
Drought conditions reduce root-feeding nematode predator populations (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyClimate change is expected to cause numerous negative impacts on plant populations. An under considered area that will be affected are the communities of soil organisms that rely on a delicate balance of environmental conditions, particularly in grasslands that receive moderate precipitation (mesic grasslands).…

A chloroplast-localized mitochondrial calcium uniporter transduces osmotic stress in Arabidopsis (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCalcium and chloroplasts are both at the heart of the signal transduction during environmental stress. Teardo et al. studied whether the chloroplast-localized mitochondrial calcium uniporter has a role in stress signaling. The group identified 6 homologs of mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU) in Arabidopsis,…
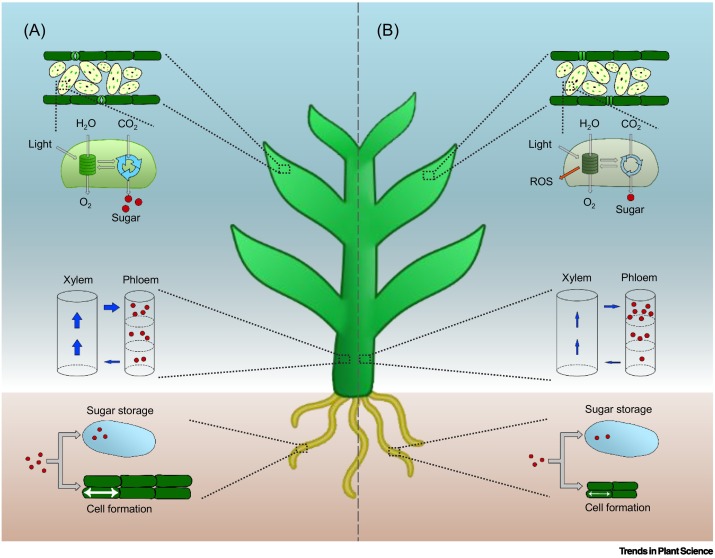
Review: Source–sink regulation in crops under water deficit ($) (Trends Plant Sci)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants have a remarkable ability to coordinate cellular activities across huge distances, yet we have only a basic understanding of how these remote activities are coordinated. A review by Rodrigues et al. summarizes what we know about the relationship between source (e.g., photosynthetic tissues) and…
