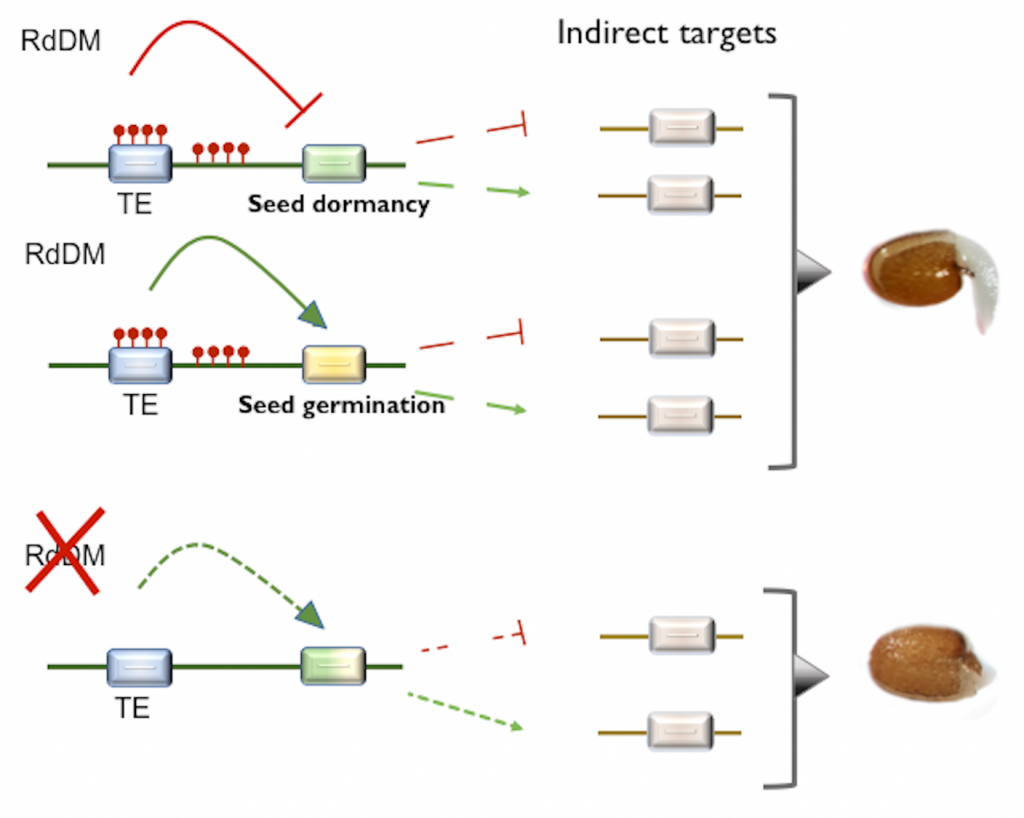
The canonical RdDM pathway mediates the control of seed germination timing under salinity ($) (Plant J.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe canonical RdDM pathway mediates the control of seed germination timing under salinity ($)
Epigenetic regulation can ensure that plant developmental programs and stress responses are tightly coordinated so that environmental changes do not compromise plant fitness. One of the mechanisms to achieve…
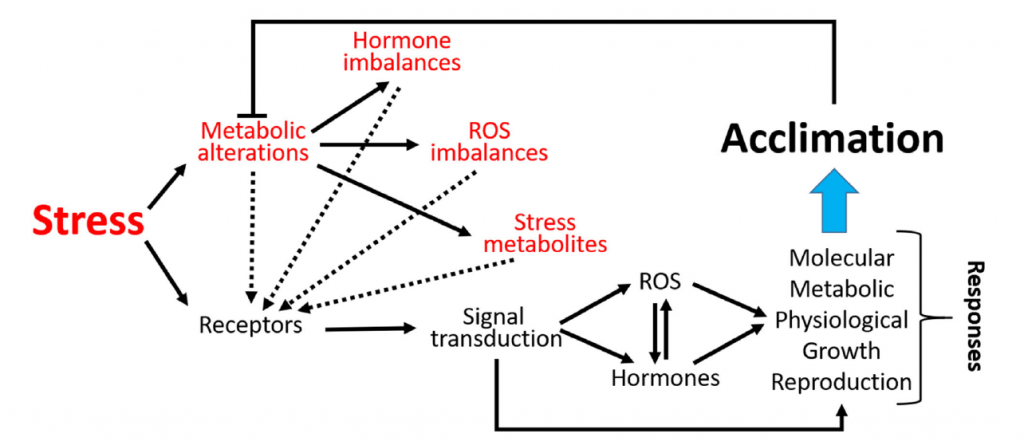
Review: Integration of reactive oxygen species and hormone signaling during abiotic stress (Plant J.)
