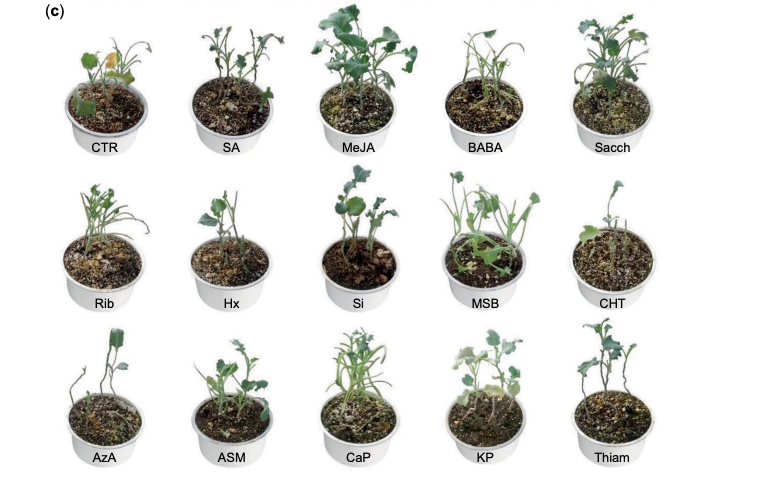

Induced tolerance to abiotic and biotic stresses of broccoli and Arabidopsis after treatment with elicitor molecules (Sci. Rep.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant hormones such as jasmonates (JAs) and salicylic acid (SA) are known for their role in regulating plant growth under both abiotic and biotic stresses. These hormones, which are synthesized within the plant, can modulate cellular processes in targeted cells locally and can be moved to other parts…
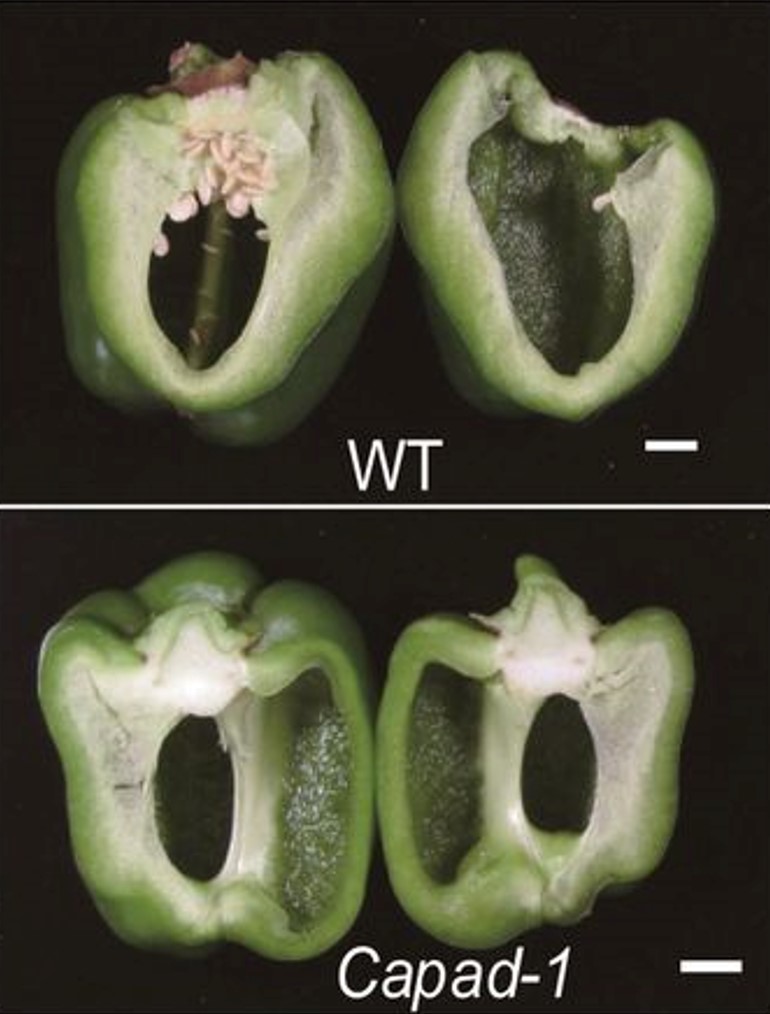
A gene knock-out that leads to seedless parthenocarpic fruits in Solanaceae plants ($) (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyParthenocarpy, or the ability to make fruit without fertilization, is desirable for many reasons including the opportunity to make seedless fruits and a greater resiliency in crop production in the face of climate change. Matsuo et al. identified a new gene involved in parthenocarpy, starting with a…
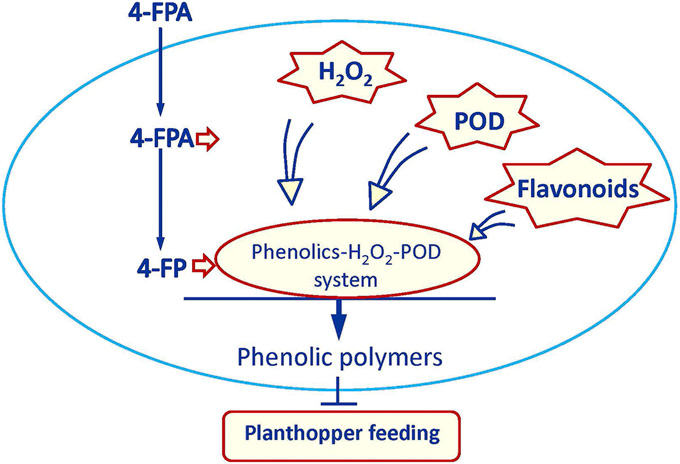
