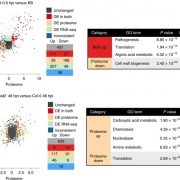
Multidimensional gene regulatory landscape of a bacterial pathogen in plants (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe outcome of a plant-bacteria interaction is determined by the bacterial virulence and plant immune systems. Individually, these systems, and to an extent their interactions, have been well studied. However, certain aspects of their interactions remain elusive, particularly how plant immunity affects…
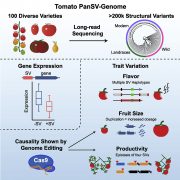
Major impacts of widespread structural variation on gene expression and crop improvement in tomato (Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyStructural Variants (SVs) are large genomic deletions, insertions, and duplications with underexplored roles in determining plant phenotypes. Recognizing the extent to which SVs define quantitative trait variation was previously constrained by the fact that popular short-read sequencing technologies…
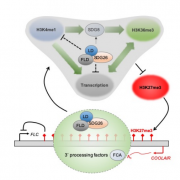
The 3′ processing of antisense RNAs physically links to chromatin-based transcriptional control (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn Arabidopsis, multiple genetic pathways control the floral transition in response to external and internal stimuli. Among these, components of the autonomous pathway promote flowering by negatively regulating the central floral repressor FLOWERING LOCUS C (FLC). Despite the wealth of information on…
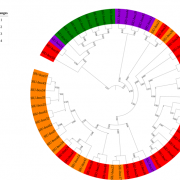
Genome-wide analysis of the U-box E3 ubiquitin ligase enzyme gene family in tomato (Sci. Reports)
Plant Science Research WeeklyUbiquitination is a process of adding ubiquitin (a small regulatory protein) to a substrate protein, leading to its degradation. A wide variety of cellular processes necessary for plant growth and development are regulated by ubiquitination. E3 ubiquitin ligases are the largest family of proteins involved…
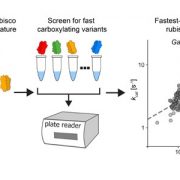
Highly active rubiscos discovered by systematic interrogation of natural sequence diversity (EMBO J)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThis is a fascinating and very well-written paper that investigates the diversity of rubisco's kinetic properties. Rubisco’s relationship with its substrate CO2 is complicated by its relationship with O2, and it has often been suggested that for this reason rubisco is locked into a slow rate of catalysis.…

Protein complex stoichiometry and expression dynamics of transcription factors modulate stem cell division (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyStem cells are a group of undifferentiated cells that can divide and differentiate to form new organs. In Arabidopsis roots, the quiescent center (QC: the mitotically inactive group of cells) helps regulate the division of surrounding initials and maintain the stem cell fate. What makes the QC different…
Macroevolutionary patterns in seed component mass and different evolutionary trajectories across seed desiccation responses ($) (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklySeeds are made out of two functionally distinct components: the seed coat and the seed reserves (which include endosperm and embryo). It is known that the relative contribution of these parts to the total seed mass varies greatly among species. Still, little is known about the evolution of each component's…
Plant Science Research Weekly: June 26th
WWR Full PostReview: Plant small heat shock proteins – evolutionary and functional diversity
Heat shock proteins are rapidly induced by heat treatment and were among the first plant genes and proteins characterized in the early days of molecular biology, nearly 40 years ago. Waters and Vierling review the family…
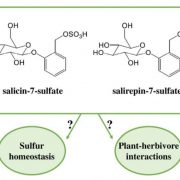
Sulfotransferase 1 is the enzymatic hub of sulfated salicinoids in poplar.
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchPlants produce a plethora of specialized metabolites serving as a chemical arsenal against abiotic and biotic challenges during their lifetime. Core metabolites serve as building blocks for diverse decorating enzymes like oxidases, reductases or transferases that introduce new functionalities expanding…