Plant Science Research Weekly
During its life cycle, a plant experiences many types of abiotic stress including drought. While waiting for the next drops of water, a thirsty plant acclimates by initiating a series of tolerance responses. Stress perception is followed by stress-induced signaling which can include reactive oxygen…
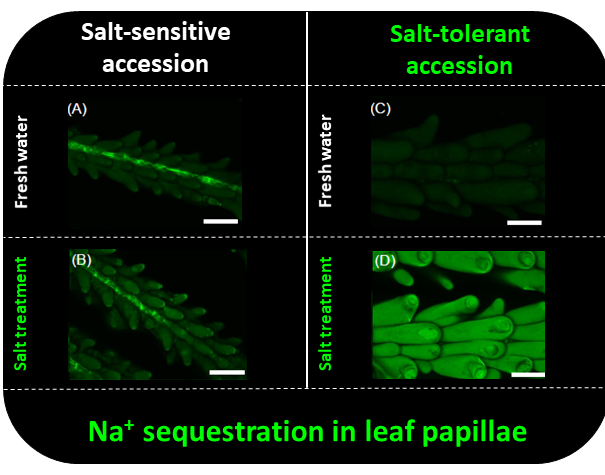
The halophyte seashore paspalum uses adaxial leaf papillae for sodium sequestration (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyGlobal warming and intensive farming are increasing soil salinity, which is predicted to affect 30% of cultivated land by 2050. Salinity represents a major threat for agriculture as most crops drastically reduce their growth and productivity in saline environments. Understanding the strategies used by…
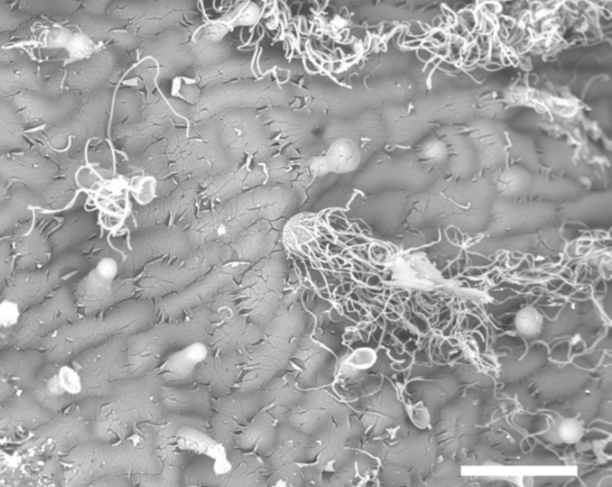
Formation of flavone-based wooly fibres by glandular trichomes of Dionysia tapetodes (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Many people are familiar with the popular houseplant Cephalocereus senilis, which also known as old man cactus because it is covered with long white hairs that are thought to protect it from frost and UV light. A similar function is described for the wooly fibers that cover the alpine plant Dionysia…