A chemical elicitor, 4- fluorophenoxyacetic acid suppresses insect pest populations and increases crop yields (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant strengtheners, synthetic chemical elicitors, have been shown to enhance plant resistance against various insect pests without toxic effects on the environment, but evidence is lacking for a significant increase in crop growth and yield after using these elicitors. To address this, Wang et al. studied…
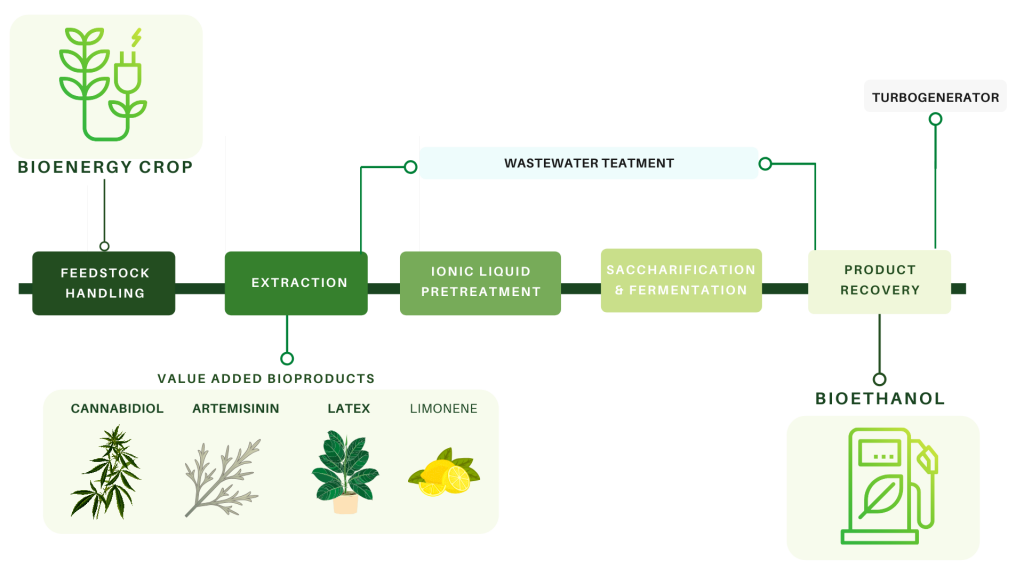
Accumulation of high value bioproducts in planta can improve the economics of advanced biofuels (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyBiofuels can be obtained from bioenergy crops such as sorghum, maize and sugarcane. However, the production of bioethanol is still more expensive than that of petroleum. Given the importance of replacing conventional fossil fuels with renewable liquid fuels, the biorefinery system should be improved…
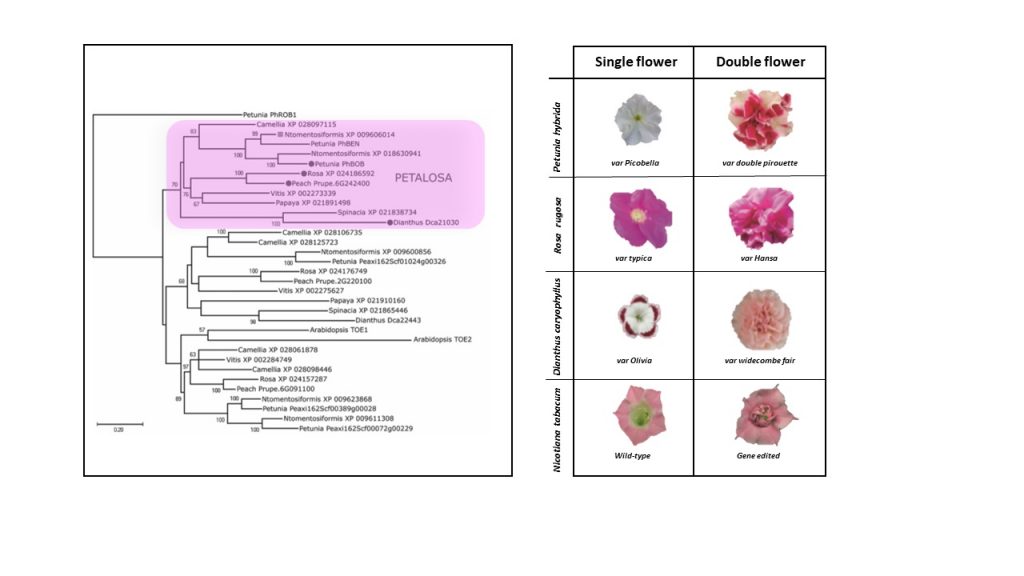
