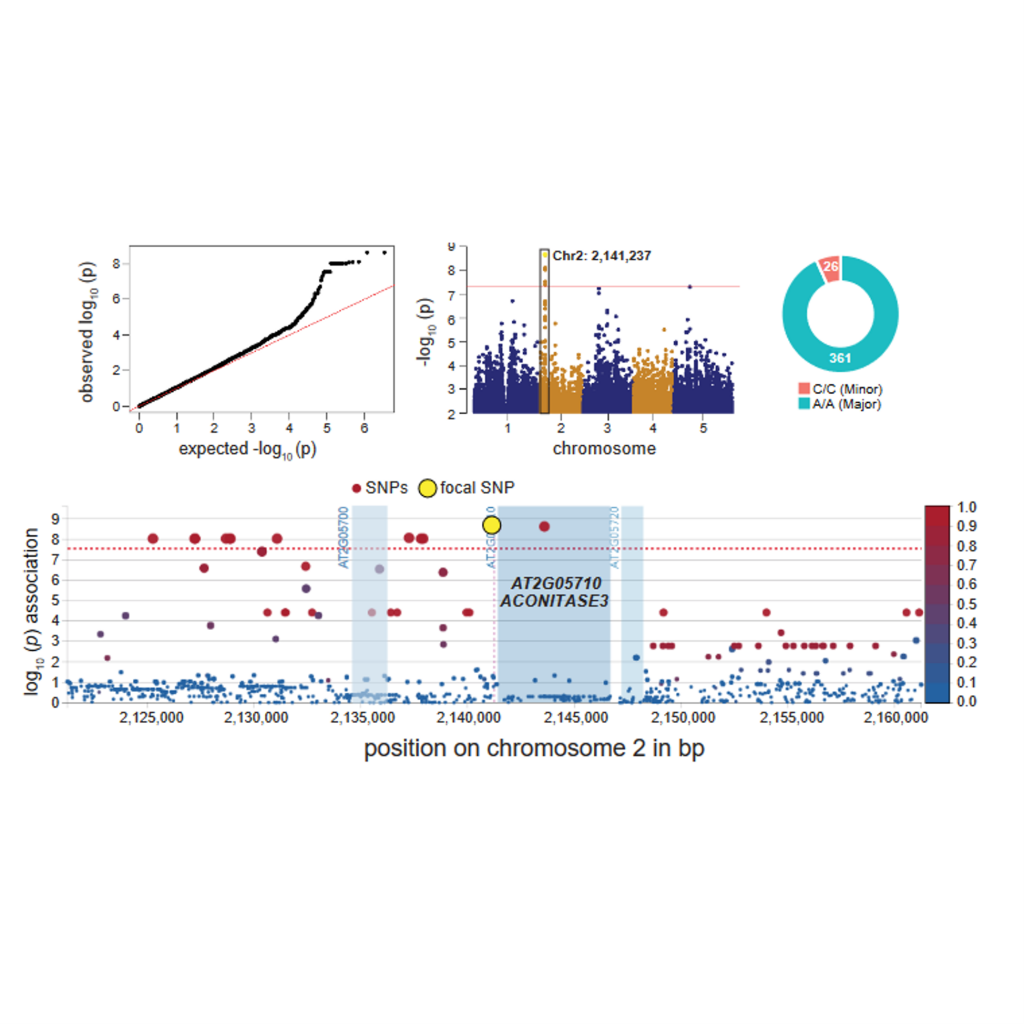
GWAS on multiple traits identifies mitochondrial ACONITASE3 as important for acclimation to submergence stress (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyClimate change is affecting the frequency and intensity of extreme climatic events such as floods, reducing crop production severely. Submergence might lead to a lack of O2, light, and carbon dioxide, having an impact on the carbohydrate content and ATP synthesis. In this work, Xiangxiang et al. characterise…
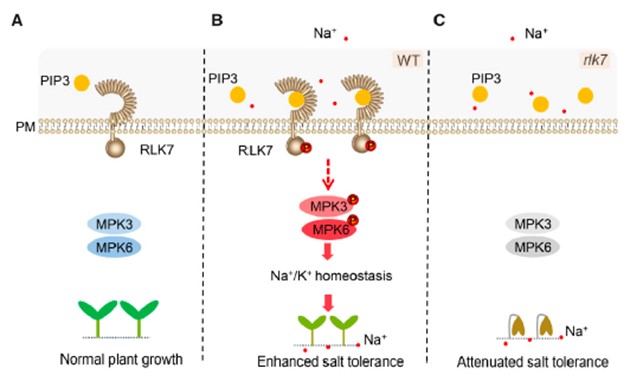
Plant salt tolerance through a peptide and receptor like kinase pathway (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklySoil salinity is a major stress that hampers plant growth, but plants have evolved signaling pathways to sense and respond to salinity. Zhou and colleagues have recently reported a novel pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana that that involves a peptide ligand, PAMP-INDUCED SECRETED PEPTIDE 3 (PIP3) and…
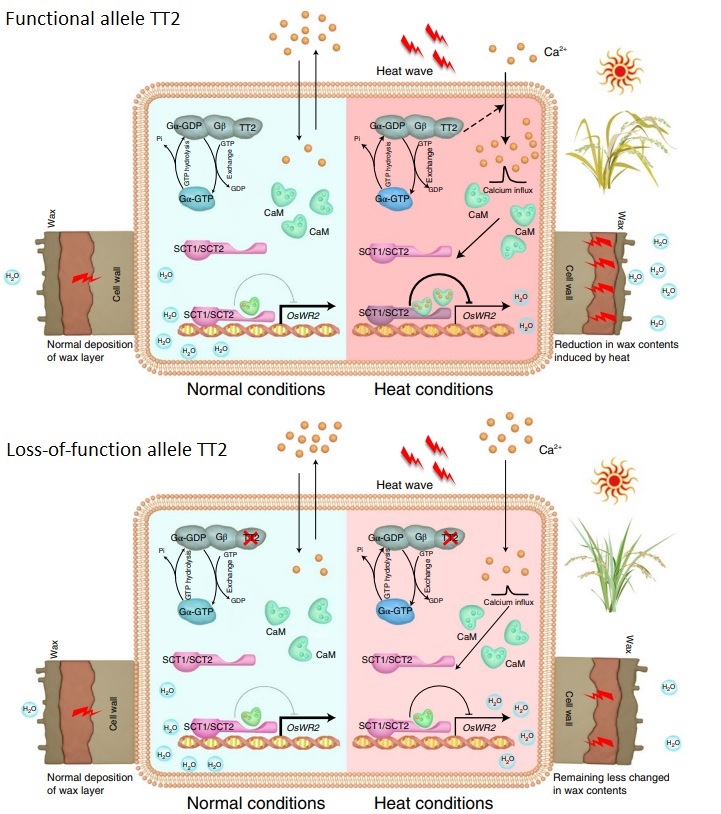
