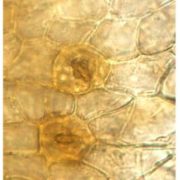
Evolutionary origins of stomata ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research0 Comments
/
Questions remain about the evolutionary origins and functions of stomata. They are absent from liverworts, present to a limited extent in mosses, and are found on 410 million year-old fossils of Cooksonia, a leafless plant. Chater et al. show that orthologs of two key transcription factors that control…
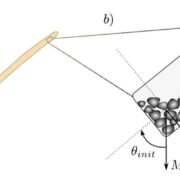
Inclination, not force, is detected in shoot gravitropism
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchPlant cells detect gravity as a consequence of the movement of dense starch granules called statoliths when the statoctyte, the cell that encompasses, them reorients. An open question has been whether the position of the statoliths within the statocyte or the force exerted by them is the primary gravisensing…
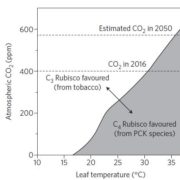
Improving Rubisco
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchRubisco (Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase / oxygenase) is the enzyme responsible for fixing almost all inorganic carbon into organic form, but it is not optimized for current conditions. As temperature and CO2 levels increase, there is an opportunity to increase photosynthetic efficiency by engineering…
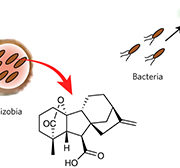
Gibberellin biosynthesis in bacteria: Still more convergent evolution ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchGibberellin hormones were famously identified as the product of Gibberella fujikuroi, a fungal pathogen that stimulates host cell elongation, and then subsequently recognized as a hormone produced by plants as well. Fungi and plants produce gibberellins from distinct biochemical pathways, in an example…
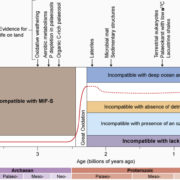
Review: Biogeochemical effects of early life on land
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchEarth colonization by life happened billions of years ago. Weathering of soils by microbial mats leave a characteristic signal that can be used to shed light on the mechanisms involved in colonization. In this review, Lenton and Daines discuss the growing mass of evidence that points to the biogeochemical…
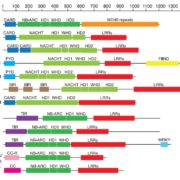
Review: Intracellular innate immune surveillance devices in plants and animals ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchCells recognize invaders through both cell-surface receptors and intracellular receptors, the latter of which can recognize the invader directly or indirectly, for example through its effects on host proteins. Intracellular surveillance proteins in animals and plants share a core domain, the nucleotide…
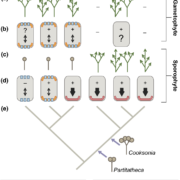
Review: Evolutionary perspective on auxin’s role in shoot branching
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchShoot branching increases the photosynthetic surface area and the points at which reproductive structures can form. In angiosperms, auxin (specifically, auxin depletion) has been shown to be involved in the initiation and outgrowth of shoot branches. For example, in apical dominance the primary shoot…
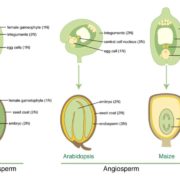
Review: Endosperm and Imprinting
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research"The endosperm is often viewed as a complicated and rather strange tissue" begins this review by Gehring and Satyaki. They go on to describe that the endosperm is the site of expression of imprinted genes, which are genes that are expressed soley when inherited from the mother or father. The authors…
Biofortification of plants: New Reviews ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchBiofortification is the nutritional enhancement (using conventional or genetic engineering approaches) of food with vitamins or micronutrients with the goal of improving the human diet. A set of new reviews in Current Opinion in Biotechnology summarizes progress towards biofortification of plants to…