Mutations PETALOSA cause a dominant double-flower phenotype (J. Exp. Bot.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyFlower development has always been a fascinating field of research in plant biology. While molecular studies in the past focused on regulatory genes involved in the formation of floral organs in model species, current investigations are addressing the genetic determinants underlying the huge variety…
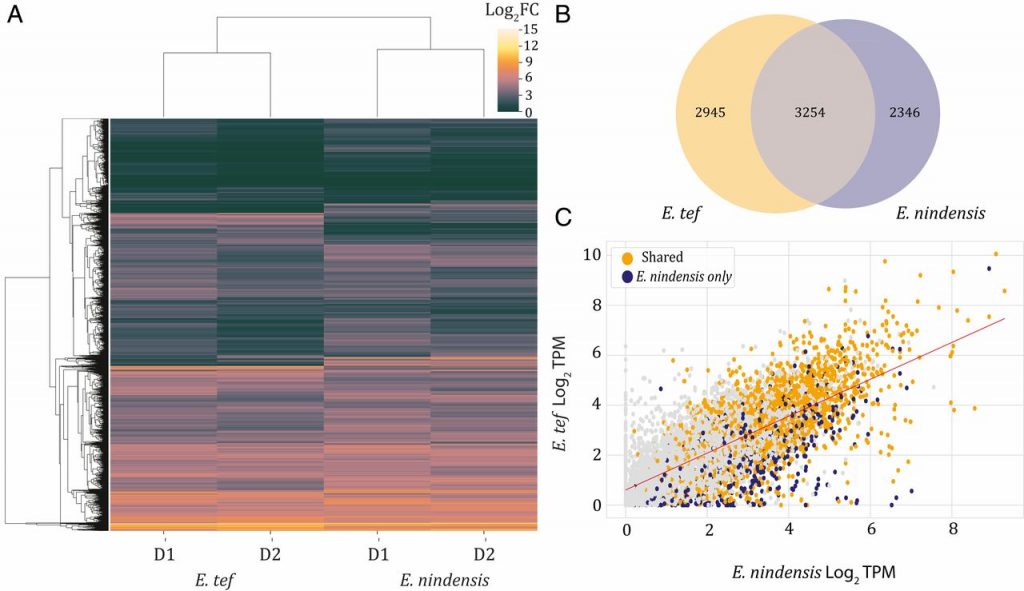
Intertwined signatures of desiccation and drought tolerance in grasses (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyDesiccation tolerance (i.e., the capacity of surviving with very low water content) is widespread in seeds and pollen, but quite rare in vegetative organs. Most authors agree that in angiosperms it originated multiple independent times from rewiring seed desiccation tolerance pathways. Here, Pardo et…
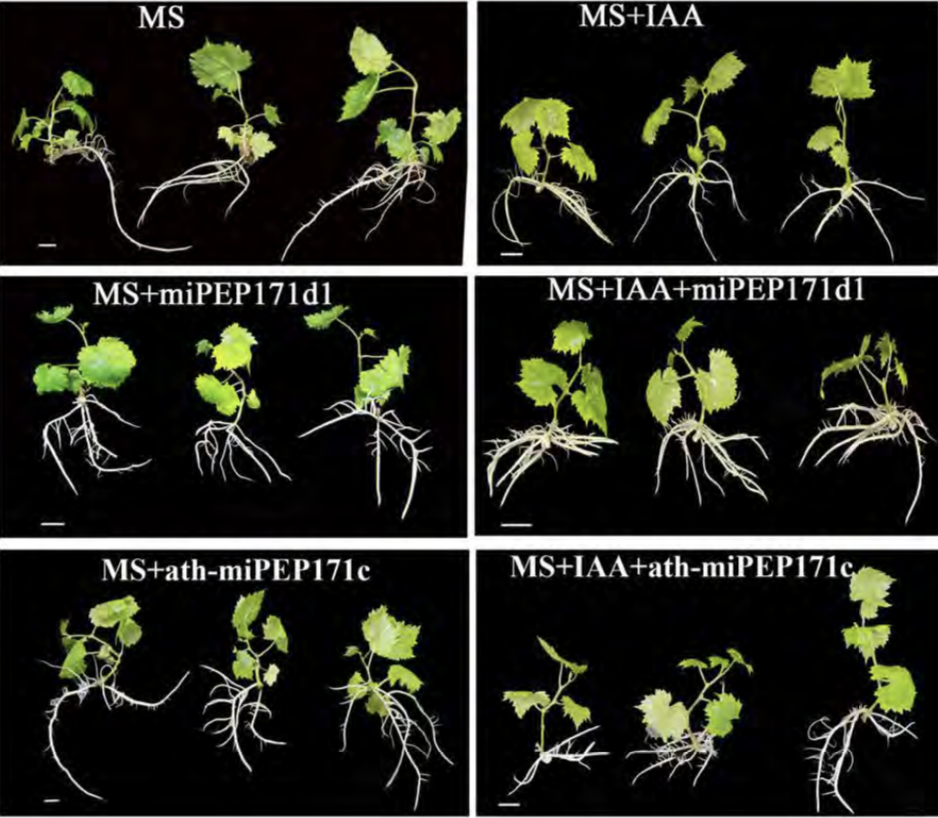
Mystery of adventitious root formation in grapevine (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyGrapevines (Vitis vinifera L.) are clonally propagated by stem cuttings, which depends on the formation of adventitious (stem-borne) roots. In this paper Chen at al., showed the function of microRNA encoded peptides (miPEPs) in adventitious root formation of cultured grape plantlets. MicroRNA biogenesis…
