
Review: The challenges of delivering genetically modified crops with nutritional enhancement traits (Nature Plants) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyDespite the widespread success of genetically modified (GM) crops resistant to herbicides and insect herbivory, GM food crops with nutritional enhancement traits remain on the fringes of commercial agriculture. In this review, Napier et al. examine the current state of GM food crops and the obstacles…

A bifunctional dipeptide functionalizes crop surfaces for sustainable pest management (Green Chemistry)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMost synthetic pesticides do not stick well on plants especially during raining season and can be washed off during irrigation shorty after application. Therefore, the farmer may need to apply several times or hope for dry days to spray. Swinges et al. developed a synthetic peptide with two separate…
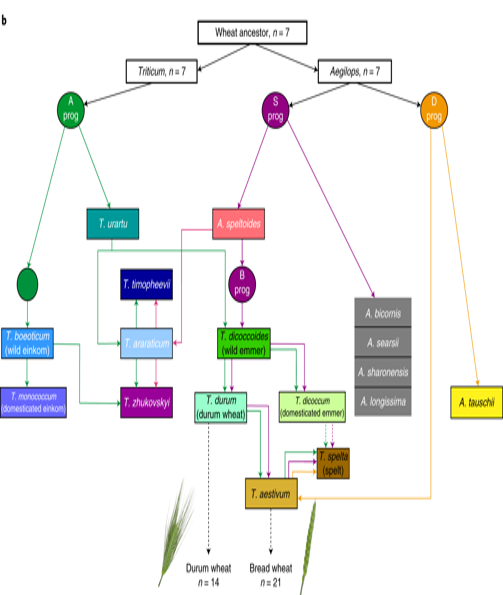
Wheat exome sequencing and wheat ancestry (Nature Genetics)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWheat is of course a hugely important food for humans, and has been selectively bred across the globe for millennia. Modern bread wheats are hexaploid and contain three distinct subgenomes (AABBDD). As with other crops, there is a need to understand wheat’s ancestry and explore the greater genetic…

