Gain-of-function variants of cytokinin receptors ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research0 Comments
/
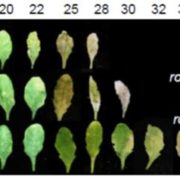
Arabidopsis has three membrane-located, histidine-kinase cytokinin (CK) receptors (AHK2, 3, and 4). Loss-of-function mutants suggest that AHK2 and AHK3 function somewhat redundantly. To further explore the roles of these receptors, Bartrina and Jensen et al. isolated dominant gain-of-function mutants,…
Time-resolved analysis of protein synthesis in native plant tissue
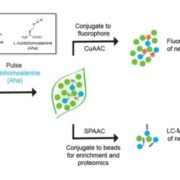
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchGlenn et al. introduce a new method for the labeling and purification of newly-synthesized proteins from intact tissues. The method, named BONCAT (Bioorthogonal Non-Canonical Amino Acid Tagging) involves the incorporation of the non-canonical methionine surrogate azidohomoalanine (Aha) into newly synthesized…
Peptide-mediated regulation of receptor scaffolding in plant immune signaling ($)
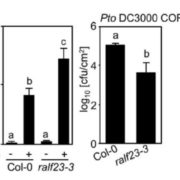
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchContinuing the theme of peptide signaling, Stegmann et al. showed that a subset of the RALF (RAPID ALKALINIZATION FACTOR) family of plant peptides can negatively regulate plant immune responses. When plants are treated with flg22, a peptide epitope of bacterial flagellin, they produce reactive oxygen…
Peptide diffusion as a signal for Casparian strip diffusion barrier formation ($)
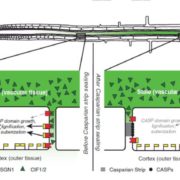
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe Casparian strip is a permeability barrier that seals the spaces between root endodermis cells and so prevents bulk-flow uptake of solutes. Previously, a leucine-rich repeat receptor kinase called SCHENGEN3 or GASSHO1 (GSO1/SGN3) was identified as necessary for normal Casparian strip formation. Now,…

Review: mlo-based resistance: An apparently universal “weapon” to defeat powdery mildew disease ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchPowdery mildew disease is a broad term that encompasses more than 650 species of powdery mildew fungi that affect about 10,000 plant species, with serious economic consequences. In the 1930s/40s, broad-spectrum resistance to powdery mildew was found in barley with a loss-of-function of the Mildew resistance…
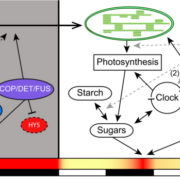
Review: Dark signaling in plants ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchPlants use light as a source of energy and information; however, they are also sensitive and respond to light/dark diurnal cycling, with many processes happening during the dark phase of the diurnal cycle. In this review, Seluzicki et al. emphasize the importance of studying and understanding what…
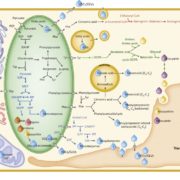
Review: The sexual advantage of looking, smelling and tasting good, the metabolic network that produces signals for pollinators ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe interaction between angiosperms and their pollinators provides an excellent system to study co-evolution, and underpins the evolution of the biosynthesis of numerous interesting and useful specialized metabolites, from pigments to fragrances. Borghi et al. review the metabolic pathways that produce…

Basal vs. Non-basal Polarity: Different Endomembrane Trafficking Pathways Establish Different Patterns
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefIN BRIEF: Nancy R. Hofmann [email protected]
Plant development and responses to the environment hinge on the ability to target proteins to different areas of the plasma membrane within a cell. Indeed, the establishment of polar distributions of proteins such as PIN auxin transporters is among the…
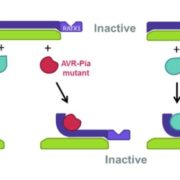
Effector-binding by integrated decoy domain of immune receptor RGA5 required for resistance activation
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchMagnaporthe oryzae is the fungus that causes rice blast disease, which is a serious threat to food security. Ortiz et al. explore the interaction between AVR-Pia, a fungal effector protein, and RGA5, a rice NLR (nucleotide-binding domain and leucine-rich repeat protein) immune receptor protein. RGA5…

