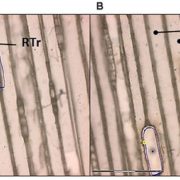
Protocol: Laser capture microdissection for woody tissues
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research0 Comments
/
Laser capture microdissection (LCM) was developed 20 years ago as a way to isolate single cells or clusters of cells for subsequent –omic analysis. In LCM, thin sections are generated, the cells of interest cut out using a focused laser, and the isolated cells collected for subsequent studies. Several…

Three Reviews: Phytochrome, shade avoidance and far-red light ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchPlant Cell Environ. has a set of reviews on light responses. Ballaré and Pierik (10.1111/pce.12914) review The shade avoidance syndrome: Multiple signals and ecological consequences, Sheerin and Hiltbrunner (10.1111/pce.12915) review the Molecular mechanisms and ecological function of far-red light…
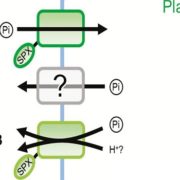
Review: Role of vacuoles in phosphorus storage and remobilization ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchPhosphorus (P) is a non-renewable soil nutrient essential for plant growth. The vacuole serves as a crucial dynamic store of P that helps maintain cytosolic homeostasis. Yang et al. review vacuolar P stores, comparing P storage species and membrane proteins in yeast, algae and plants. In yeast, polyphosphate…

Review: Cyanobacterial metabolites as a source of sunscreens and moisturizers
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe cosmetic industry uses a lot of different chemicals to produce the seven or so skin care products used by the average American every day. Efforts are underway to develop renewable sources for some of these. Derikvand et al. review the chemistry and potential applications behind compounds used by…
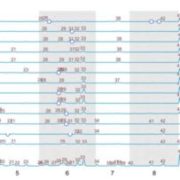
Network-based integration of systems genetics data reveals lignocellulosic metabolic pathways
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchEucalypts are fast-growing trees increasingly exploited for pulp, paper, bioenergy and other wood-based products. Using genetics tools and a network-based data integration (NBDI) approach, Mizrachi et al. explore a segregating Eucalyptus hybrid population for genes and pathways underlying biomass / bioenergy…
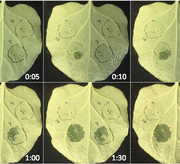
A pectase lyase that is an indirect target of a Xanthomonas TAL effector promotes susceptibility
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchOne of the many ways that Xanthomonas bacteria manipulate their host plants is by the production of transcription activator-like (TAL) effectors, which the bacterium introduces into the host cell where they alter gene expression in the host nucleus. Schwartz et al. investigated the targets of the TAL…
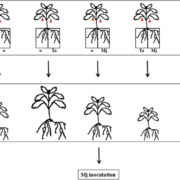
Transgenerational biocontrol against root-knot nematode following priming by biocontrol fungus
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchRoot-knot nematodes including Meloidogyne javanica are major agricultural pests. Previous studies have shown that biocontrol agents including species of the fungal genus Trichoderma interfere with root-knot nematode pathogenicity, directly through effects on the nematode, and indirectly through a stimulation…
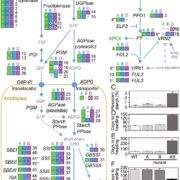
Uncovering hidden variation in polyploid wheat
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchOne of the big challenges of working with wheat, as compared to rice, is that the wheat we eat is polyploid; bread wheat (Triticum aestivum) is hexaploid (six copies of each gene) and pasta wheat (Triticum turgidum) is tetraploid (four copies each). Polyploidy makes forward genetics difficult; knocking…

Regulation of tulip flowering by temperature ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchCultivation of Tulipa gesneriana (tulip), an economically important species due to its ornamental value, can be affected by warming winters, leading to low quality flowers produced out of season. Leeggangers et al. have sequenced RNA and used top-down and bottom-up approaches in tulips grown in two contrasting…

