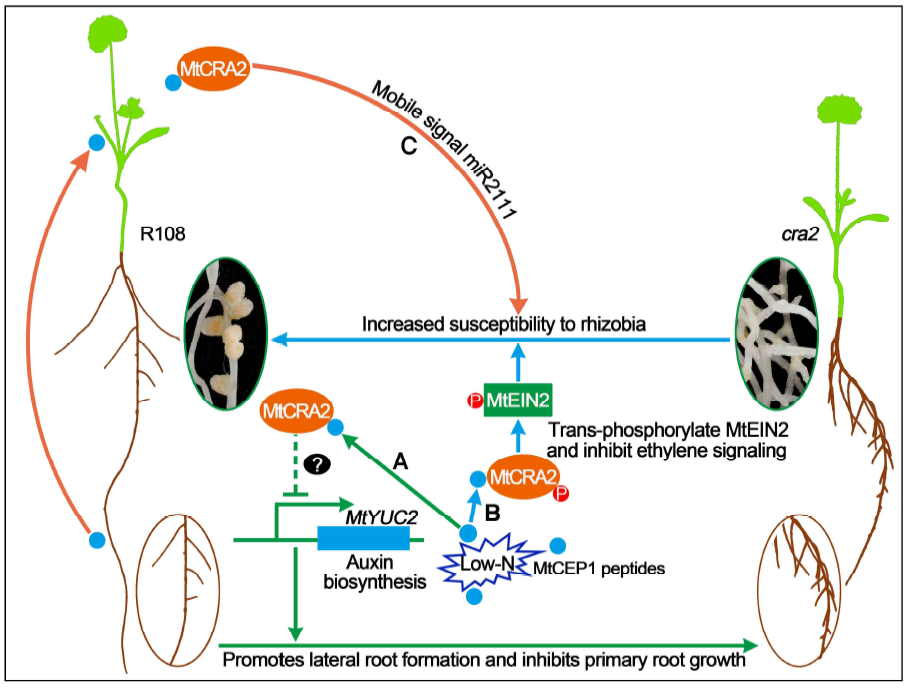
A CEP Peptide receptor-like kinase regulates root growth and symbiotic nodulation (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyUnder low N condition, plants form more lateral roots to facilitate N-uptake efficiency, and legumes such as Medicago truncatula develop more nodules to fulfill plant nitrogen requirements. Since both lateral root formation and nodulation are energy-consuming processes, plants balance these developmental…
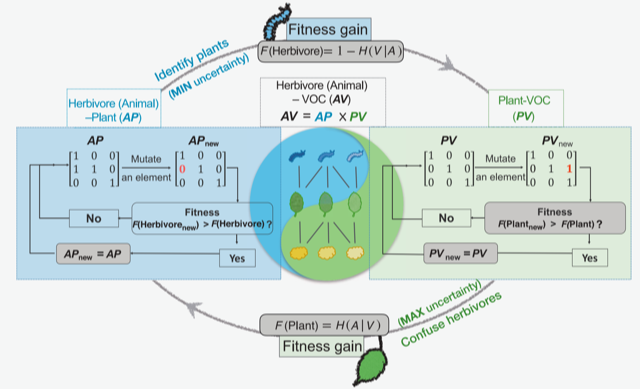
Plant-herbivore chemical communication decoded (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyChemical communications between species are prevalent in nature. For instance, herbivorous insects can spot their host plants by sensing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted by plants. Despite our knowledge about interactions between individual plant and herbivore species, little is known about…
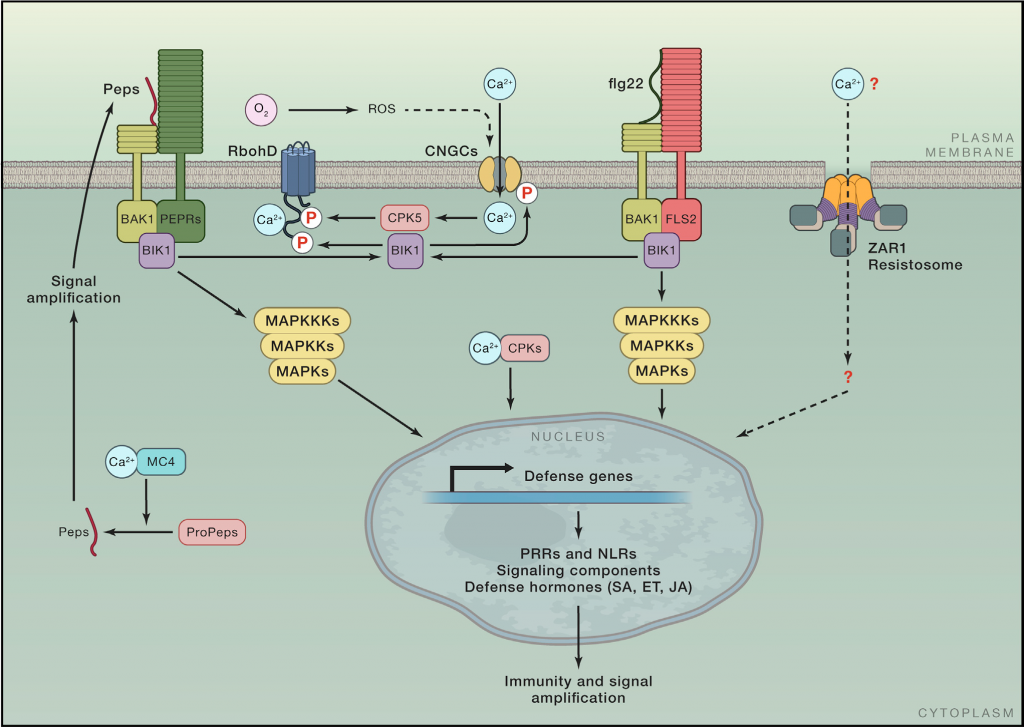