Linking CRISPR-Cas9 interference in cassava to the evolution of editing-resistant geminiviruses (Genome Biol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCRISPR/Cas9 is a promising gene editing tool that has already been successfully used to modify many plant genes. In these applications, the gene editing machinery is transiently employed to make a stable genomic change which is then passed on to the progeny. A different application is to use CRISPR/Cas9…
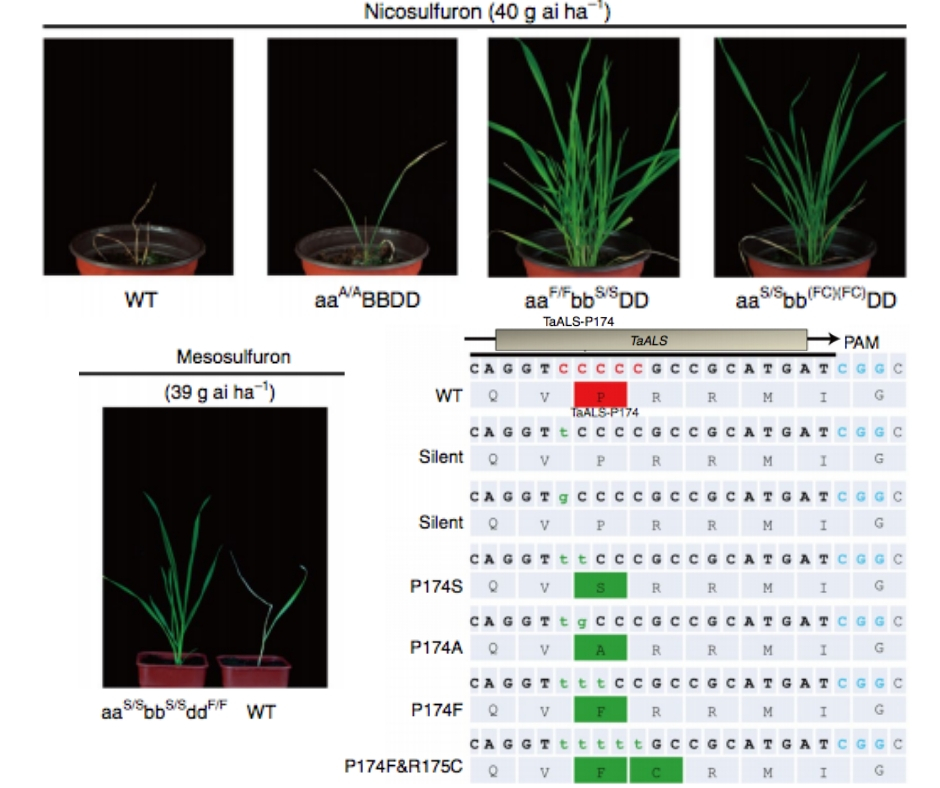
Generation of herbicide tolerance traits and a new selectable marker in wheat using base editing (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyNowadays, weeds represents a major problem to agriculture due to the limited availability and expense of tools to manage them. Using new technologies to create herbicide-tolerant, non-transgenic varieties could improve weed control. Here, Li et al. analyzed multiallelic editing of the wheat TaALS (encoding…
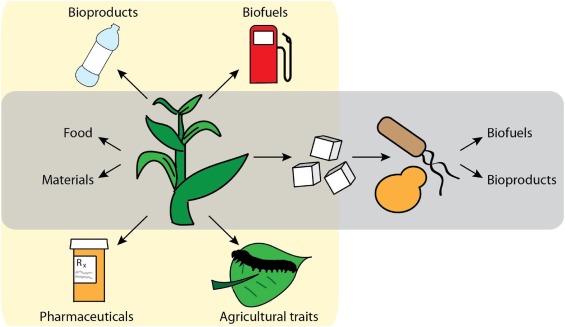
Review: Towards a sustainable bio-based economy through plant synthetic biology ($) (Plant Sci)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant synthetic biology is heating up, as ideas and methods initially developed for single-celled organisms are moving into the more interesting and complicated space of multicellular organisms; this leads to greater potentials as well as greater challenges. Why plants? One important reason is that they…
