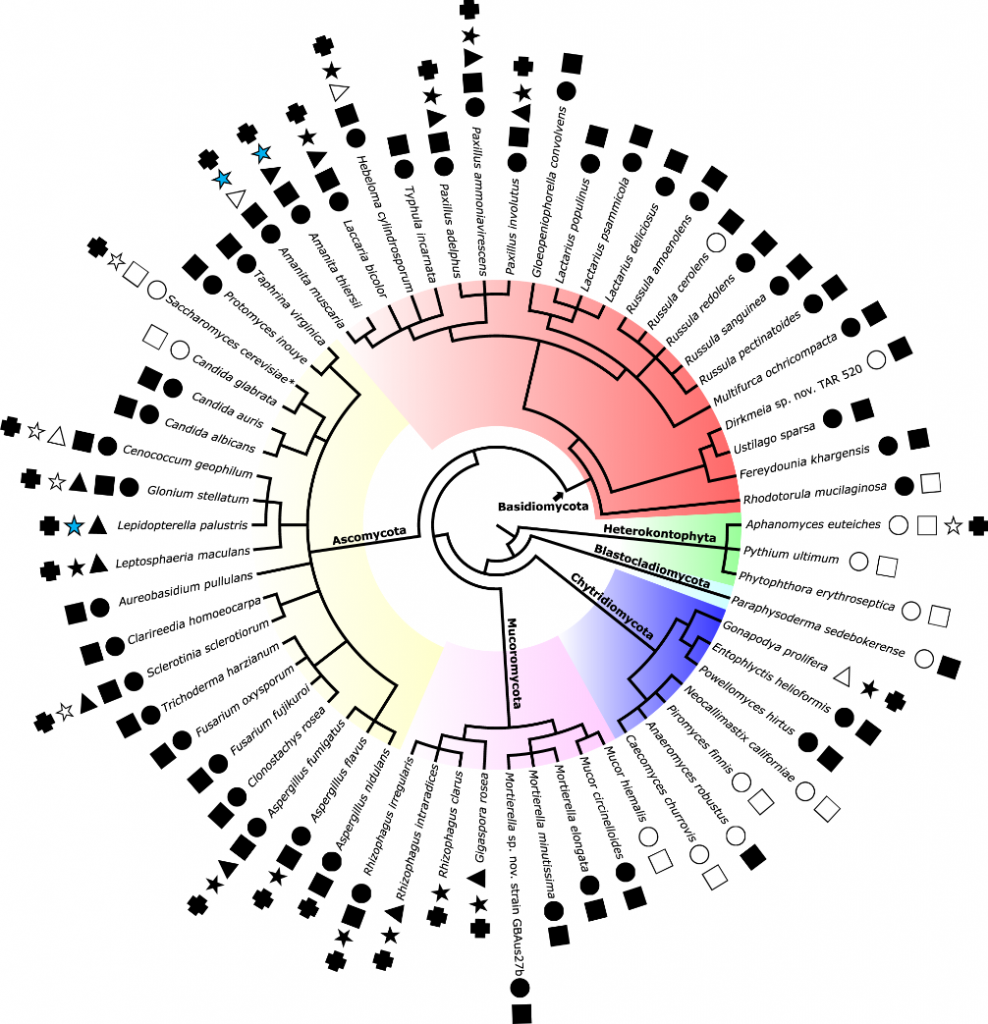
Lipo-chitooligosaccharides as regulatory signals of fungal growth and development (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyDuring symbiosis, the rhizobia bacteria rely on their lipo-chitooligosachharide signals (LCOs) to associate with plants. This signal is perceived by plant receptor like kinase, LysM-containing receptors which activate the common symbiosis signaling pathway (CSSM). Fungal symbiosis with plants has also…
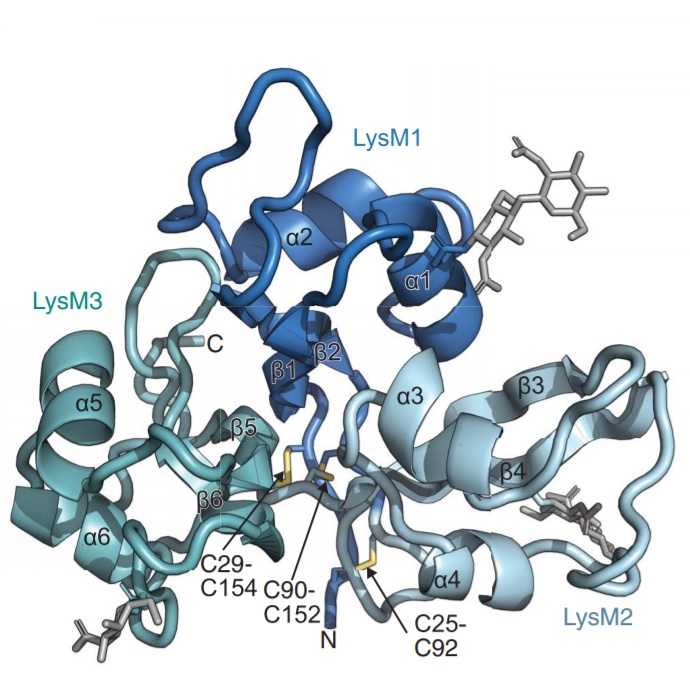
Friend vs. foe: molecular insight towards microbial recognition and specificity in legume signaling (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyEcosystems are founded by relationships between organisms, such as the mutualism between plants and microbes. An example is the agriculturally important symbiosis between legumes and nitrogen-fixing bacteria that reside in nodules of legumes. Legumes must be able to differentiate, through undetermined…

