
Tobacco leaf tissue rapidly detoxifies direct salt loads without activation of calcium and SOS signaling (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklySalinity stress is one of the primary abiotic causes of crop loss worldwide. In roots, the early response to high salt levels is coordinated largely via the well characterized salt-overly sensitive (SOS) pathway, which is dependent on Ca2+ signaling. However, how plants cope with elevated salt levels…
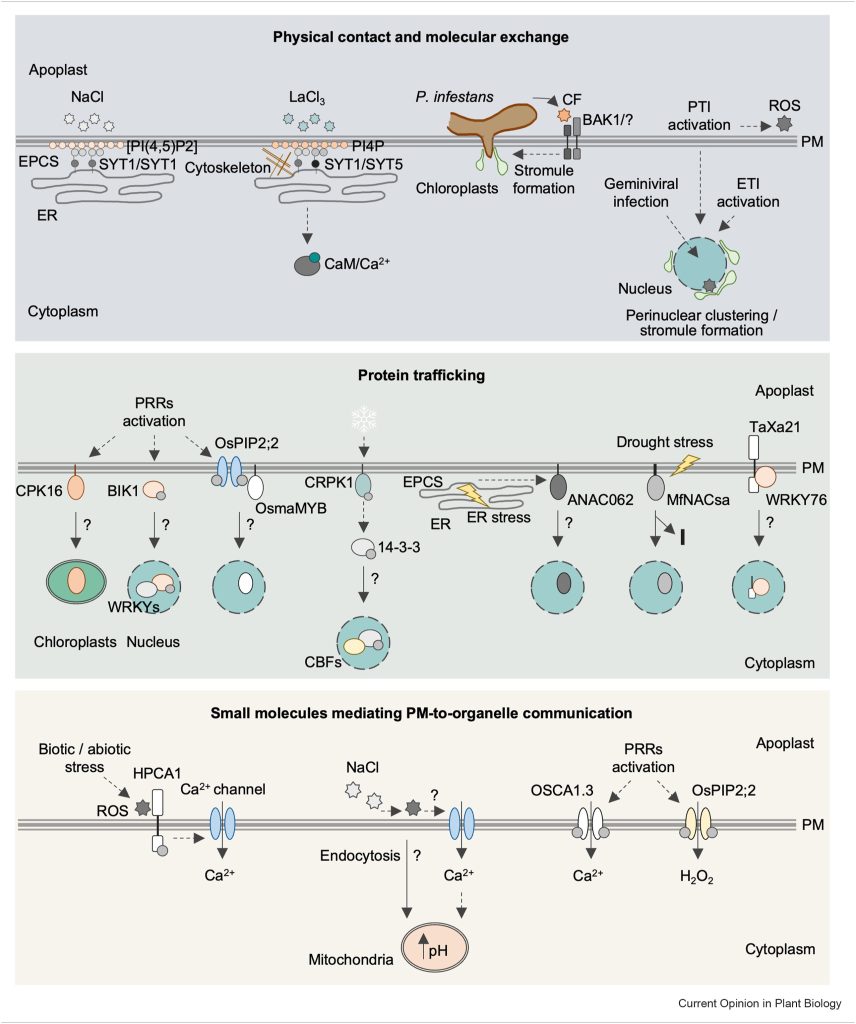
Review: Plasma membrane-to-organelle communication in plant stress signaling (Curr. Opin. Plant Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe plasma membrane (PM) is a critical interface between the cell and its environment and serves crucial sensing and transducing roles. This timely review by Medina-Puche and Lozano-Durán updates exciting new developments in understanding communication between the PM and intracellular organelles, focusing…