TT2 controls rice thermotolerance through SCT1-dependent alteration of wax biosynthesis (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyGlobal warming severely affects agricultural harvests, risking food security. To deal with heat stress, plants show different strategies. Indeed, heat increases intracellular Ca2+ levels to activate a heat shock response. In addition, GTP-binding proteins, which transduce extracellular signals to intracellular…
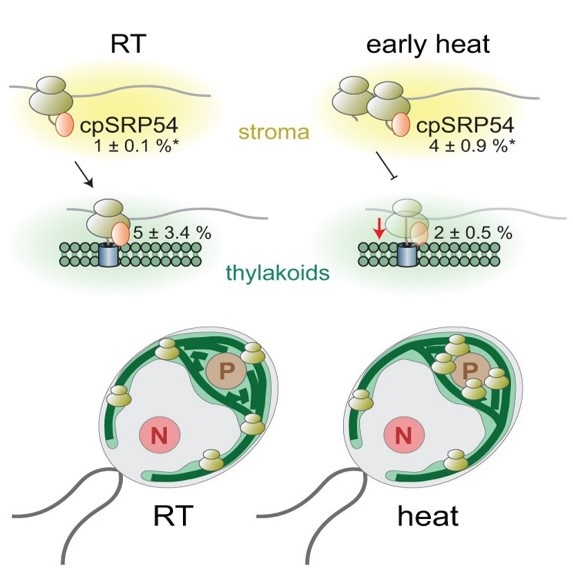
Fast and global reorganization of the chloroplast protein biogenesis network during heat acclimation (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWith the rising climatological extremes, heat stress is a major concern towards sustainable crop yield and productivity as it impairs several physiological and developmental processes. Due to the sessile lifestyle of land plants, they undergo various acclimation responses to cope with fluctuating temperatures.…
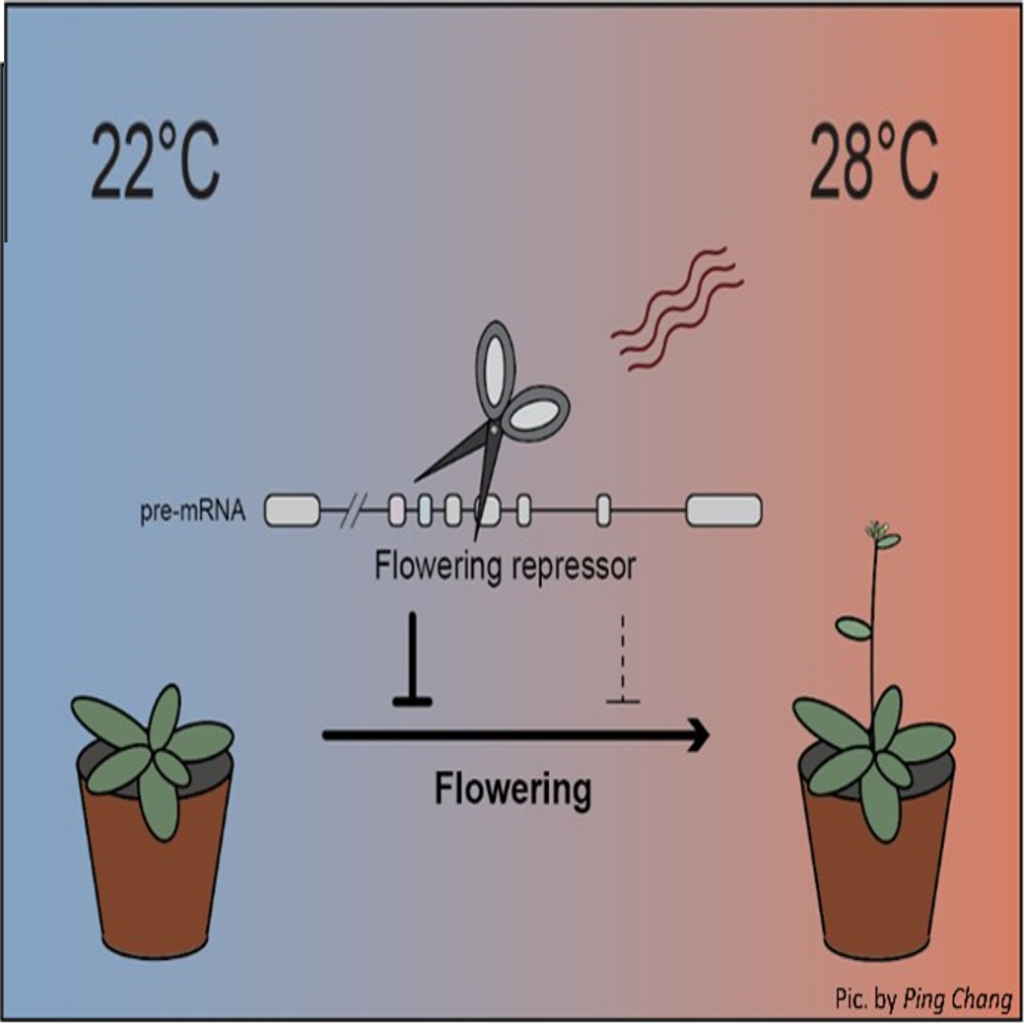