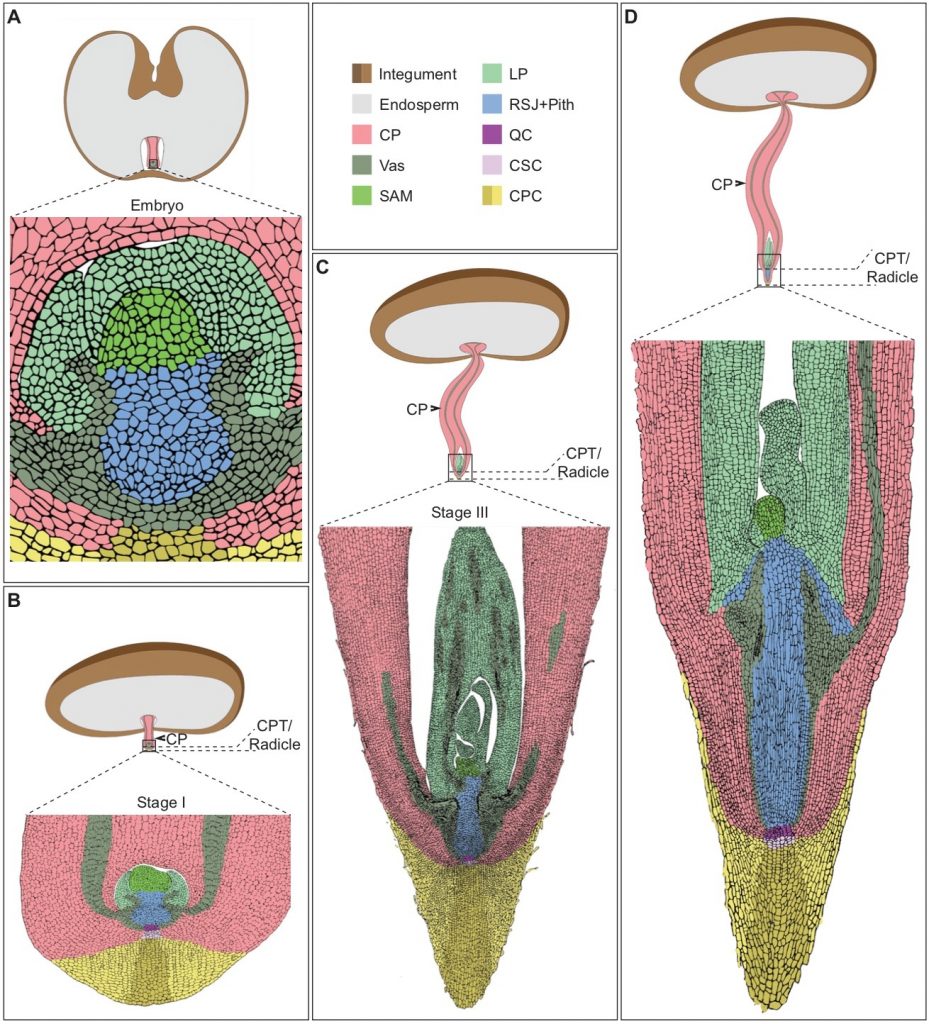
Embryo protection after germination in date palm (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant morphogenesis is a dynamic process that can be modulated in response to environmental cues. In this work, Xiao et al. characterized germination and seedling development in date palm. After germination, the cotyledonary petiole grows, but the embryo development is paused. At early stages of development…
A diversity of traits contributes to salinity tolerance of wild Galapagos tomatoes seedlings (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyDomestication has been accompanied by a decrease in genetic diversity, so efforts to improve stress tolerance can be aided by exploring the crop’s wild relatives. Here, Pailles et al. examined salt tolerance in Galapagos tomatoes (Solanum cheesmaniae and Solanum galapagense), which grow “constantly…
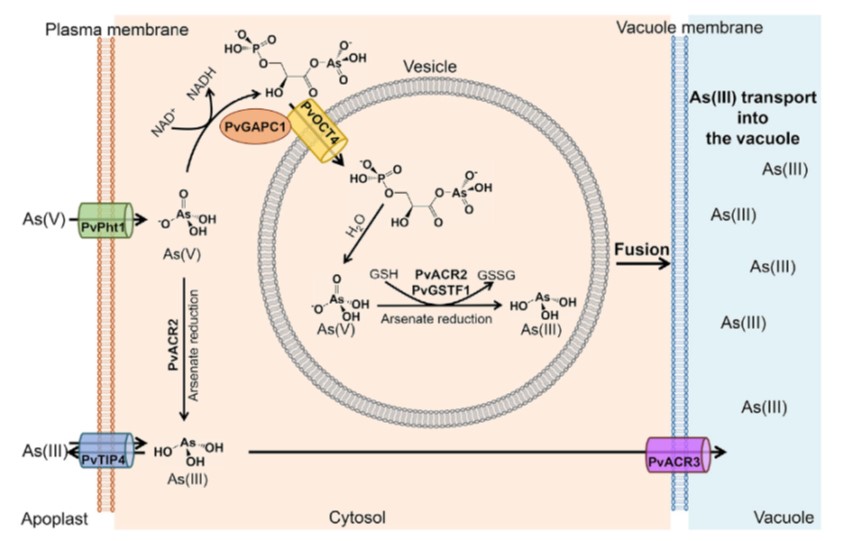
A simple arsenic detoxification strategy in the fern Pteris vittata ($) (Curr Biol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyArsenic contamination is a growing human health threat. The fern Pteris vittata demonstrates a remarkable capacity to accumulate and sequester high levels of the toxic heavy metal arsenic from contaminated environments. Cai et al. used an ‘omics’-guided approach to identify and characterize the molecular…