Review. Plant immunity: Danger perception and signaling (Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyResearch from the last three decades has discovered many genes and pathways involved in plant immunity and how they are connected. Here, Zhou and Zhang highlight new research regarding activation and signaling of cell surface pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) and intracellular nucleotide-binding,…
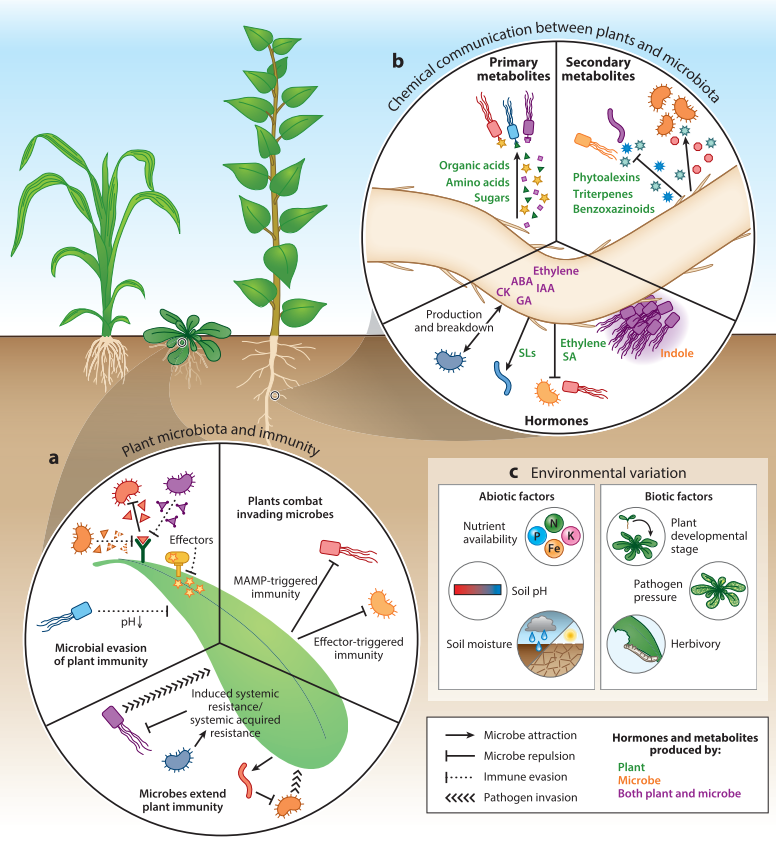
Review. The plant microbiome: From ecology to reductionism and beyond (Annu. Rev. Microbiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe last two decades have witnessed tremendous progress in our understanding of plant microbiota. Fitzpatrick, Salas-González et al. highlight recent discoveries from culture-dependent and culture-independent approaches and discuss the future path towards integrating these approaches. Culture-independent…
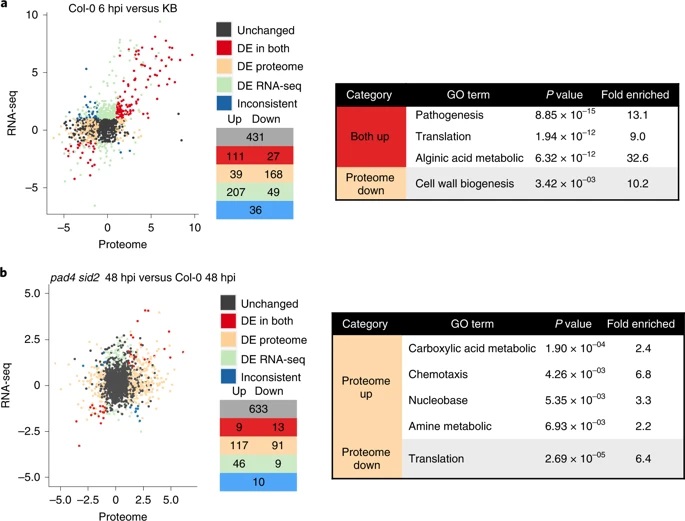
Multidimensional gene regulatory landscape of a bacterial pathogen in plants (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe outcome of a plant-bacteria interaction is determined by the bacterial virulence and plant