
Low Phytate Rice Grains
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research0 Comments
/
Phosphorus (P) is an important macronutrient for crop productivity. In cereal crops like rice, about 60-85% of total plant P is allocated to grains and therefore removed from fields at harvest. Furthermore, the major form of P in the grains is phytate (C6H18O24P6), which cannot be digested by humans…
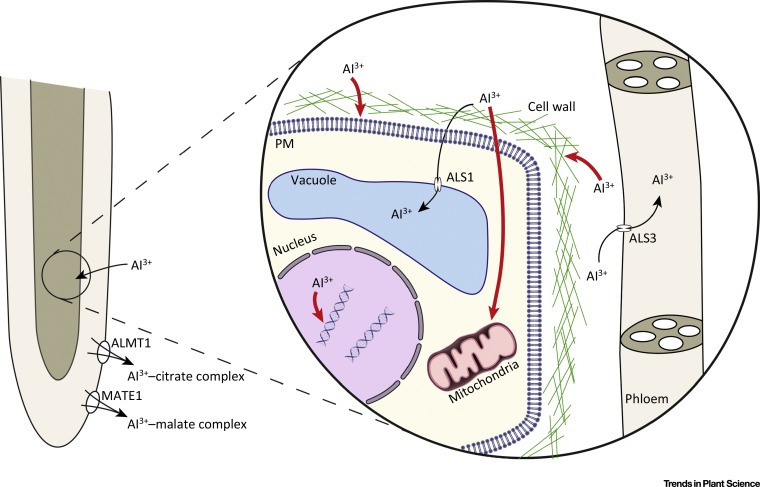
Review: DNA Checkpoints and Aluminum Tolerance ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchAluminum (Al) toxicity is an important agricultural problem, limiting crop production globally. Al toxicity causes a reduction in nutrient uptake, resulting in nutritional deficiency and leading to an overall reduction in shoot biomass and crop yield. Eekhout et al. discuss Al toxicity and strategies…

Effect of selective logging on recovery of stored carbon in Amazonian forests
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe Amazon rainforest stores 30% of land-based ecosystem carbon. How are carbon stores affected by selective tree removal and subsequent regrowth? Stored carbon continues to be lost for several years after logging due to damage-associated mortality of surviving trees. Piponoit et al. use data from more…
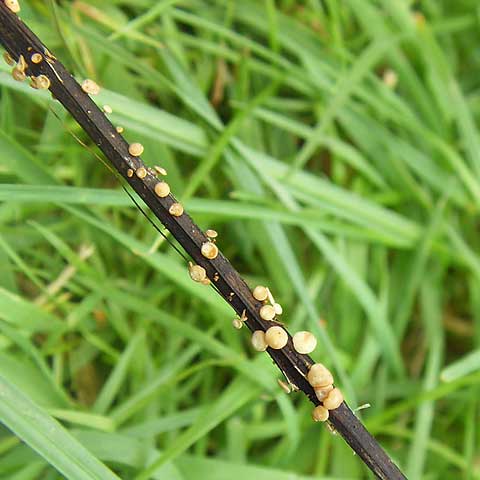