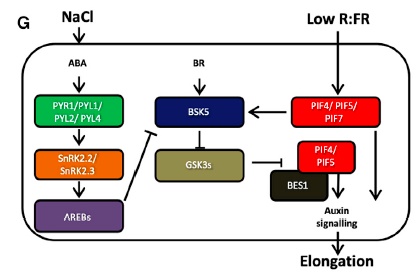
Soil salinity limits plant shade avoidance (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research Weekly
The agriculture sector is going to face big challenges to feed the 10 billion people that are going to inhabit the planet in the upcoming years with limited arable land. One effective practice to enhance the yield per unit area is to increase crop planting density. However, in dense stands, plants…
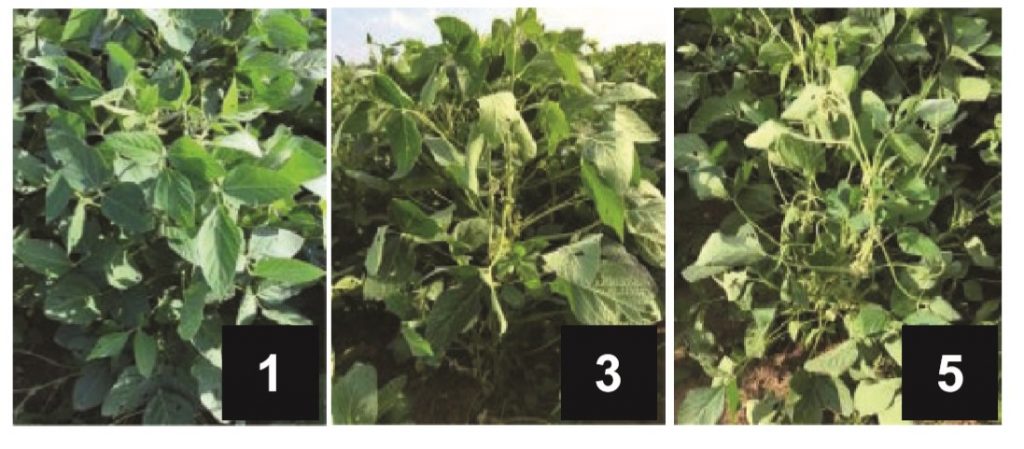

Slow canopy wilting enhances drought-tolerance in soybean (J Exp Bot)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAs plants are sessile organisms, they have developed highly sophisticated mechanisms to allow the modulation of development in response to environmental changes, thus maximizing their chance of survival. When soil dries, soybeans with a slow canopy wilting (SW) phenotype have delayed canopy/leaf wilting…
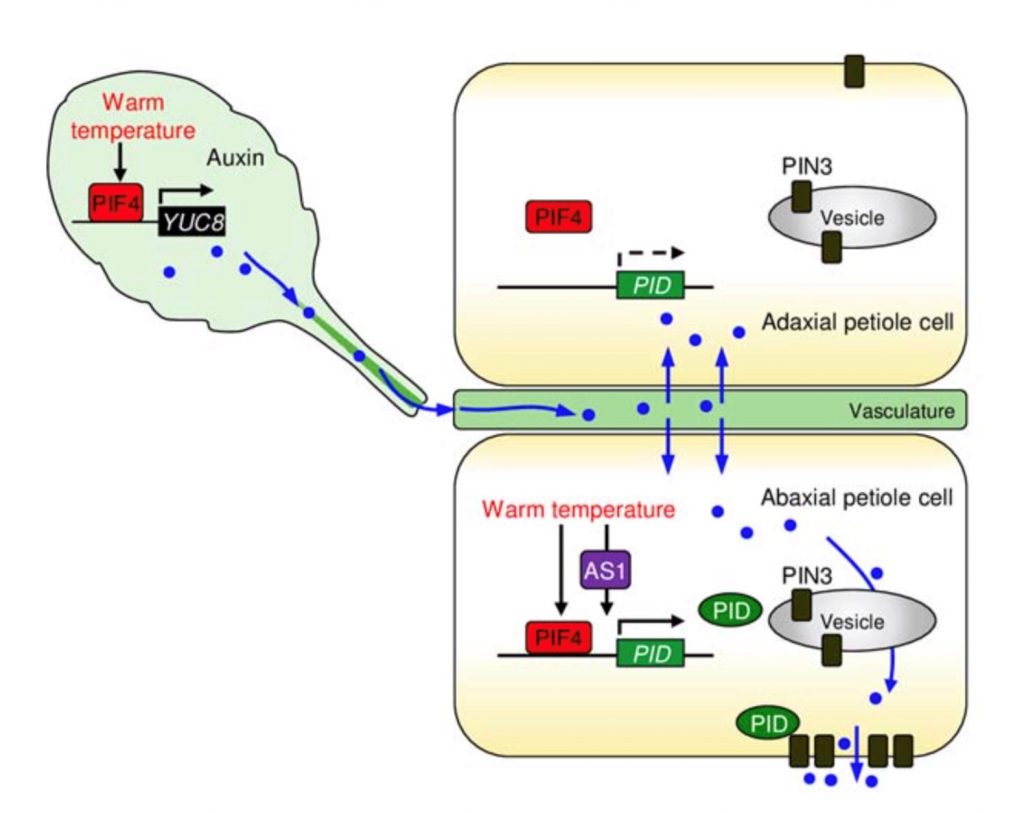
Thermal response in plants: leaf hyponasty (Plant Phys)
Plant Science Research WeeklyNon-directional stimuli can trigger directional movements in plant organs. For instance, high temperature causes the upward bending of leaf petioles, a process known as leaf hyponasty, which helps to cool the leaves. In this study Park et al. explored the link between leaf thermonasty and auxins. Gene…

