Review: Stem-borne roots as a framework to study trans-organogenesis
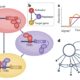
 Plants develop new organs and tissues throughout their lifespan as they grow new leaves, roots and reproductive structures. Many of these tissues arise from similar tissues, such as lateral roots arising from primary roots, and the mechanisms guiding their formation are well understood. But what about ‘trans-organogenesis’: where structures arise from completely different tissue types? The development of roots from stems – also known as adventitious roots – is one such example. And while stem-borne roots have been described for many species, the mechanisms controlling their development remain elusive. In this review, Rasmussen et al. summarise the current knowledge on development of stem-borne roots, including their occurrence throughout the plant kingdom and diversity of form and function. They consider open questions of whether stem-borne roots share an evolutionary history, or have arisen multiple times, possibly through rewiring of ancient developmental pathways. The authors provide a framework to better classify types of stem-borne roots based on their form, function and tissue of origin – and propose stem-borne roots as a model for understanding trans-organogenesis, plasticity and adaptation in plants. (Summary by Alicia Quinn @AliciaQuinnSci). Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 10.1016/j.pbi.2024.102604
Plants develop new organs and tissues throughout their lifespan as they grow new leaves, roots and reproductive structures. Many of these tissues arise from similar tissues, such as lateral roots arising from primary roots, and the mechanisms guiding their formation are well understood. But what about ‘trans-organogenesis’: where structures arise from completely different tissue types? The development of roots from stems – also known as adventitious roots – is one such example. And while stem-borne roots have been described for many species, the mechanisms controlling their development remain elusive. In this review, Rasmussen et al. summarise the current knowledge on development of stem-borne roots, including their occurrence throughout the plant kingdom and diversity of form and function. They consider open questions of whether stem-borne roots share an evolutionary history, or have arisen multiple times, possibly through rewiring of ancient developmental pathways. The authors provide a framework to better classify types of stem-borne roots based on their form, function and tissue of origin – and propose stem-borne roots as a model for understanding trans-organogenesis, plasticity and adaptation in plants. (Summary by Alicia Quinn @AliciaQuinnSci). Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 10.1016/j.pbi.2024.102604