Review: Impacts of fungal hitchhikers on biosecurity
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchWhen a plant species is introduced to a new region, it brings with it “hitchhikers” – other associated organisms. Sometimes, these hitchhikers negatively impact the environment into which they are introduced, for example by facilitating the host’s invasiveness, or through direct detrimental effects…
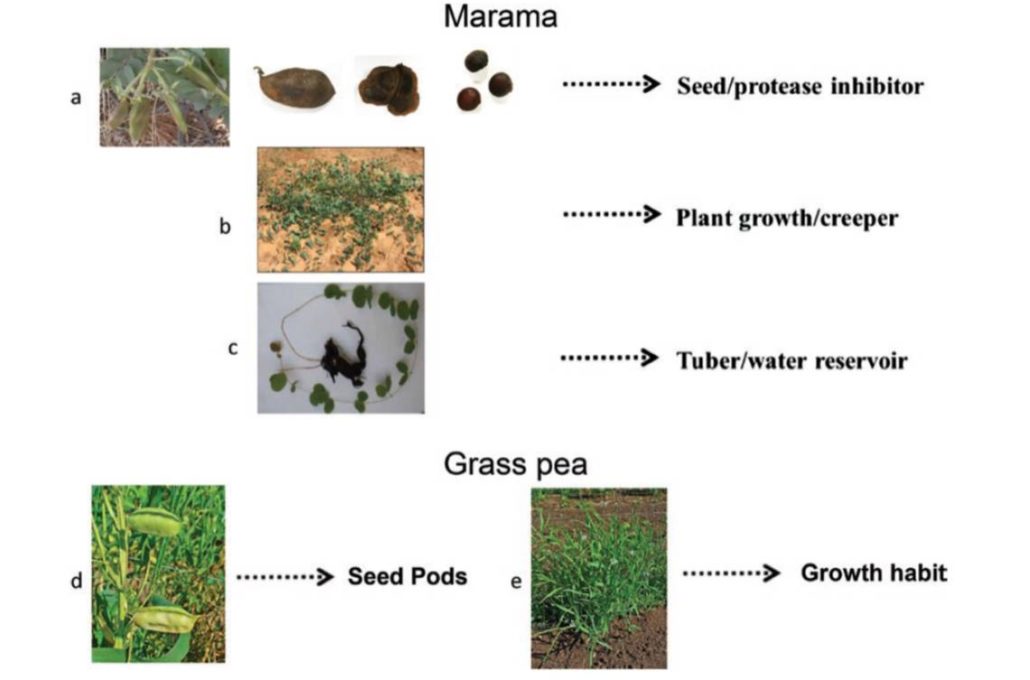

Review: Unlocking the potential of orphan legumes ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchOrphan legumes, which include cowpea (Vigna unguiculata), Bambara groundnut (V. subterranea), grass pea (Lathyrus sativus) and marama bean (Tylosema esculentum), are important food sources for many farmers, but have largely been ignored by breeders and industry. Cullis and Kunert argue that some of these…

Comment: Protecting the origins of coffee
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchCoffee is a hugely popular beverage and contributes immeasurably to human productivity, but demand has risen by 50% in the past 20 years while coffee production is vulnerable to disease and climate change. Mehrabi and Lashermes observe that the popular arabica coffee comes from the plant Coffea arabica,…

Genome sequence and genetic diversity of European ash trees
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchAsh dieback (a fungal disease) and the beetle Agrilus planipennis (a herbivore) are crushing ash tree populations in the Northern Hemisphere. To shed light on the genetic basis of the trees' susceptibility and to understand the genetic diversity of these trees, Sollars et al. have sequenced one individual…
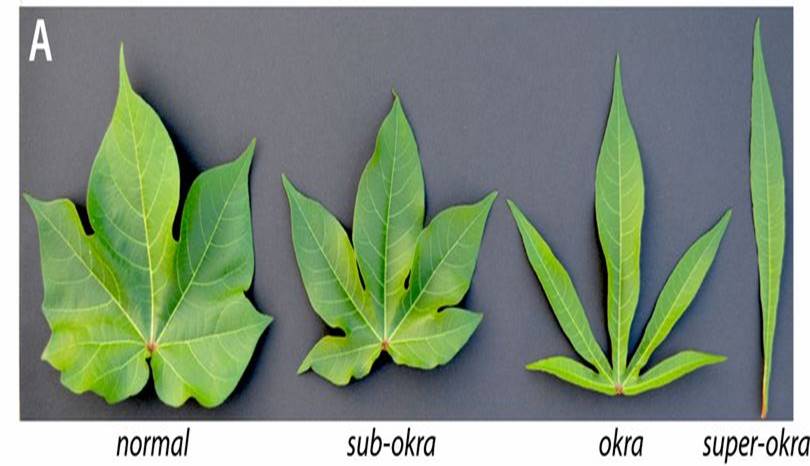
Homeodomain protein underpins leaf shape variation in cotton ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchHomeodomain transcription factors are well-known as regulators of developmental patterning, including in leaves. Andres et al. examine the molecular basis behind leaf shape in cotton, particularly the Okra locus that was identified by breeders as a regulator of leaf shape. They show that the Okra locus…

Domestication impacts on plant–herbivore interactions: a meta-analysis
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchIt is widely stated that domestication has contributed to a decrease in plant resistance to herbivory, but to what extent is this true? In a contribution to a special issue on “Human influences on evolution”, Whitehead et al. describe results of their meta-analysis. Although their data show a consistent…