immune systems. Individually, these systems, and to an extent their interactions, have been well studied. However, certain aspects of their interactions remain elusive, particularly how plant immunity affects…
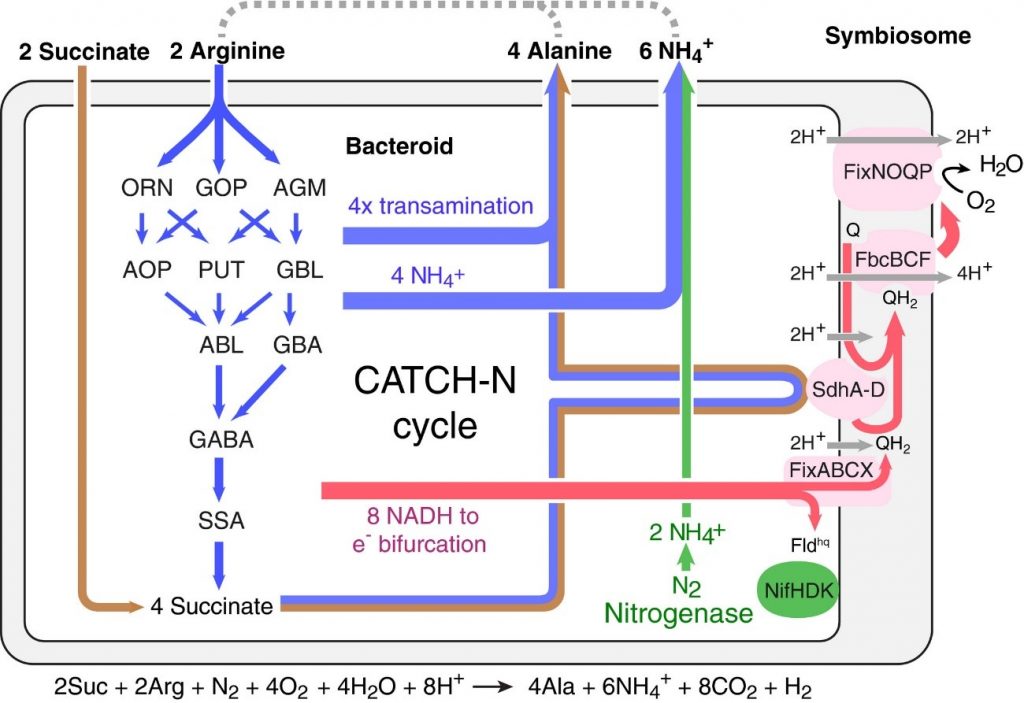
Co‐catabolism of arginine and succinate drives symbiotic nitrogen fixation (Mol Sys Biol)
Plant Science Research WeeklySymbiotic nitrogen fixation is a mutualistic relationship between plants and microbes in which plants supply fixed carbon to bacteria in exchange for nitrogen. During this process, the microbes use nitrogenase enzyme to convert atmospheric nitrogen into a plant-usable form, but the metabolic interaction…
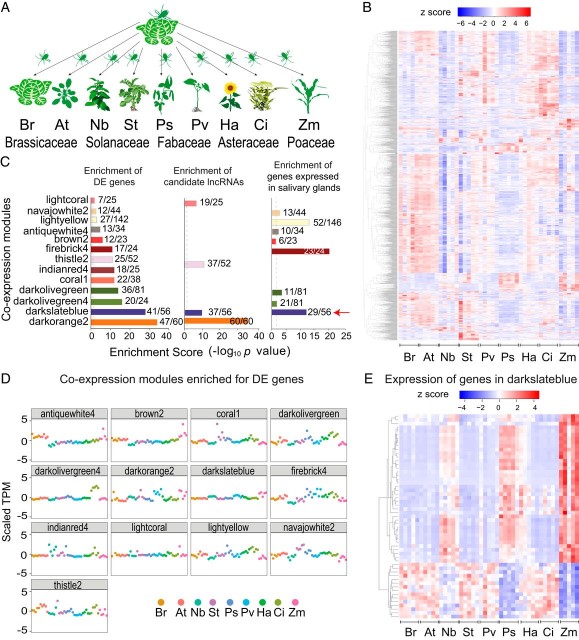
An aphid RNA transcript migrates systemically within plants and is a virulence factor (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAphids are an important insect pest that can cause significant yield loss to crops, particularly through feeding damage and as vector for devasting plant pathogens. How aphids and other sap-feeding insects use their stylet to penetrate the plant vascular tissues is well studied but the factors involved…
