
Wei Wei: The Plant Cell First Author
The Plant Cell: Author Profiles
Wei Wei, first author of "Proteasomal degradation of MaMYB60 mediated by the E3 ligase MaBAH1 causes high temperature-induced repression of chlorophyll catabolism and green ripening in banana"
Current Position: Postdoctoral Fellow, College of Horticulture, South China Agricultural University
Education:…

Hongye Sun: Plant Physiology First Author
Plant Physiology: Author Profiles
Hongye Sun, first author of "ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTORS 4.1/4.2 with an EAR motif repress anthocyanin biosynthesis in red-skinned pears"
Current Position: School of Food and Biological Engineering, Hefei University of Technology, doctoral candidate
Education: Successive postgraduate and doctoral…
ADP-ribosylation and plant immunity
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellYoon, Middleditch, and Rikkerink explore how a Pseudomonas syringae ADP-ribosyl transferase effector modifies RPM1-INTERACTING PROTEIN4 to activate the host R protein RPM1 in disease resistance.
Minsoo Yoon, The New Zealand Institute for Plant and Food Research Limited, Auckland, New Zealand
Background:…

Review: Photorespiration is the solution, not the problem
Plant Science Research WeeklyRubisco (ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase) is one of a kind, simultaneously recognized as one of the most abundant and important enzymes, and also widely characterized as flawed because it uses both O2 and CO2 as substrates, leading to both carboxylation and oxygenation of ribulose bisphosphate.…
Review: One plant’s poison
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants synthesize interesting chemicals that attract, deter, amuse, and harm their predators. Some of the most harmful to humans have been selectively eliminated through the process of domestication, but others render potential food sources inedible. This review by Liu et al. discusses four approaches…
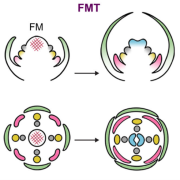
Review: How floral meristem termination shapes flowers
Plant Science Research WeeklyFlowers come in a breathtaking variety of shapes and sizes. The structures making up a flower, called sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels, all derive from the tightly regulated differentiation of a pool of stem cells in the so-called floral meristem. Floral meristem termination (FMT) is a crucial stage…
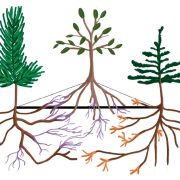
Roots of misinformation on common mycorrhizal networks in forests
Plant Science Research WeeklyAs an educator, I reply on metaphors and stories to engage my readers, yet the line between hyperbole and engagement is thin. The concept of plant-plant communication is exciting, and certainly has some truth, but unfortunately has spilled over into a narrative that perhaps is more fiction than fact.…
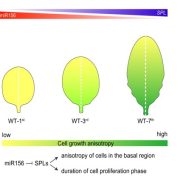
Anisotropic cell growth at the leaf base promotes age-related changes in leaf shape
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe Arabidopsis thaliana leaf exhibits dramatic phenotypic changes across the juvenile-to-adult phase transition during vegetative development. For example, juvenile leaves are small, round, and lack trichomes (leaf hairs). By contrast, adult leaves contain trichomes on the abaxial (or lower) leaf surface,…

PIF4 regulates microtubule organization to mediate high temperature–induced hypocotyl elongation
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant growth adaptation to heat stress (thermomorphogenesis) is regulated by changes in plant morphology such as petiole and hypocotyl elongation. One of the known players in this response is PHYTOCHROME-INTERACTING FACTOR 4 (PIF4), a central regulator of hypocotyl elongation. However, the mechanisms…