The splicing factor RNA BINDING PROTEIN 45d regulates temperature-responsive flowering (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPosttranscriptional events such as splicing are part of the gene regulation toolbox. Previous studies have demonstrated a role for U-rich small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs) such as U1 in the control of splicing. In a recent paper in The Plant Cell, Chang et al. identified a splicing factor, RNA…
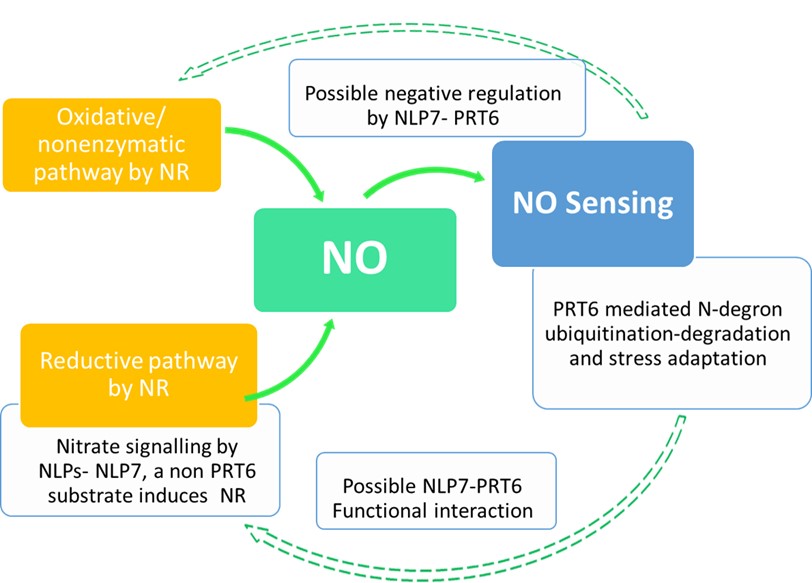
Functional interaction of nitrate signaling regulator NLP7 and N-degron “recognin” PRT6 enhances abiotic stress tolerance (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn addition to the vast array of metabolic and signaling roles, nitric oxide (NO) is prominently involved in low oxygen sensing in seeds and waterlogged plants. In Arabidopsis, the cytosolic nitrate reductase (NR) isoforms NIA1/NIA2 catalyze the reductive pathway of NO generation. NO sensing in plants…
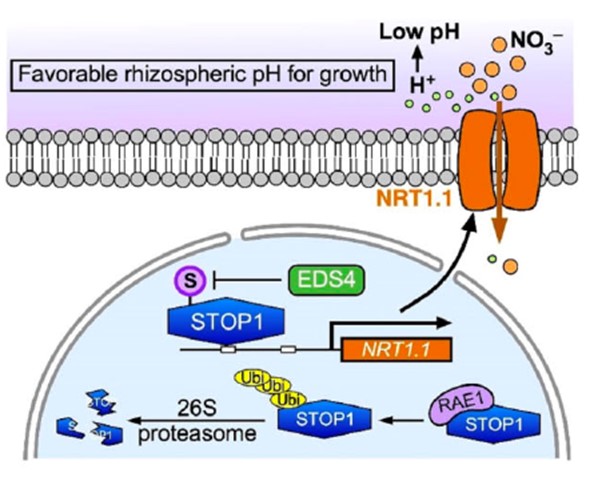
STOP1-NRT1.1: a new module to optimize nitrogen and growth in acidic media for plants (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAcidic soils often negatively impact plant growth, yet the application of fertilizers