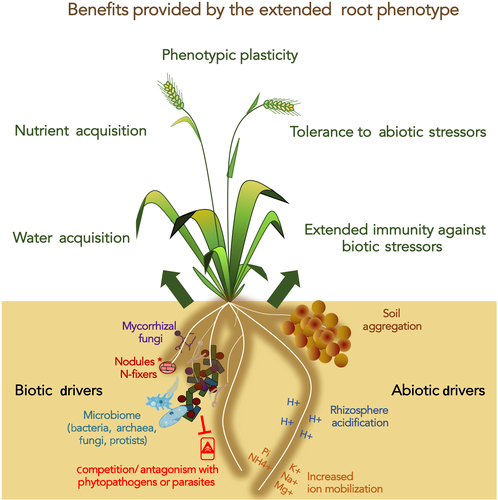
Review: An extended root phenotype: the rhizosphere, its formation and impacts on plant fitness (Plant J.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe rhizosphere is a continuous space for microbial colonization that comprises the rhizospheric soil, the rhizoplane (root surface), and the root endosphere, which is the apoplastic space in the root cortex. It is inhabited by unique populations of microorganisms, influenced by plant genotype and the…
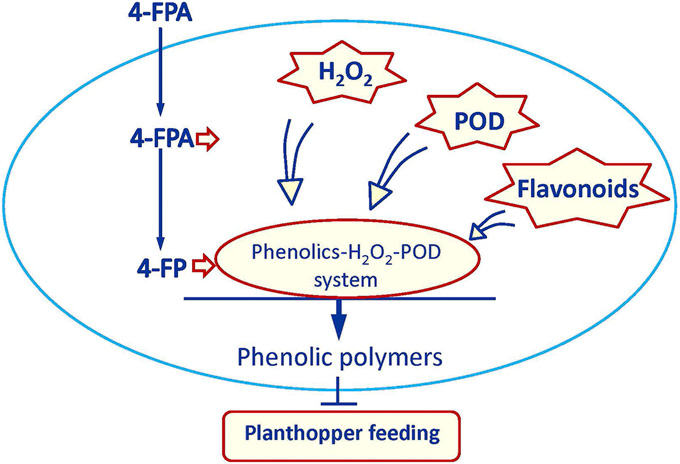
A chemical elicitor, 4- fluorophenoxyacetic acid suppresses insect pest populations and increases crop yields (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant strengtheners, synthetic chemical elicitors, have been shown to enhance plant resistance against various insect pests without toxic effects on the environment, but evidence is lacking for a significant increase in crop growth and yield after using these elicitors. To address this, Wang et al. studied…