Increasing the resilience of plant immunity to a warming climate (Nature)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants demonstrate increased susceptibility to pathogens upon exposure to heat stress, apparently due to suppressed salicylic acid (SA) accumulation and subsequently decreased effector-triggered immunity. How exactly does heat stress cause this suppression, and how can we take advantage of genetics to…
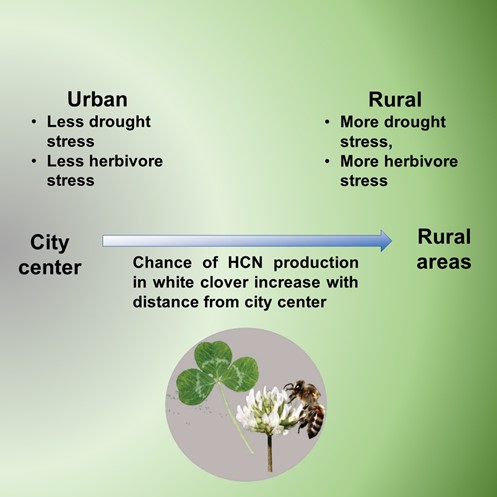
The urban environment led to unintended adaptive evolution in plants (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyGenerally, evolution is driven by natural selection, but not always. Human activities lead to the creation of unique niches, and other organisms must adapt accordingly. Cities are unique niches that are significantly different from rural areas and natural conditions. The urban habitat provides plants…
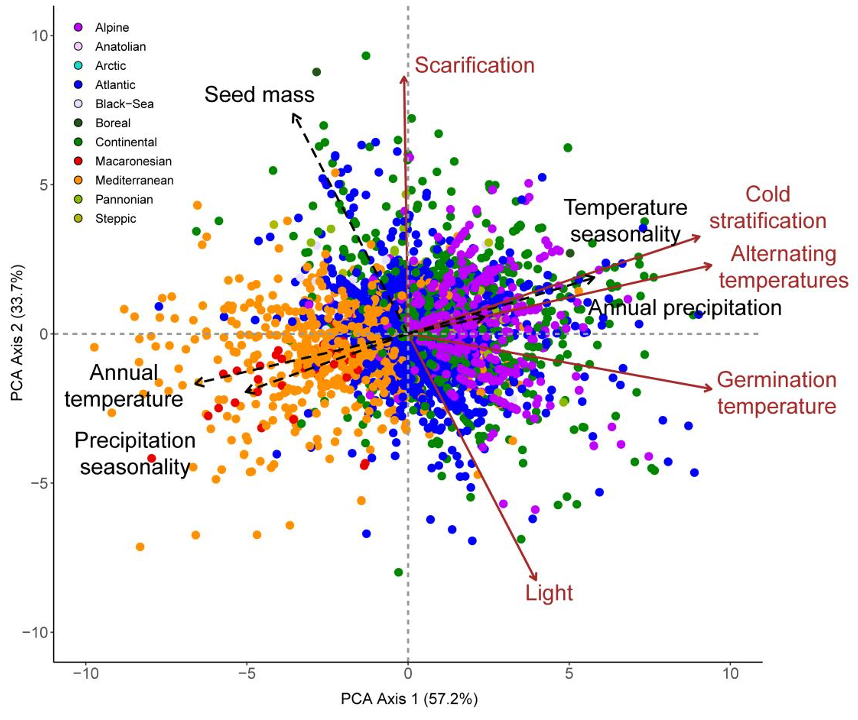
Climate shapes the seed germination niche of temperate flowering plants: a meta-analysis of European seed conservation data (Ann. Bot.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe seed germination niche is the set of environmental conditions in which a seed can germinate. This collection of requirements is