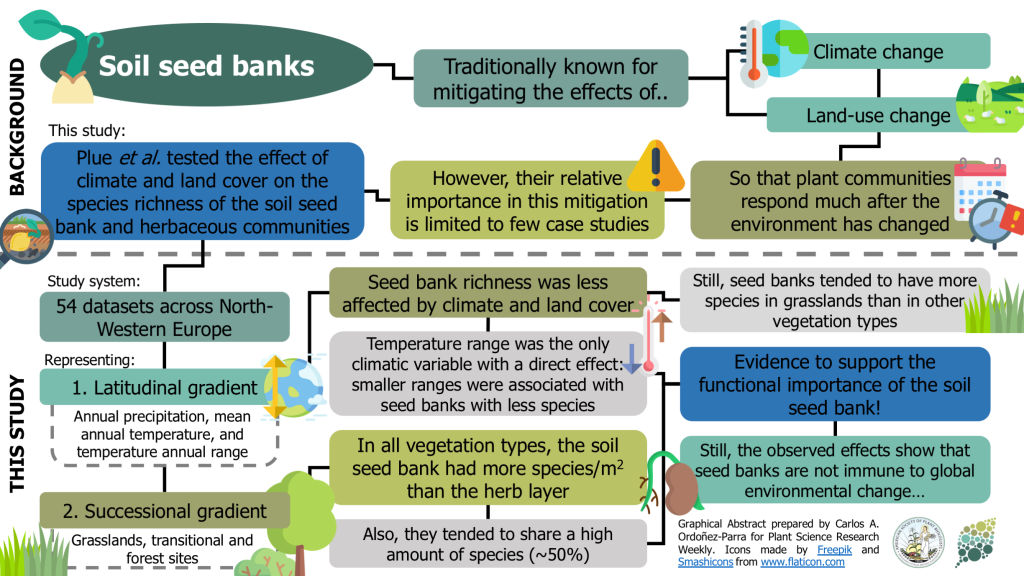
Buffering effects of soil seed banks on plant community composition in response to land use and climate (Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr.)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Plant communities seem to be able to mitigate the effects of climate and land-use change, given their responses are usually observed long after environmental conditions have changed. This lagged response has been attributed to the presence of persistent soil seed banks. Still, the evidence of their…

The genomic and transcriptomic foundations of viviparous seed development in mangroves (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklySome mangrove species are viviparous, meaning their seeds germinate while still attached to the mother plant. This behavior is thought to facilitate seedling establishment in the tropical and subtropical intertidal zones they inhabit. However, the genetic and molecular mechanism behind it remains to…
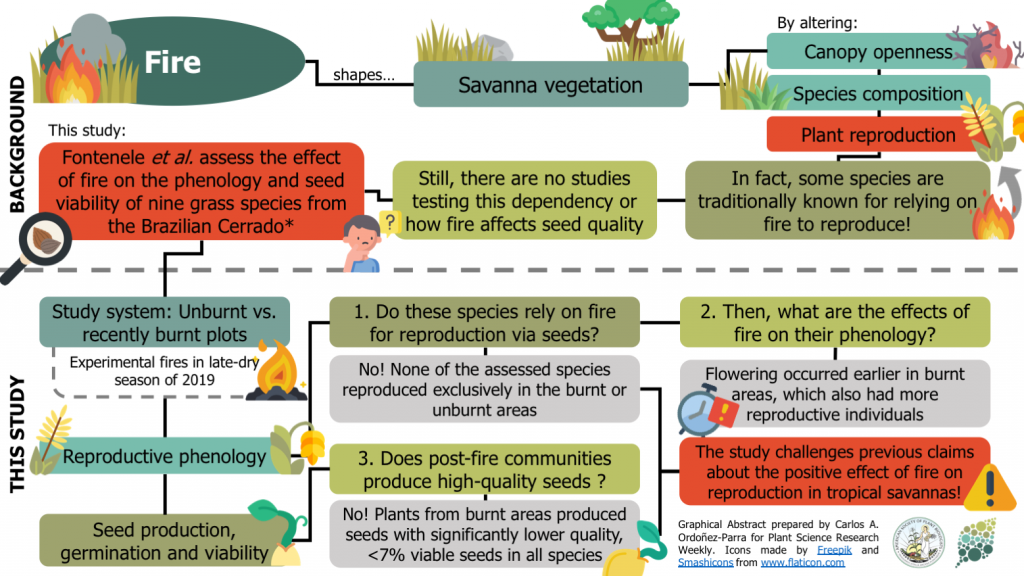
