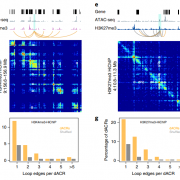
Widespread long-range cis-regulatory elements in the maize genome ($) (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe chromatin landscape is key in the regulation of gene expression. Many studies have been made in Arabidopsis, but its genomic architecture is different to other plants. Here Ricci et al. present a very comprehensive study of chromatin analysis in maize. This work includes a huge amount of sequencing…

The prevalence, evolution and chromatin signatures of plant regulatory elements ($) (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWith a wide range of genome sizes and varying architectures, understanding the evolution and function of non-coding regions is not straightforward in plants. Nevertheless, many advances are coming out that will shed light on this complex scientific problem. Lu et al. performed ATAC-seq to study chromatin…
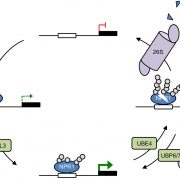
Dynamic ubiquitination determines transcriptional activity of the plant immune coactivator NPR1 (eLIFE)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Dynamic ubiquitination determines transcriptional activity of the plant immune coactivator NPR1
Plants (and animals) need to strike a delicate balance when activating their immune responses: not too much and not too little. The transcriptional coactivator NPR1 [nonexpressor of pathogenesis-related…
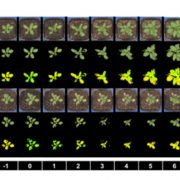
The use of high throughput phenotyping for assessment of heat stress-induced changes in Arabidopsis (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWith global temperatures rising, tolerance to heat is becoming increasingly important as a breeding target for crop plants, but it is a highly complex response that includes processes including plant cooling capacity, growth recovery, and maintenance of photosynthesis. Using Arabidopsis, Gao et al. developed…
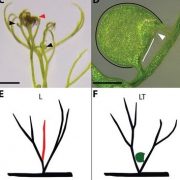
Evolution of carnivorous traps from planar leaves through simple shifts in gene expression (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWhen is a leaf not a leaf? When it’s a trap. Just about everyone, including Charles Darwin, has been fascinated by carnivory in plants, which involves the development of structures that capture or trap food. Whitewoods, Gonçalves, Cheng et al. investigated how traps form in the humped bladderwort…

Genetic contribution of paleopolyploidy to adaptive evolution in angiosperms (Mol Plant)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Genetic contribution of paleopolyploidy to adaptive evolution in angiosperms
Comparative genomics has revealed that the angiosperms have experienced numerous whole-genome duplications (WGD), which have been proposed to have contributed to their global dominance. Following WGD, many of the…
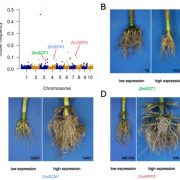
Shared genetic control of root system architecture between Zea mays and Sorghum bicolor (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRoot research got a boost from Arabidopsis grown on Petri plants, but what do you do if you study something bigger, or want to see how roots grow in soil? Zheng et al. developed a new set of tools they call CREAMD-COFE [Core Root Excavation using Compressed-air (to extract the roots from soil), and Core…
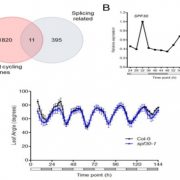
Global transcriptome analysis reveals circadian control of splicing events in Arabidopsis thaliana (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyDevelopmental programming, metabolism and plant growth are regulated by the circadian rhythm that integrates environmental signals and plant growth. In this paper, Romanowski et al. have used the RNAseq approach to determine post-transcriptional regulation in Arabidopsis thaliana, specifically alternate…
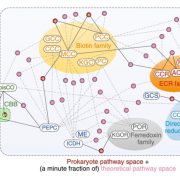
Perspective: Revolutionizing agriculture with synthetic biology (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn a new Perspective by Wurtzel et al., the authors lay out SynBio’s tremendous potential to transform agriculture. Consider how we might leverage the “vast design space that plants have not occupied.” As an example, plants employ two pathways to fix carbon, and prokaryotes another six, but scientists…