expected to be tuned to the climate each species encounters in its natural habitat, but this hypothesis remains to be formally tested. Here, Carta and colleagues make use…
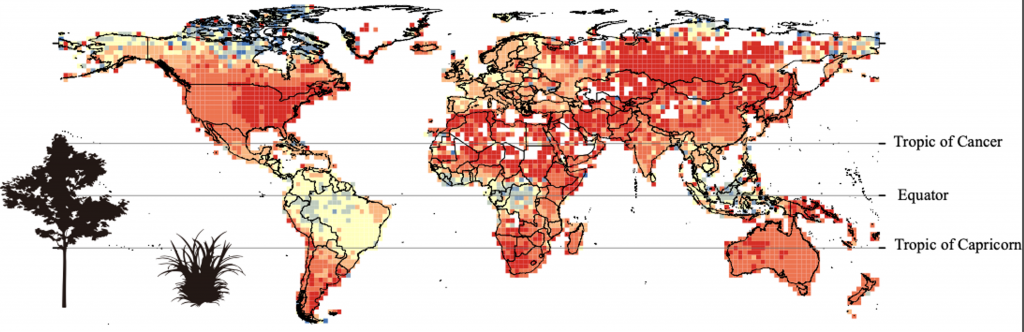
Seed dormancy in space and time: global distribution, paleo- and present climatic drivers and evolutionary adaptations ($) (New Phytol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklySeed dormancy is widely recognized as a key mechanism to ensure that germination takes place under the most suitable conditions. Such is its importance that multiple studies have described the morphological, physiological, and genetic mechanisms behind it, yet its global distribution and the past and…
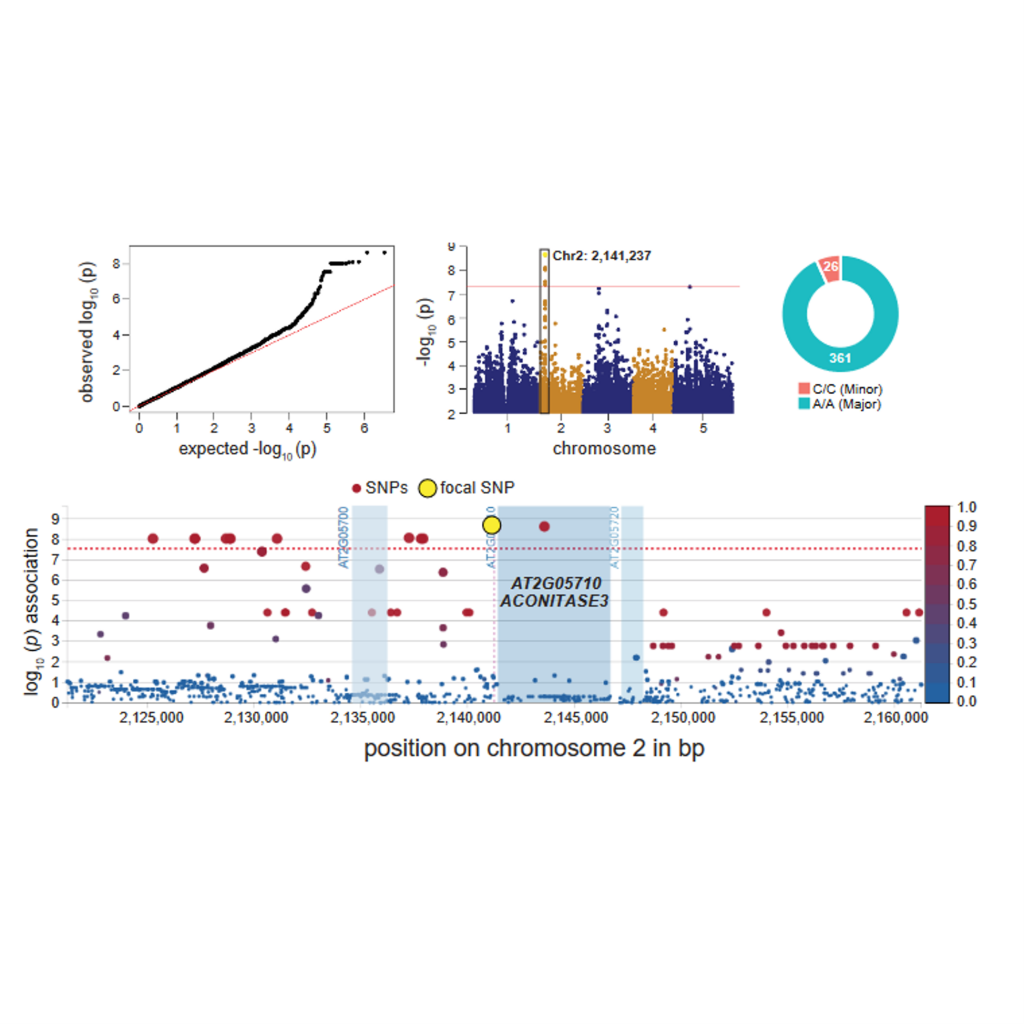
GWAS on multiple traits identifies mitochondrial ACONITASE3 as important for acclimation to submergence stress (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyClimate change is affecting the frequency and intensity of extreme climatic events such as floods, reducing crop production severely. Submergence might lead to a lack of O2, light, and carbon dioxide, having an impact on the carbohydrate content and ATP synthesis. In this work, Xiangxiang et al. characterise…
