Review: Linking autophagy to abiotic and biotic stress responses (Trends Plant Sci)($)
Autophagy means “self-eating” in ancient Greek. It’s a process in which cellular components are delivered to lytic vacuoles to be reused. This recycling process promotes abiotic and biotic stress tolerance. In this review, Signorelli et al. highlight in detail plant autophagy in abiotic and biotic…
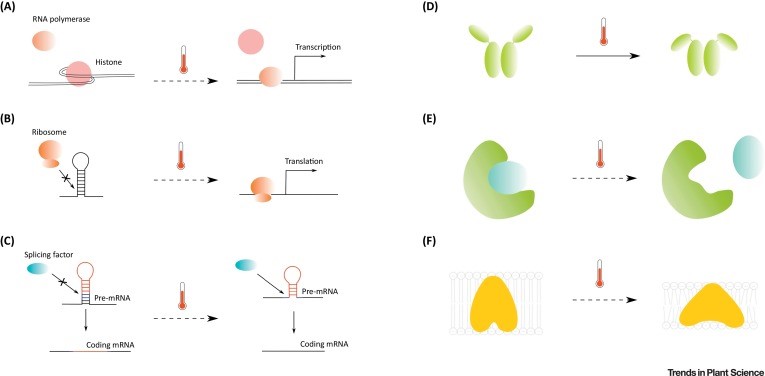
Opinion. Feeling the heat: Searching for plant thermosensors (Trends Plant Sci)
How does a plant sense the elevation in atmospheric temperature? What are the missing links betweena rise in atmospheric temperature, its sensing, and responses triggered? Vu et al. discuss how conformational and structural changes of DNA, RNA and proteins could be the sensors to temperature change.…
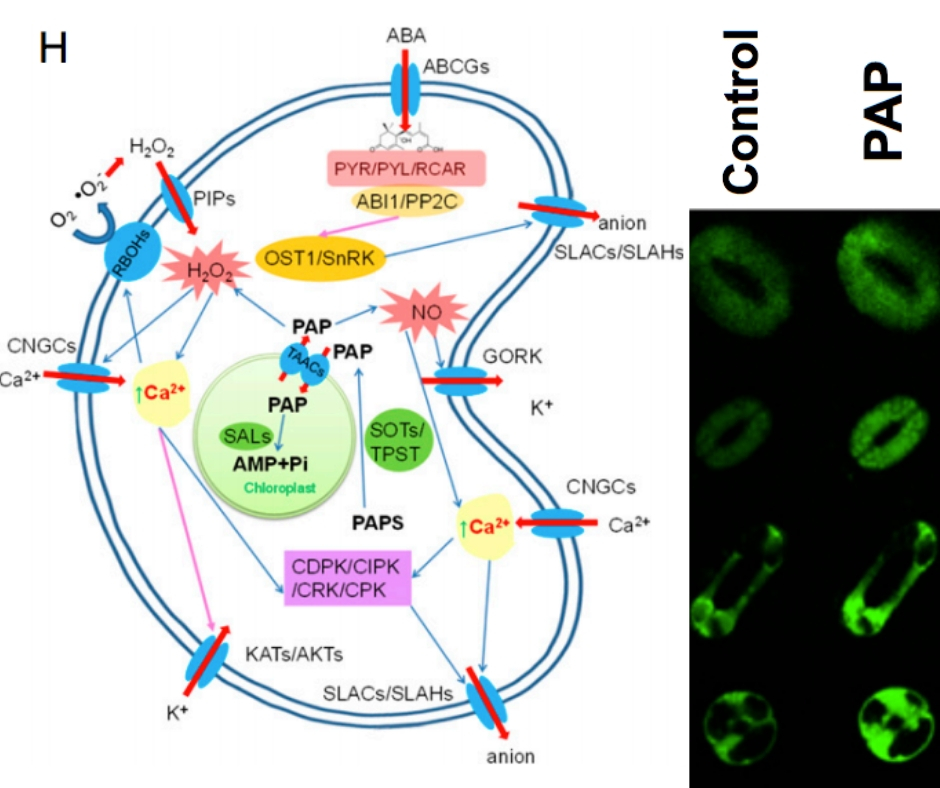
Evolution of chloroplast retrograde signaling facilitates green plant adaptation to land (PNAS)
The evolution of signaling pathways in plants enabled the water to land transition, during which drought response was crucial for the adaptation to terrestrial habitats. Here, Zhao et al. reveal the role of drought- induced phosphoadenosine (PAP) in the regulation of abscisic acid (ABA) synthesis in…

SME1 shapes plant development and freezing tolerance
Huertas et al. show that SME1 modulates spliceosome activity to shape plant development and tolerance to freezing temperatures. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00689
By Raúl Huertas, Noble Research Institute, Admore, Oklahoma, USA. Rafael Catalá, Centro de Investigaciones Biológicas-CSIC,…
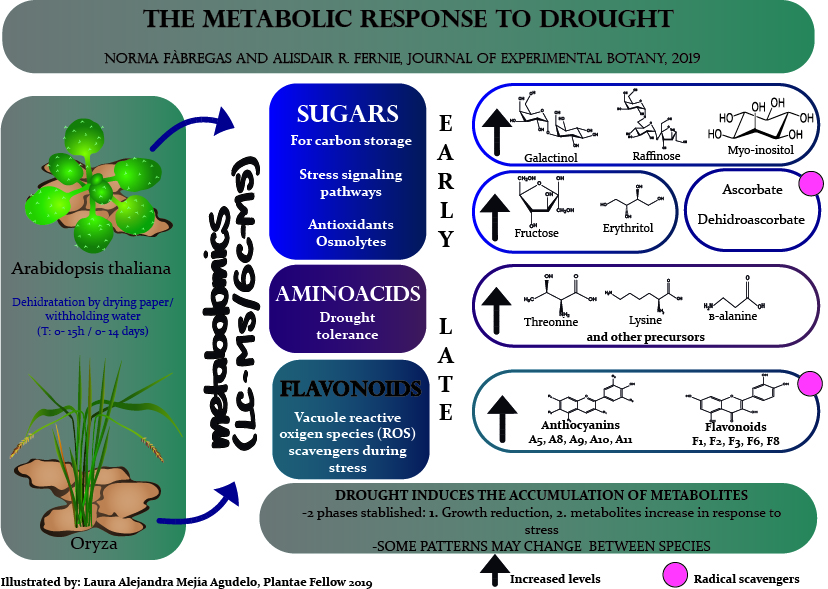
Review: The metabolic response to drought (J Exp Bot) ($)
Understanding environmental stress in plants is undoubtedly important due to the consequences of climate change in crop productivity and survival of plants. Metabolomics based on liquid chromatography and gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (LC-MS, GC-MS) allows an understanding of the metabolic…