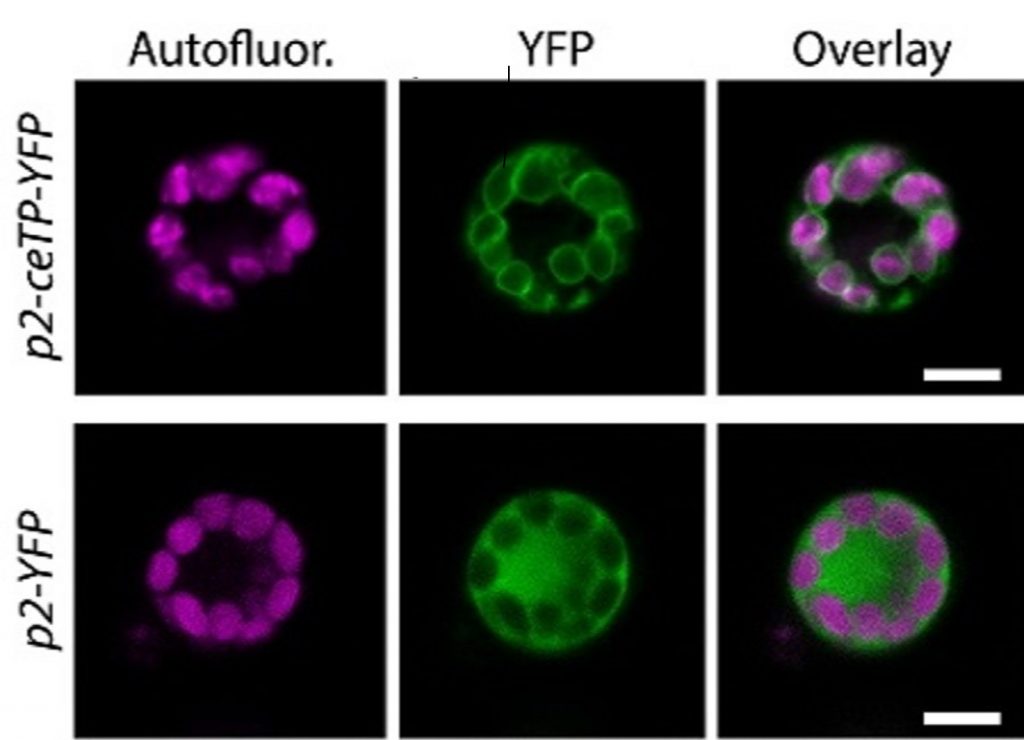
A high‐throughput transient expression system for rice (Plant Cell Environ)
Plant Science Research WeeklyTransient expression platforms allow short-term expression of candidate genes in the host plant, without the integration of DNA into the host genome. The expression cassettes are delivered to the host cells either by Agrobacterium- or microprojectile-mediated approaches. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation…
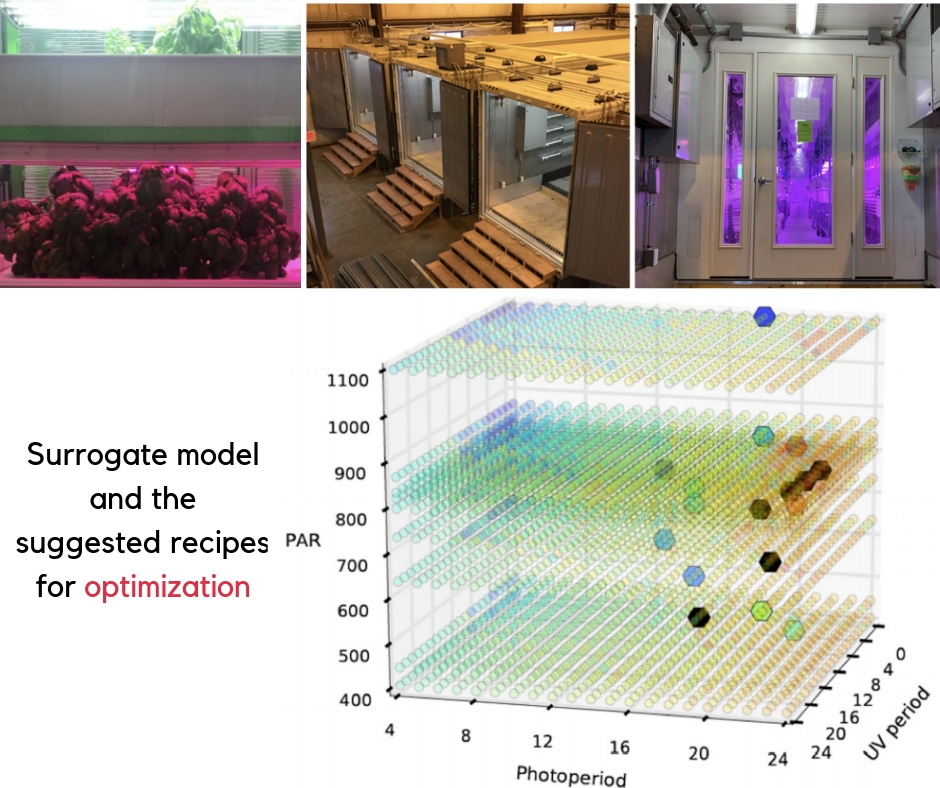
Flavor-cyber-agriculture: Metabolite optimization through surrogate modeling (PLOS One)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCyber-agriculture is a computer-controlled plant growing environment which regulates climatic conditions through machine learning, finding optimized variables (“recipes”) to maximize a specific plant trait. Here, Johnson et al. applied cyber-agriculture to chemotype optimization for flavor in basil…
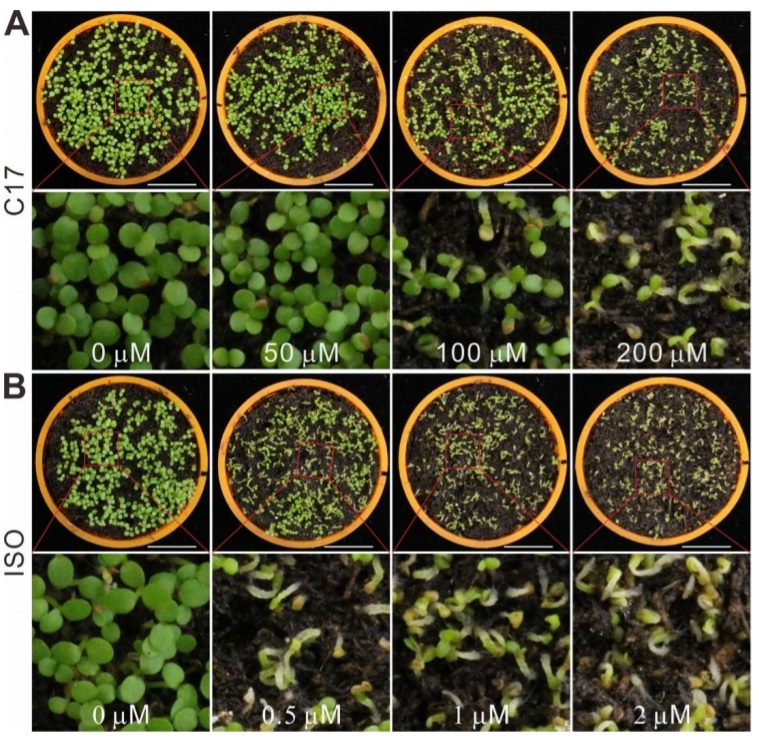
Generating novel, dual herbicide-resistant crops using CRISPR-mediated gene editing (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThere is an ever-growing need for novel herbicides as more weeds are becoming resistant to commonly used herbicides. In a recent report from Hu et al., the authors identified that a previously described cellulose biosynthesis-inhibiting chemical, C17, possesses an herbicidal quality. The authors showed…