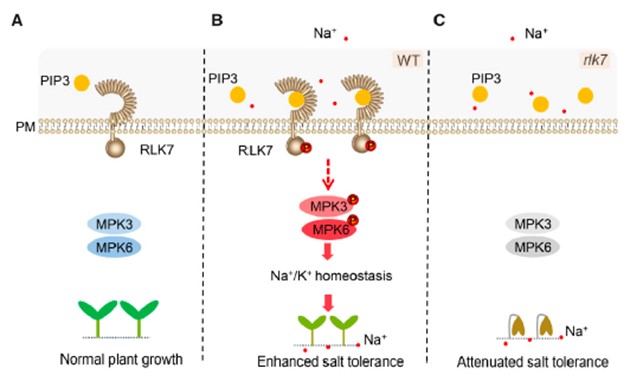
Plant salt tolerance through a peptide and receptor like kinase pathway (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklySoil salinity is a major stress that hampers plant growth, but plants have evolved signaling pathways to sense and respond to salinity. Zhou and colleagues have recently reported a novel pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana that that involves a peptide ligand, PAMP-INDUCED SECRETED PEPTIDE 3 (PIP3) and…
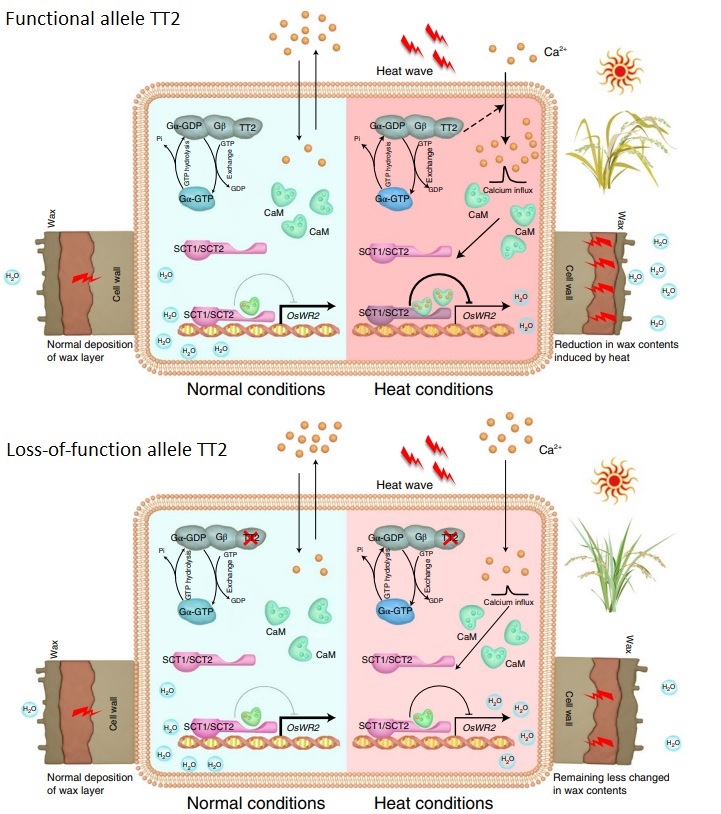
TT2 controls rice thermotolerance through SCT1-dependent alteration of wax biosynthesis (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyGlobal warming severely affects agricultural harvests, risking food security. To deal with heat stress, plants show different strategies. Indeed, heat increases intracellular Ca2+ levels to activate a heat shock response. In addition, GTP-binding proteins, which transduce extracellular signals to intracellular…