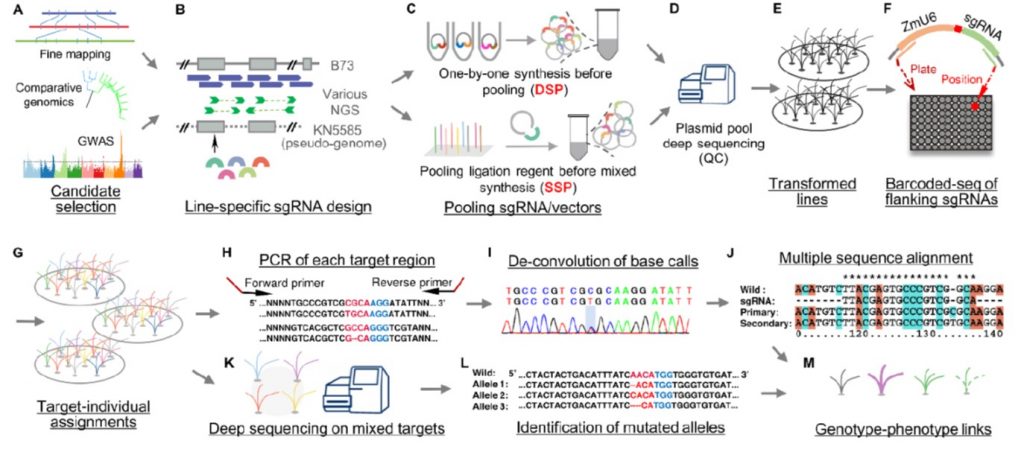
High-throughput CRISPR/Cas9 mutagenesis streamlines trait gene identification in maize (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMaize has provided some fascinating mutants and developmental insights, but its genomic complexity has made it more difficult (for example as compared to rice) to identify agronomically important genes. Liu et al. describe a new high-throughput method to integrate forward- and reverse-genetics to identify…

Base-editing-mediated artificial evolution of OsALS1 in planta to develop novel herbicide-tolerant rice germplasms (Mol. Plant)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe trait of herbicide tolerance allows farmers to use chemical means to eliminate weed competitors. Acetolactate synthase (ALS) is an enzyme targeted by more than 50 different herbicides. In order to generate novel herbicide tolerance traits, Kuang et al. used a base-editing artificial evolution approach,…

