Mechanism of auxin-dependent gene regulation through composite auxin response elements
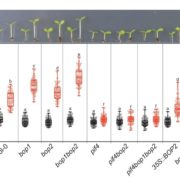
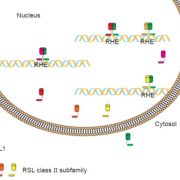
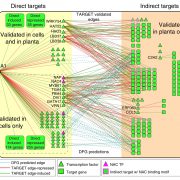
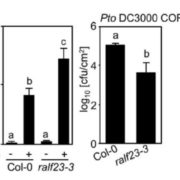
 Auxin signaling influences plant growth and development by controlling gene expression, often through binding of transcription factors from the Auxin Response Factor (ARF) family to ARF elements (AuxRE) present in the promoters of auxin-responsive genes. However, given that auxin signaling produces many varied effects on growth, it’s not clear how diverse responses are achieved with only a limited set of ARF transcription factors. One possibility is that sequences adjacent to the AuxRE, forming composite auxin response elements, influence the response by facilitating interactions between the ARF and other transcription factors. Novikova et al. investigated how these composite AuxRE’s contribute to regulation of auxin-responsive genes using computational, functional genomics, and classic genetic analyses. They demonstrated that ARF transcription factors interact with an array of binding partners to regulate composite AuxRE’s and fine-tune gene expression. They explored the role of a composite AuxRE module present in the promoter of the auxin-responsive INDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID INDUCIBLE 30 (IAA30) gene and demonstrated that stacking of composite AuxRE’s is important for IAA30‘s function in root development. Composite AuxRE modules may provide a mechanism for nuanced control of auxin signaling and are likely important for mediating auxin growth responses during development and in stressful environments. (Summary by Alicia Quinn @AliciaQuinnSci). bioRxiv 10.1101/2024.07.16.603724
Auxin signaling influences plant growth and development by controlling gene expression, often through binding of transcription factors from the Auxin Response Factor (ARF) family to ARF elements (AuxRE) present in the promoters of auxin-responsive genes. However, given that auxin signaling produces many varied effects on growth, it’s not clear how diverse responses are achieved with only a limited set of ARF transcription factors. One possibility is that sequences adjacent to the AuxRE, forming composite auxin response elements, influence the response by facilitating interactions between the ARF and other transcription factors. Novikova et al. investigated how these composite AuxRE’s contribute to regulation of auxin-responsive genes using computational, functional genomics, and classic genetic analyses. They demonstrated that ARF transcription factors interact with an array of binding partners to regulate composite AuxRE’s and fine-tune gene expression. They explored the role of a composite AuxRE module present in the promoter of the auxin-responsive INDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID INDUCIBLE 30 (IAA30) gene and demonstrated that stacking of composite AuxRE’s is important for IAA30‘s function in root development. Composite AuxRE modules may provide a mechanism for nuanced control of auxin signaling and are likely important for mediating auxin growth responses during development and in stressful environments. (Summary by Alicia Quinn @AliciaQuinnSci). bioRxiv 10.1101/2024.07.16.603724