Burning grasses, poor seeds: Post-fire reproduction of early-flowering Neotropical savanna grasses produces low-quality seeds (Plant Ecol.) ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Fire is a disturbance that underpins several ecological processes in tropical savannas. For instance, some plant species from these ecosystems are traditionally known for relying on fires to reproduce. However, this dependency remains to be formally tested. Also, the impact of fire on seed quality…

Seed germination of mudflat species responds differently to prior exposure to hypoxic (flooded) environments (Seed Sci. Res.) ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Mudflats species experience rapid changes in their environment due to wetlands' drawdown and refill throughout the year. For instance, species that inhabit these sites deal with contrasting oxygen environments: hypoxic when the water level is high, and aerobic when it recedes. Most studies have aimed…
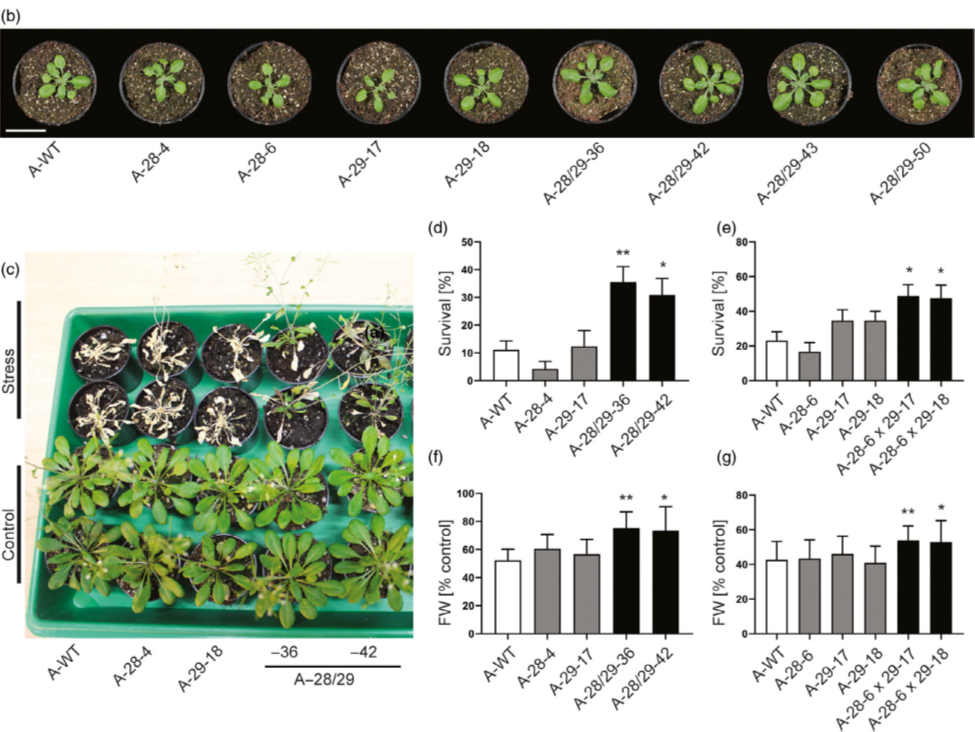
Combinatorial engineering of signaling networks for drought tolerance (Plant Biotechnol. J.)
Plant Science Research WeeklySeveral potential targets have been suggested to improve drought tolerance and water-use efficiency of crops, but many genes when upregulated can cause negative growth trade-offs. Stress recognition and signaling proteins are attractive targets as they may exert control over multiple downstream pathways…

