
Transport-coupled ubiquitination of BOR1
Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellYoshinari et al. demonstrate that boron-dependent poly-ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of BOR1 is coupled with its boron transport activity. Plant Cell https://bit.ly/2JYEooF
By Akira Yoshinari
Background: Abundance and activity of nutrient transporters are continuously tuned to both…
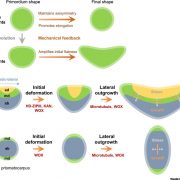
Review: The mechanical feedback theory of leaf lamina formation ($) (Trends Plant Sci.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe contribution of microtubule orientation to the direction of cell expansion is familiar to most; when microtubules wrap around the middle of a cell like a belt, the cell expands in the perpendicular direction to become longer. Recent studies have extended this idea and proposed that the mechanical…

Review: Mesophyll conductance: walls, membranes and spatial complexity (New Phytol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThere’s been a lot of talk lately about how to improve the carboxylation efficiency of Rubisco, but of course this also depends on how much CO2 reaches the enzyme within the chloroplasts. To do so, it needs to pass through several distinct barriers: the boundary layer to reach the leaf surface, the…
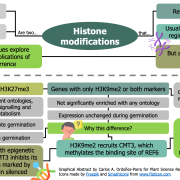
Combinations of maternal-specific repressive epigenetic marks in the endosperm control seed dormancy (bioRxiv.)
Plant Science Research Weekly
H3K27me3 [K27 (Lysine 27) trimethylation on histone H3] and H3K9me2 are two epigenetic modifications that repress gene activity in plants. While they are typically present in different genomic regions, both marks are found in the seed endosperm. Here, Sato and colleagues show that this histone modification…

A novel GUN1-independent retrograde signaling pathway represses photomorphogenesis (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklySeedlings emerging in light undergo photomorphogenic development, forming short hypocotyls and green, fully opened cotyledons. Disruption of chloroplast development by drugs such as lincomycin induces retrograde signals (RS) that inhibit photomorphogenesis. The retrograde signaling pathway has been known…
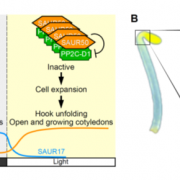
SAURs protein antagonistically regulate a phosphatase activity during apical hook development and cotyledon opening (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Upon germination in dark, plants adopt a strategy known as skotomorphogenesis, or etiolation, to protect the shoot apical meristem and cotyledon from damage while the seedling moves through the soil. The seedlings de-etiolate when they perceive light and the apical hook and cotyledon open. Wang et…
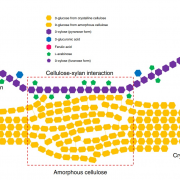
A grass-specific cellulose-xylan interaction dominates in sorghum secondary cell walls (Nature Communications)
Plant Science Research Weekly
The cell walls of plants are intricate structures. Their complexity is due to multiple biochemical components and interactions, but while many of the components have been identified, their interactions have yet to be fully elucidated. A major component of the cell wall is cellulose, of which multiple…

Allelic variation of MYB10 controls natural variation in skin and flesh color in strawberry (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyFew fruits have a more distinctive color than strawberry (Fragaria spp). Anthocyanins are responsible for strawberry’s characteristic red pigmentation with variations in receptacle color caused by altered anthocyanin levels. While the flavonoid synthesis pathway accountable for anthocyanin accumulation…

Spiral down: Rice plants adopt helical root growth under ammonium stress (Plant J.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWhile ammonium ions (NH4+) serve as important sources of nitrogen nutrition, higher concentrations are toxic and inhibit plant growth and development. In an attempt to understand how roots of rice plant adapt to high concentrations of NH4+, Jia and colleagues found the roots coil and adopt a helical…