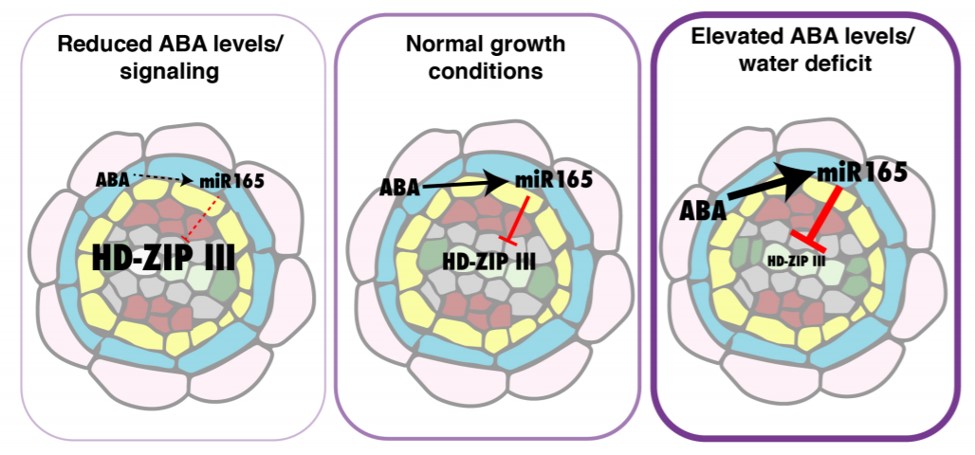
Root xylem formation and vascular acclimation to water deficit involves endodermal ABA signaling via miR166 ($) (Development)
Abiotic stress influences plant development, with the phytohormone ABA playing an important role. Ramachandran et al. have demonstrated ABA mediated activation of microRNA 166, which regulates expression levels of the HD-ZIP III transcriptional factor family. Exogenously supplied ABA alters xylem patterning…
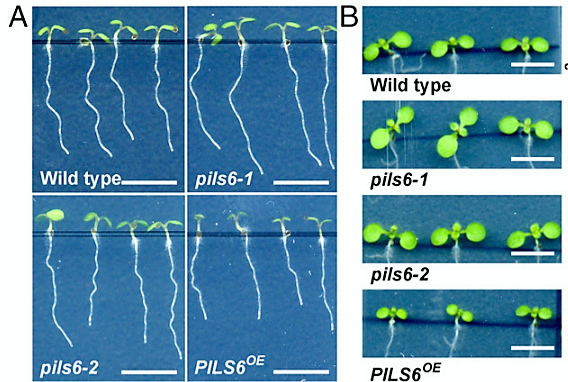
PILS6 is a temperature-sensitive regulator of nuclear auxin input and organ growth (PNAS)
Auxin, a plant hormone and major growth regulator, is fundamental for adaptations to climatic variation in shoots but its role in roots under elevated temperatures is more controversial. PIN-LIKES (PILS) 2, 3 and 5 proteins have previously been identified to restrict nuclear auxin signalling but the…
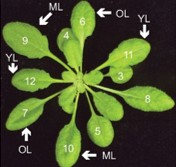
Leaf age dictates abiotic versus biotic stress signalling in Arabidopsis (PNAS)
Plants sense and respond to various external stimuli throughout their lifespan. During stress responses brought forth by abiotic or biotic factors, molecular and physiological adjustments mediated by distinct yet interconnected hormone pathways play critical roles in plant survival. Berens et al. investigate…

Auxin efflux carrier ZmPGP1 mediates root growth inhibition under aluminum stress (Plant Physiology)
Acid soils (pH < 5.5) mobilize aluminum (Al) in the rhizosphere, which damages the root meristem and hinders exploration for nutrients and water. Zhang et al. demonstrate that a mutation in ZmPGP1, an auxin transport protein, imparts enhanced root growth under toxic Al conditions. The enhanced root…

