Review: Root development and symbiosis: an epigenetic perspective
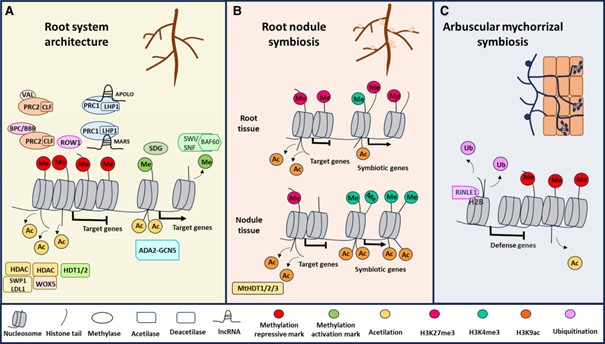 Roots do not grow in isolation but occupy a space inhabited by a variety of organisms. With certain fungi and bacteria, they form partnerships or symbiotic relationships that increase the plant’s nutrient uptake and assimilation. While the knowledge on the genetic programs required to establish these symbiotic relationships is a topic of many studies, the epigenetic regulation of the involved genes is less known. In this recent review by Zanetti et al. (2024), the authors provide a comprehensive overview of the current knowledge on epigenetic regulation of root development. Specifically, the review covers three aspects of root development, namely lateral root development, nodule formation, and symbioses with mycorrhizae, and it discusses how both DNA methylation and histone modifications act to control the relevant genes. In particular, the article highlights differences in the epigenetic regulation among different root zones, tissues, and even cell-types. The emphasis on these spatial characteristics provide interesting, novel perspective on the subject. Finally, the authors argue for more research towards unravelling the epigenetic regulation of root system architecture and symbiosis, especially with respect to the role of chromatin remodelling and histone modifications, to better understand the underlying drivers for the enormous phenotypic plasticity demonstrated by a plant root. (Summary by Thomas Depaepe @thdpaepe). Plant Physiology 10.1093/plphys/kiae333
Roots do not grow in isolation but occupy a space inhabited by a variety of organisms. With certain fungi and bacteria, they form partnerships or symbiotic relationships that increase the plant’s nutrient uptake and assimilation. While the knowledge on the genetic programs required to establish these symbiotic relationships is a topic of many studies, the epigenetic regulation of the involved genes is less known. In this recent review by Zanetti et al. (2024), the authors provide a comprehensive overview of the current knowledge on epigenetic regulation of root development. Specifically, the review covers three aspects of root development, namely lateral root development, nodule formation, and symbioses with mycorrhizae, and it discusses how both DNA methylation and histone modifications act to control the relevant genes. In particular, the article highlights differences in the epigenetic regulation among different root zones, tissues, and even cell-types. The emphasis on these spatial characteristics provide interesting, novel perspective on the subject. Finally, the authors argue for more research towards unravelling the epigenetic regulation of root system architecture and symbiosis, especially with respect to the role of chromatin remodelling and histone modifications, to better understand the underlying drivers for the enormous phenotypic plasticity demonstrated by a plant root. (Summary by Thomas Depaepe @thdpaepe). Plant Physiology 10.1093/plphys/kiae333