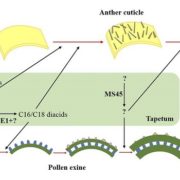
IRREGULAR POLLEN EXINE1 Is a novel factor in anther cuticle and pollen exine formation
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research0 Comments
/
Chen et al. identified a novel male-sterile Zea mays mutant, named ipe1. Mutant pollen grains show defective development of the tapetum and pollen exine (outer surface), causing microspore abortion. In addition, ipe1 anthers are smooth instead of reticulate, suggesting defects in anther cuticle formation. …
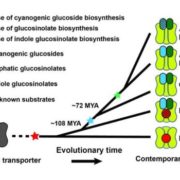
Origin and evolution of transporter substrate specificity within the NPF family
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchWhich arose first during evolution- a metabolite molecule or a transporter that could move it across a membrane? Jørgensen et al. studied transporters for glucosinolate defense molecules in Brassicales species. Glucosinolates are derived from the broad class of cyanogenic glucosides, and glucosinolates…
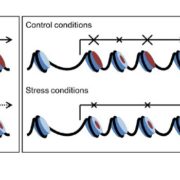
Dual role of the histone variant H2A.Z in regulation of stress-response genes
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchHistones are protein complexes around which genomic DNA is wrapped; post-translational modifications to histone proteins and alterations of histone protein composition affect transcription. H2A.Z is a widely conserved variant form of histone H2A that has been implicated in various forms of transcriptional…

Spotlight: The fate of the world’s plants
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchIn 2016, Kew Gardens released a report “The State of the World’s Plants”, which includes estimates of the total number of plant species on Earth and the percentage of those facing extinction. Pimm and Raven delve into those numbers and offer the opinion that many species will be lost before they…
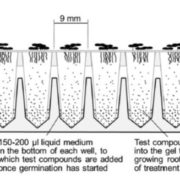
Method: Microphenotron, a miniaturized robotic phenotyping platform
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchHigh-throughput screening greatly extends the number of individuals that can be screened, so is particularly crucial for genetic or chemical genetic approaches. Burrell et al. report on a miniaturized robotic phenotyping platform, “Microphenotron” designed for chemical genetic screening. Seeds…
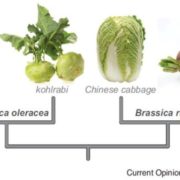
Review: Using mustard genomes to explore the genetic basis of evolutionary change ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchBrassicaceae is one of the largest angiosperm families and provides many opportunities for studies of evolution. Of course, its most famous species, Arabidopsis thaliana is an important resource, but Brassicaceae also includes the very interesting Brassica crops (cabbage, turnip) that demonstrate the…
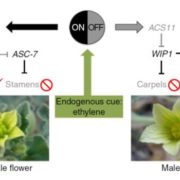
Review: Plant sex determination
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchMost angiosperms are hermaphrodites and produce flowers that have both male (stamens / sperm) and female (carpels / egg) parts. Pannell reviews the developmental and genetic programs that lead to these “perfect” flowers, as well as those that underlie reproductive structure development in dioecious…
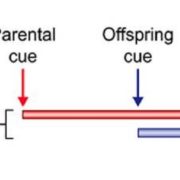
Review: Progeny responses to maternal vs progeny environmental cues
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe range of responses an individual could display is a contribution of the inheritance of gene variants that determine such responses and the environments experienced by the individual itself and prior generations (nongenetic inheritance). In this review, we discuss recent empirical data to help us…

Review: Methods of cell-specific hormone analysis ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchPlant hormones are active at very small quantities and often act differently in different cell types. Various methods, primarily involving mass spectrometry and sensors, have been developed to identify and quantify hormones with cellular-level precision. Novák et al. review these methods and discuss…