containing urea or ammonia have the effect of acidifying soils. In a recent paper, Ye and colleagues investigated how nitrate uptake through the nitrate transporter NITRATE TRANSPORTER 1.1 (NRT1.1) can mitigate some…
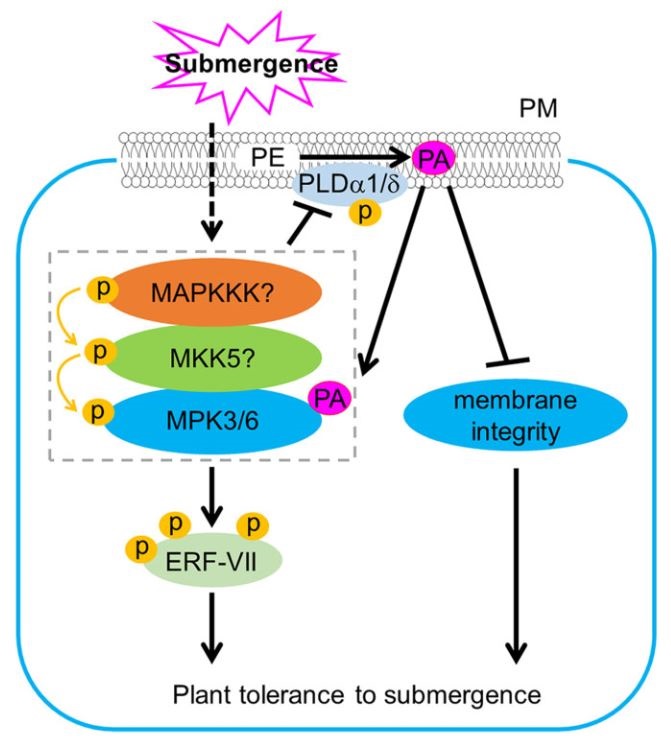
Phosphatidic acid modulates MPK3- and MPK6- mediated hypoxia signaling in Arabidopsis (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants experience changes in gene expression and cellular metabolism to improve their survival to abiotic stresses, such as hypoxia. It has been observed that environmental signals induce phospholipase D (PLD) which generates phosphatidic acid (PA) by cleaving membrane phospholipids. Indeed, submergence…

Focus Issue on Architecture and Plasticity (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe November issue of Plant Physiology is a Focus Issue on Architecture and Plasticity. One of the most intriguing aspects of plant growth and development is the environmental responsiveness (also known as “plasticity”) of plant architecture (growth form). Depending on environmental conditions, roots…

